
If \[\cos^{ - 1}\left( {\dfrac{1}{x}} \right) = \theta \]. Then what is the value of \[\tan\theta \]?
A. \[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{x^2} - 1} }}\]
B. \[\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} \]
C. \[\sqrt {1 - {x^2}} \]
D. \[\sqrt {{x^2} - 1} \]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Use the given trigonometric equation and find the value of \[\cos \theta \]. Then using the Pythagoras theorem in a right-angled triangle, get the value of \[\sin \theta \]. In the end, take the ratio of \[\sin \theta \] to \[\cos \theta \] and get the required answer.
Formula used:
\[\sin A = \dfrac{{Opposite Side}}{{Hypotenuse}}\]
\[\cos A = \dfrac{{Adjacent Side}}{{Hypotenuse}}\]
\[\tan A = \dfrac{{Opposite Side}}{{Adjacent Side}} = \dfrac{{\sin A}}{{\cos A}}\]
Pythagoras Theorem: In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Complete step by step solution:
The given trigonometric equation is \[\cos^{ - 1}\left( {\dfrac{1}{x}} \right) = \theta \].
Let’s simplify the given equation.
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{x}\] \[.....\left( 1 \right)\]
Now substitute the value of \[cos \theta \] in a right-angled triangle.
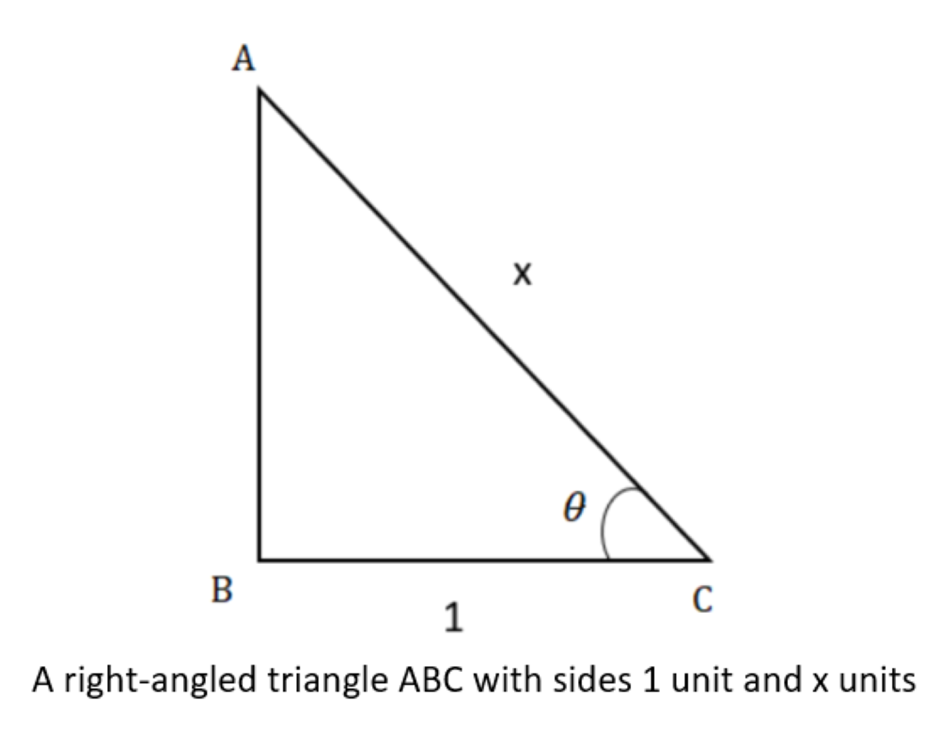
Apply Pythagoras theorem to calculate the length of \[AB\].
\[{\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = \left( {AC} \right){}^2\]
Substitute the values from the above triangle.
\[{\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( 1 \right)^2} = \left( x \right){}^2\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[{\left( {AB} \right)^2} = x{}^2 - 1\]
Take square root of both sides.
\[AB = \sqrt {x{}^2 - 1} \]
Now use the trigonometric ratio and find the value of \[\sin \theta \].
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} - 1} }}{x}\] \[.....\left( 2 \right)\]
Apply the trigonometric ratio \[\tan A = \dfrac{{\sin A}}{{\cos A}}\].
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}\]
Substitute equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] and \[\left( 2 \right)\] in the above equation.
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} - 1} }}{x}}}{{\dfrac{1}{x}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} - 1} }}{1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\tan \theta = \sqrt {{x^2} - 1} \]
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: Trigonometry is based upon the ratios of the sides of a right triangle. These ratios are called trigonometric ratios. Three common trigonometric ratios are the sine, cosine, and tangent.
Formula used:
\[\sin A = \dfrac{{Opposite Side}}{{Hypotenuse}}\]
\[\cos A = \dfrac{{Adjacent Side}}{{Hypotenuse}}\]
\[\tan A = \dfrac{{Opposite Side}}{{Adjacent Side}} = \dfrac{{\sin A}}{{\cos A}}\]
Pythagoras Theorem: In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Complete step by step solution:
The given trigonometric equation is \[\cos^{ - 1}\left( {\dfrac{1}{x}} \right) = \theta \].
Let’s simplify the given equation.
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{x}\] \[.....\left( 1 \right)\]
Now substitute the value of \[cos \theta \] in a right-angled triangle.

Apply Pythagoras theorem to calculate the length of \[AB\].
\[{\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = \left( {AC} \right){}^2\]
Substitute the values from the above triangle.
\[{\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( 1 \right)^2} = \left( x \right){}^2\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[{\left( {AB} \right)^2} = x{}^2 - 1\]
Take square root of both sides.
\[AB = \sqrt {x{}^2 - 1} \]
Now use the trigonometric ratio and find the value of \[\sin \theta \].
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} - 1} }}{x}\] \[.....\left( 2 \right)\]
Apply the trigonometric ratio \[\tan A = \dfrac{{\sin A}}{{\cos A}}\].
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}\]
Substitute equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] and \[\left( 2 \right)\] in the above equation.
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} - 1} }}{x}}}{{\dfrac{1}{x}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} - 1} }}{1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\tan \theta = \sqrt {{x^2} - 1} \]
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: Trigonometry is based upon the ratios of the sides of a right triangle. These ratios are called trigonometric ratios. Three common trigonometric ratios are the sine, cosine, and tangent.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits




