
What happens when tertiary butyl alcohol is passed over heated copper at $300{}^\circ C$?
(A) Secondary butyl alcohol is formed
(B) $\text{2-methylpropene}$ is formed
(C) $\text{1-butene}$ is formed
(D) Butanal is formed
Answer
526.3k+ views
Hint: Normally the reaction would have been an oxidation reaction. But things change when a tertiary alcohol is present. Formation of double-bond will take place.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first know about the reaction that is mentioned in the question. Generally when primary or secondary alcohol vapours are passed over heated copper at $300{}^\circ C$ then dehydrogenation or in other words oxidation takes place. It converts the primary alcohol into aldehyde and the secondary one into ketone. The reaction is as below:
- Primary alcohol

- Secondary alcohol

This is not the case with tertiary alcohols as they are difficult to oxidise. In their case, dehydration takes place rather than dehydrogenation. The dehydration takes a hydroxyl and hydrogen atom from adjacent carbons, which results in the formation of a double bond. The reaction is as follows:
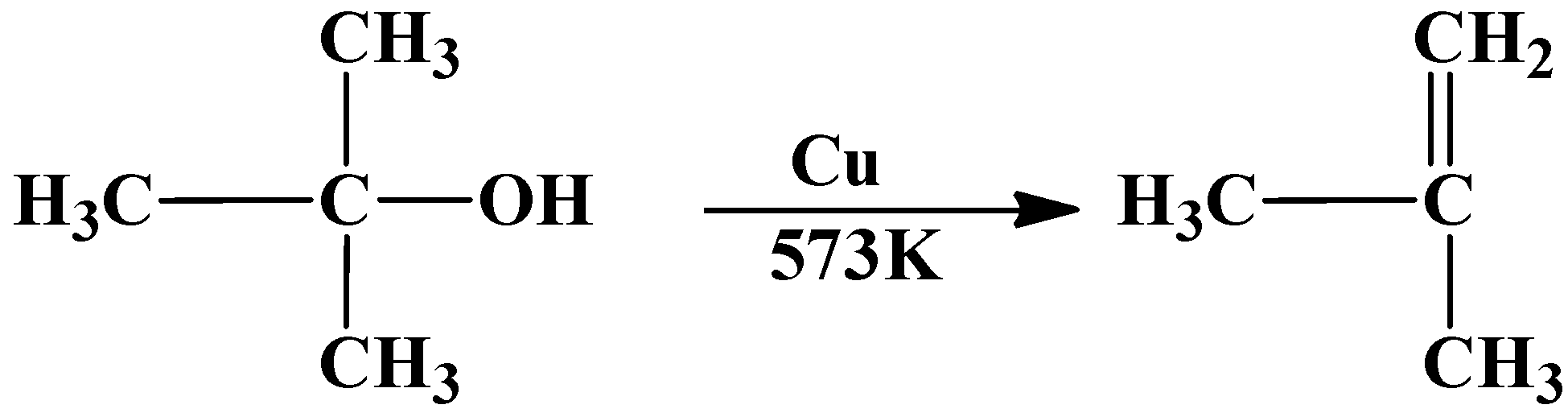
As you can see the tertiary butyl alcohol has been dehydrated into an alkene.
So the answer to the above question is option (C) $\text{1-butene}$ is formed.
Additional information:
The formation of the double bond takes place in such a way as to ensure maximum number of hyperconjugative structures. An example is given below:
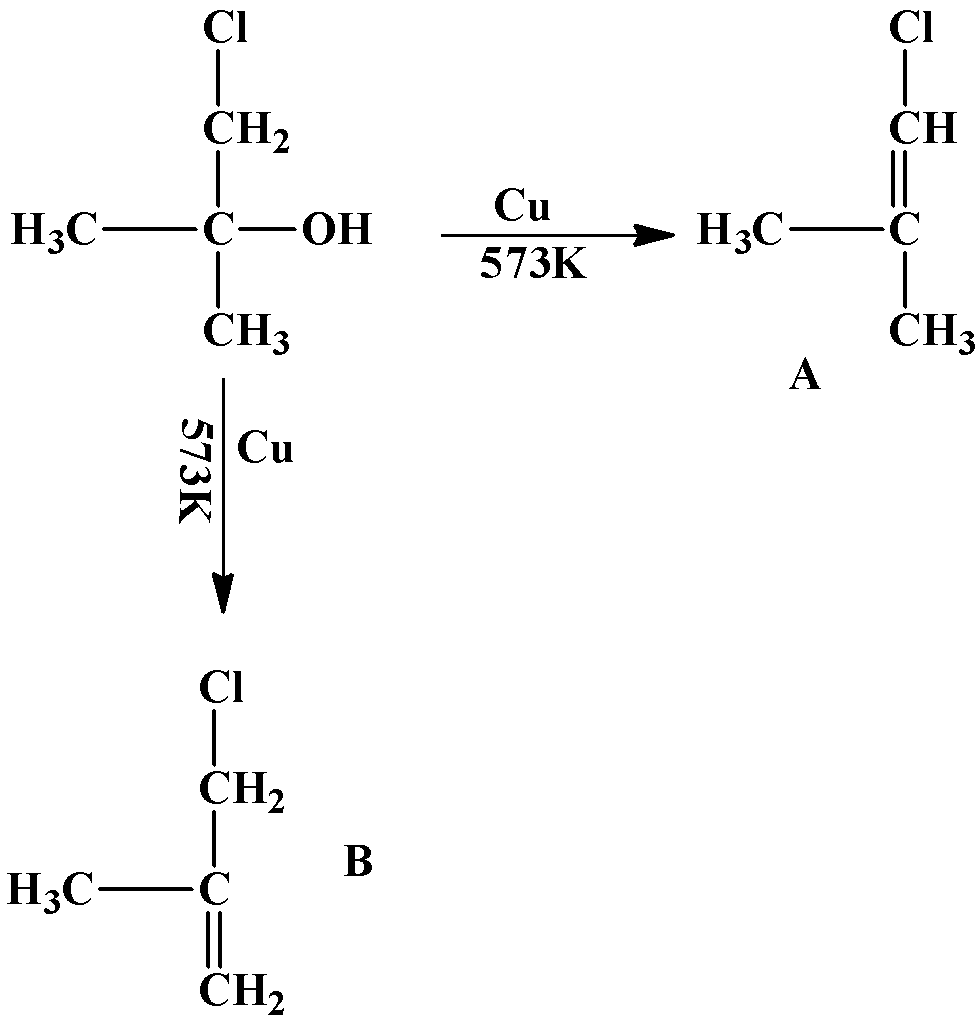
The product will only be “A” because the number of hyperconjugative structures is $6$while that in “B” is $5$. Number of hyperconjugative structures is equal to the number of hydrogen atoms that are attached to the carbon atoms adjacent to the double bond.
Note:
Tertiary alcohols are not oxidised into carbonyl compounds or acids by mild oxidising agents such as chromic oxide. When subjected to strong oxidising agents such as potassium permanganate, they convert into acids with lower number of carbon atoms.
The heated copper process which is described above is an industrial one, and is seldom used in laboratories.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first know about the reaction that is mentioned in the question. Generally when primary or secondary alcohol vapours are passed over heated copper at $300{}^\circ C$ then dehydrogenation or in other words oxidation takes place. It converts the primary alcohol into aldehyde and the secondary one into ketone. The reaction is as below:
- Primary alcohol

