
If 1.26g of oxalic acid is dissolved in 250 ml of solution, find its normality. The equivalent mass of oxalic acid is 63.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Normality is defined as the number equivalents of solute dissolved per litre of solution. Normality is the expressions used to measure the concentration of a solution. It is abbreviated as ‘N’ and is sometimes referred to as the equivalent concentration of a solution.
Step by step solution:
- Molecular formula of oxalic acids in dehydrate form is:
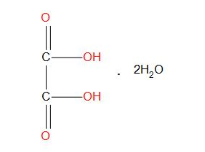
- Weight of sample taken is =1.26g
Equivalent weight is given that is= 63
-The volume of solution =250 ml
- Now, let’s calculate the normality of the solution,
Formula for calculating normality is:
\[Normality\text{ =}\dfrac{weight\text{ }of\text{ }sample\text{ }taken}{equivalent\text{ }weight\text{ }of\text{ }sample}\times \dfrac{1000}{volume\text{ }of\text{ }solution}\]
So, by solving we get,
\[Normality=\dfrac{1.26}{63}\times \dfrac{1000}{250}\]
\[=0.08N\]
Hence, we can say that the normality of the solution is 0.08 N.
Additional information:
- It is found that Many chemists use normality in acid-base chemistry to avoid the mole ratios in the calculations or we can say simply to get more accurate results. while normality is used commonly in precipitation and redox reactions. There are some Limitations found in using Normality, some of them are:
- It is not a proper unit of concentration. It is an ambiguous measure and we can say that molarity or molality are better options for units.
- It is also found that normality is not a specified value for a particular chemical solution. The value can significantly change depending on the chemical reaction. To elucidate further, we can say that one solution can actually contain different normalities for different reactions.
Note: We should not get confused in terms of normality and molarity. Normality is the number equivalent of solute dissolved per litre of solution. And, Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per litre of solution. The unit of normality is N. The unit of molarity is M.
Step by step solution:
- Molecular formula of oxalic acids in dehydrate form is:

- Weight of sample taken is =1.26g
Equivalent weight is given that is= 63
-The volume of solution =250 ml
- Now, let’s calculate the normality of the solution,
Formula for calculating normality is:
\[Normality\text{ =}\dfrac{weight\text{ }of\text{ }sample\text{ }taken}{equivalent\text{ }weight\text{ }of\text{ }sample}\times \dfrac{1000}{volume\text{ }of\text{ }solution}\]
So, by solving we get,
\[Normality=\dfrac{1.26}{63}\times \dfrac{1000}{250}\]
\[=0.08N\]
Hence, we can say that the normality of the solution is 0.08 N.
Additional information:
- It is found that Many chemists use normality in acid-base chemistry to avoid the mole ratios in the calculations or we can say simply to get more accurate results. while normality is used commonly in precipitation and redox reactions. There are some Limitations found in using Normality, some of them are:
- It is not a proper unit of concentration. It is an ambiguous measure and we can say that molarity or molality are better options for units.
- It is also found that normality is not a specified value for a particular chemical solution. The value can significantly change depending on the chemical reaction. To elucidate further, we can say that one solution can actually contain different normalities for different reactions.
Note: We should not get confused in terms of normality and molarity. Normality is the number equivalent of solute dissolved per litre of solution. And, Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per litre of solution. The unit of normality is N. The unit of molarity is M.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




