
If \[PQ\] be a normal chord of the parabola and \[S\] be the focus, prove that the locus of the centroid of the triangle \[SPQ\] is the curve \[36a{{y}^{2}}\left( 3x-5a \right)-81{{y}^{4}}=128{{a}^{4}}\].
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: If two points \[\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] and \[\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\] lie on a chord which is normal to the point with parameter \[{{t}_{1}}\], then , \[{{t}_{2}}=-{{t}_{1}}-\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}}\]
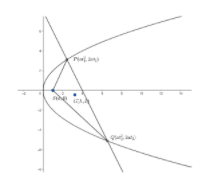
We will consider the equation of parabola be \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\].
So , the focus of the parabola is \[S\left( a,0 \right)\].
Now, we will consider a point \[P\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] on the parabola.
We need to find the equation of normal at this point.
We know , the equation of normal at the point \[(a{{t}^{2}},2at)\] is given as \[y=-tx+2at+a{{t}^{3}}\], where \[t\] is a parameter.
So , the equation of normal to the parabola at \[P\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] is given as
\[y=-{{t}_{1}}x+2a{{t}_{1}}+at_{1}^{3}....\left( i \right)\]
In the question , it is given this normal is also a chord and cuts the parabola at \[Q\].
So , let the coordinates of \[Q=\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\].
\[Q\] lies on the normal chord. So , it should satisfy the equation \[\left( i \right)\].
Also, we know if two point \[\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] and \[\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\] lie on a normal chord, then,
\[{{t}_{2}}=-{{t}_{1}}-\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}}\]
So, \[Q=\left( a{{\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}^{2}},-2a\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right) \right)\]
Now, we need to find the locus of the centroid . So , let the centroid be \[G\left( h,k \right)\].
Now , we know the centroid of a triangle formed by the points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}}),({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] and \[({{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}})\] is given by
\[\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}+{{x}_{3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}+{{y}_{3}}}{3} \right)\].
Now, since \[G\] is the centroid of triangle \[SPQ\], so
\[(h,k)=\left( \dfrac{a+at_{1}^{2}+a{{\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}^{2}}}{3},\dfrac{0+2a{{t}_{1}}-2a\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}{3} \right)\]
Now , we will equate the coordinates .
On equating the coordinates , we get
\[h=\dfrac{a+at_{1}^{2}+a{{\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}^{2}}}{3}.....\left( ii \right)\]
and \[k=\dfrac{0+2a{{t}_{1}}-2a\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}{3}.....\left( iii \right)\]
From equation \[\left( iii \right)\], we get
\[3k=2a{{t}_{1}}-2a{{t}_{1}}-\dfrac{4a}{{{t}_{1}}}\]
or, \[k=\dfrac{-4a}{3{{t}_{1}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{-4a}{3k}\]
Now , we will substitute this value of \[{{t}_{1}}\] in equation \[\left( ii \right)\].
On , substituting this value of \[{{t}_{1}}\] in equation \[\left( ii \right)\] we get,
\[h=\dfrac{a+a{{\left( \dfrac{-4a}{3k} \right)}^{2}}+a{{\left( \dfrac{-4a}{3k}+\dfrac{2}{\dfrac{-4a}{3k}} \right)}^{2}}}{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{a+\dfrac{16{{a}^{3}}}{9{{k}^{2}}}+a\left( \dfrac{16{{a}^{2}}}{9{{k}^{2}}}+\dfrac{36{{k}^{2}}}{16{{a}^{2}}}+4 \right)}{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3h=\dfrac{9a{{k}^{2}}+16{{a}^{3}}+9a{{k}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{16{{a}^{2}}}{9{{k}^{2}}}+\dfrac{36{{k}^{2}}}{16{{a}^{2}}}+4 \right)}{9{{k}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3h=\dfrac{9a{{k}^{2}}+16{{a}^{3}}+16{{a}^{3}}+\dfrac{81{{k}^{4}}}{4a}+36a{{k}^{2}}}{9{{k}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 27{{k}^{2}}h=45a{{k}^{2}}+32{{a}^{3}}+\dfrac{81{{k}^{4}}}{4a}\]
\[\Rightarrow 108a{{k}^{2}}h=180{{a}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}+128{{a}^{4}}+81{{k}^{4}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 36a{{k}^{2}}\left( 3h-5a \right)-81{{k}^{4}}=128{{a}^{4}}.........\]equation\[\left( iv \right)\]
So , the locus of \[G\left( h,k \right)\] is given by replacing \[\left( h,k \right)\] by \[(x,y)\] in equation \[\left( iv \right)\]
So, the equation of locus of the centroid is \[36a{{y}^{2}}\left( 3x-5a \right)-81{{y}^{4}}=128{{a}^{4}}\]
Note: While simplifying the equations , please make sure that sign mistakes do not occur. These mistakes are very common and can cause confusions while solving. Ultimately the answer becomes wrong. So, sign conventions should be carefully taken .

