
Give the structures and IUPAC names of monohydric phenols of molecular formula, ${C_7}{H_8}O.$
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint: Phenols are aromatic alcohols. Monohydric phenol has one hydroxyl group attached to a benzene ring.
Complete step by step answer:
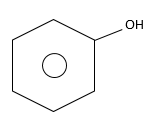
Molecular formula of the compound is ${C_7}{H_8}O.$ We have to find monohydric phenols. Phenols are aromatic alcohols in which one hydroxyl group is attached to a benzene ring.
Benzene ring has 6-carbon atoms in a ring, but total 7-carbon atoms are given in molecular formula.
Therefore, each phenol is methyl substituted phenol. They are: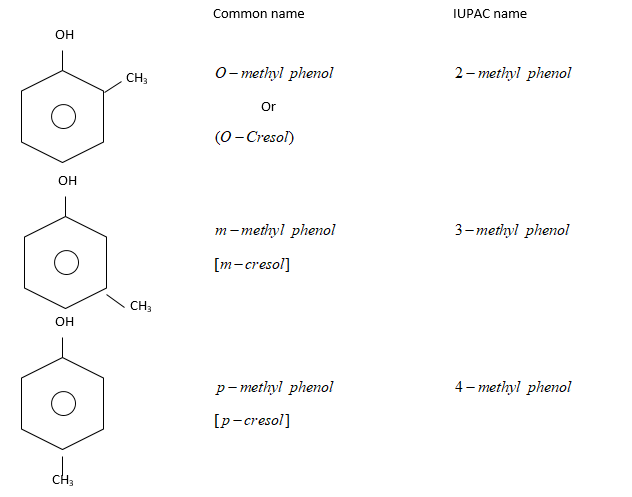 Common name of monohydric phenol is cresol.
Common name of monohydric phenol is cresol.
When two hydrogen atoms of benzene are replaced by two monovalent atom or group of atoms, then resulting product have three different forms:
(i) Ortho (or 1,2): Substituents present on adjacent carbon atom. i.e., $ - C{H_3}$and $ - OH$group are present at adjacent C-atom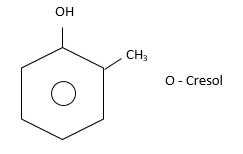
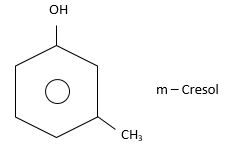
(ii) Meta (or 1,3): Substituents are present on alternate C-atoms. i.e., $ - C{H_3}$ and $ - OH$are present on alternate C-atoms.
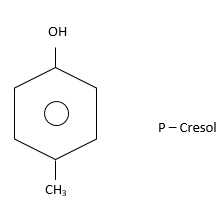
(iii) Para (or 1,4): Two substituents i.e. $ - C{H_3}$ and $ - OH$are present on diagonally situated $C - atoms.$
Ortho, meta and para are generally represented as $O - ,m - $ and $p - $respectively.
Note: The formation of different structures by using one molecular formula is called isomerism. In the given compound three isomers are formed in which position of $ - C{H_3}$group is different with respect to $ - OH$ group on benzene ring.

Complete step by step answer:
Molecular formula of the compound is ${C_7}{H_8}O.$ We have to find monohydric phenols. Phenols are aromatic alcohols in which one hydroxyl group is attached to a benzene ring.
Benzene ring has 6-carbon atoms in a ring, but total 7-carbon atoms are given in molecular formula.
Therefore, each phenol is methyl substituted phenol. They are:
 Common name of monohydric phenol is cresol.
Common name of monohydric phenol is cresol.When two hydrogen atoms of benzene are replaced by two monovalent atom or group of atoms, then resulting product have three different forms:

(i) Ortho (or 1,2): Substituents present on adjacent carbon atom. i.e., $ - C{H_3}$and $ - OH$group are present at adjacent C-atom

(ii) Meta (or 1,3): Substituents are present on alternate C-atoms. i.e., $ - C{H_3}$ and $ - OH$are present on alternate C-atoms.

(iii) Para (or 1,4): Two substituents i.e. $ - C{H_3}$ and $ - OH$are present on diagonally situated $C - atoms.$

Ortho, meta and para are generally represented as $O - ,m - $ and $p - $respectively.
Note: The formation of different structures by using one molecular formula is called isomerism. In the given compound three isomers are formed in which position of $ - C{H_3}$group is different with respect to $ - OH$ group on benzene ring.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