- Secondary alcohol

This is not the case with tertiary alcohols as they are difficult to oxidise. In their case, dehydration takes place rather than dehydrogenation. The dehydration takes a hydroxyl and hydrogen atom from adjacent carbons, which results in the formation of a double bond. The reaction is as follows:
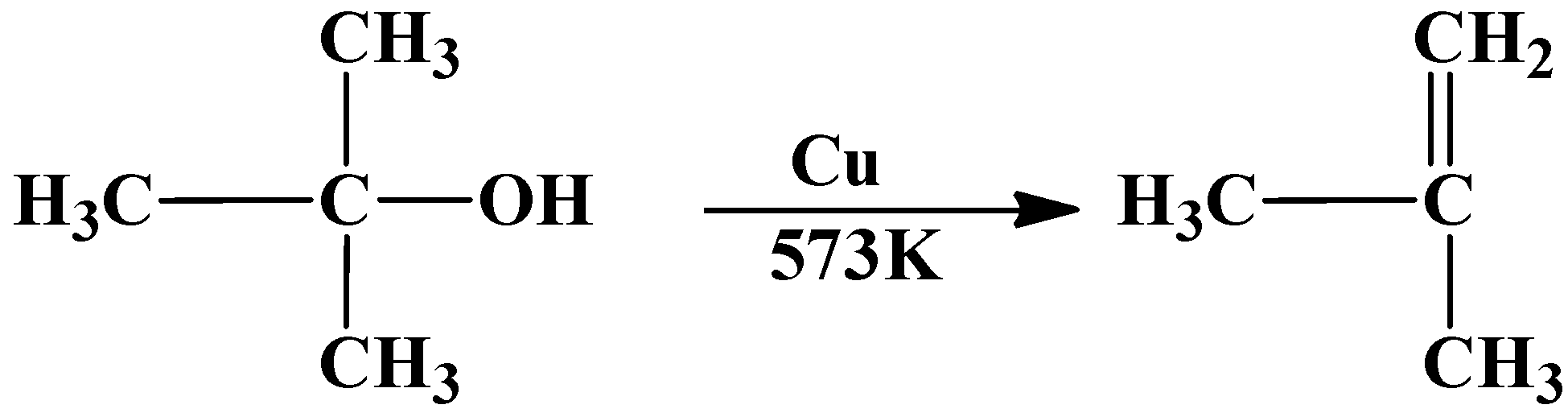
As you can see the tertiary butyl alcohol has been dehydrated into an alkene.
So the answer to the above question is option (C) $\text{1-butene}$ is formed.
Additional information:
The formation of the double bond takes place in such a way as to ensure maximum number of hyperconjugative structures. An example is given below:

The product will only be “A” because the number of hyperconjugative structures is $6$while that in “B” is $5$. Number of hyperconjugative structures is equal to the number of hydrogen atoms that are attached to the carbon atoms adjacent to the double bond.
Note:
Tertiary alcohols are not oxidised into carbonyl compounds or acids by mild oxidising agents such as chromic oxide. When subjected to strong oxidising agents such as potassium permanganate, they convert into acids with lower number of carbon atoms.
The heated copper process which is described above is an industrial one, and is seldom used in laboratories.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