We will consider the equation of parabola be \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\].
So , the focus of the parabola is \[S\left( a,0 \right)\].
Now, we will consider a point \[P\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] on the parabola.
We need to find the equation of normal at this point.
We know , the equation of normal at the point \[(a{{t}^{2}},2at)\] is given as \[y=-tx+2at+a{{t}^{3}}\], where \[t\] is a parameter.
So , the equation of normal to the parabola at \[P\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] is given as
\[y=-{{t}_{1}}x+2a{{t}_{1}}+at_{1}^{3}....\left( i \right)\]
In the question , it is given this normal is also a chord and cuts the parabola at \[Q\].
So , let the coordinates of \[Q=\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\].
\[Q\] lies on the normal chord. So , it should satisfy the equation \[\left( i \right)\].
Also, we know if two point \[\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] and \[\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\] lie on a normal chord, then,
\[{{t}_{2}}=-{{t}_{1}}-\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}}\]
So, \[Q=\left( a{{\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}^{2}},-2a\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right) \right)\]
Now, we need to find the locus of the centroid . So , let the centroid be \[G\left( h,k \right)\].
Now , we know the centroid of a triangle formed by the points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}}),({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] and \[({{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}})\] is given by
\[\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}+{{x}_{3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}+{{y}_{3}}}{3} \right)\].
Now, since \[G\] is the centroid of triangle \[SPQ\], so
\[(h,k)=\left( \dfrac{a+at_{1}^{2}+a{{\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}^{2}}}{3},\dfrac{0+2a{{t}_{1}}-2a\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}{3} \right)\]
Now , we will equate the coordinates .
On equating the coordinates , we get
\[h=\dfrac{a+at_{1}^{2}+a{{\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}^{2}}}{3}.....\left( ii \right)\]
and \[k=\dfrac{0+2a{{t}_{1}}-2a\left( {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}{3}.....\left( iii \right)\]
From equation \[\left( iii \right)\], we get
\[3k=2a{{t}_{1}}-2a{{t}_{1}}-\dfrac{4a}{{{t}_{1}}}\]
or, \[k=\dfrac{-4a}{3{{t}_{1}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{-4a}{3k}\]
Now , we will substitute this value of \[{{t}_{1}}\] in equation \[\left( ii \right)\].
On , substituting this value of \[{{t}_{1}}\] in equation \[\left( ii \right)\] we get,
\[h=\dfrac{a+a{{\left( \dfrac{-4a}{3k} \right)}^{2}}+a{{\left( \dfrac{-4a}{3k}+\dfrac{2}{\dfrac{-4a}{3k}} \right)}^{2}}}{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{a+\dfrac{16{{a}^{3}}}{9{{k}^{2}}}+a\left( \dfrac{16{{a}^{2}}}{9{{k}^{2}}}+\dfrac{36{{k}^{2}}}{16{{a}^{2}}}+4 \right)}{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3h=\dfrac{9a{{k}^{2}}+16{{a}^{3}}+9a{{k}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{16{{a}^{2}}}{9{{k}^{2}}}+\dfrac{36{{k}^{2}}}{16{{a}^{2}}}+4 \right)}{9{{k}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3h=\dfrac{9a{{k}^{2}}+16{{a}^{3}}+16{{a}^{3}}+\dfrac{81{{k}^{4}}}{4a}+36a{{k}^{2}}}{9{{k}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 27{{k}^{2}}h=45a{{k}^{2}}+32{{a}^{3}}+\dfrac{81{{k}^{4}}}{4a}\]
\[\Rightarrow 108a{{k}^{2}}h=180{{a}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}+128{{a}^{4}}+81{{k}^{4}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 36a{{k}^{2}}\left( 3h-5a \right)-81{{k}^{4}}=128{{a}^{4}}.........\]equation\[\left( iv \right)\]
So , the locus of \[G\left( h,k \right)\] is given by replacing \[\left( h,k \right)\] by \[(x,y)\] in equation \[\left( iv \right)\]
So, the equation of locus of the centroid is \[36a{{y}^{2}}\left( 3x-5a \right)-81{{y}^{4}}=128{{a}^{4}}\]
Note: While simplifying the equations , please make sure that sign mistakes do not occur. These mistakes are very common and can cause confusions while solving. Ultimately the answer becomes wrong. So, sign conventions should be carefully taken .
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




