
Following Sidgwick’s rule of EAN, $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{\text{x}}}$ will be:
A. $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{4}}$
B. $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{3}}$
C. $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{8}}$
D. $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{10}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: EAN is the effective atomic number. The formula of EAN rule is Atomic number – oxidation state + electrons by ligands. Find the oxidation state, atomic number and electron donated. Solve the question with respect to one cobalt and get the value of x, this is because there is a bridging bond $\left( \text{Co}-\text{Co} \right)$ or symmetrical structure.
Complete step by step solution:
The EAN value of period 4 will be the atomic number of the last element present in this period. The last element of this period is Krypton $\left( \text{Kr} \right)$ with atomic number 36. The last element is taken because it is a noble gas and its configuration is noble gas configuration.
Let us solve this question step by step to find the final compound:
Step (1)- The EAN value of $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{\text{x}}}$ will be 36.
Because cobalt also belongs to period 4.
Step (2)- The formula of EAN is the atomic number of central metal atom added to the number of electrons donated by ligands attached minus with its oxidation state. Mathematically, written as Atomic number – oxidation state + electrons by ligands.
We have done this question by considering only one cobalt and solving accordingly.
The atomic number of cobalt is 27.
The oxidation state of Co will be zero.
It is because the carbonyl compound has zero charge and overall charge on the compound is also.
The electrons donated by $\text{CO}$ ligand will be $\left( 2\times \text{no}\text{. of ligands} \right)$.
The EAN of $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{\text{x}}}$ will be $\left[ 27-0+1+\dfrac{\left( \text{2}\times \text{x} \right)}{2} \right]=36$.
Step (3)- Find the value of x.
The value of x will be $\left[ 28+\text{x} \right]=36$ or x = 8.
The compound formed will be $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{8}}$. The IUPAC name of the compound is dicobalt octacarbonyl.
Following Sidgwick’s rule of EAN, $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{\text{x}}}$ will be $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{8}}$.
The correct option is option (C).
Additional Information:
Dicobalt octacarbonyl compound or $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{8}}$ compound is used as a reagent and catalyst in organic synthesis and organometallic chemistry.
Note: Each molecule consists of two cobalt atoms and eight carbon monoxide ligands. The structure of $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{8}}$ is
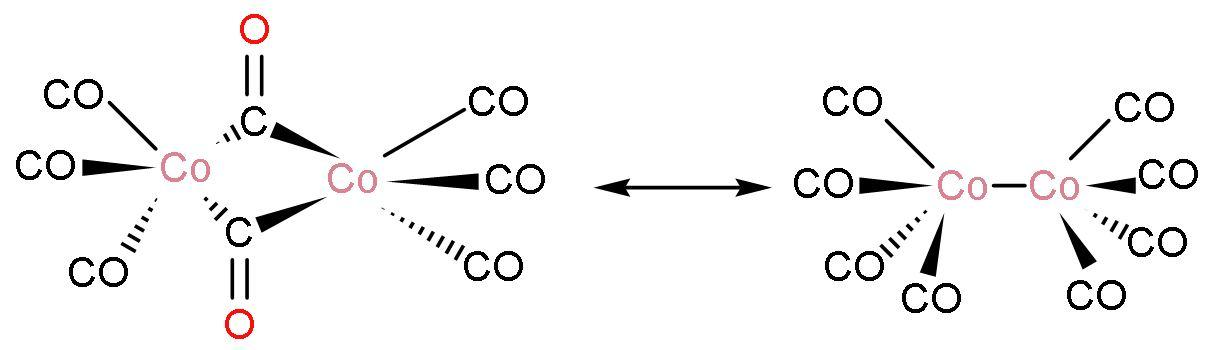
The compound exists in several isomeric forms. In solution, there are two isomers known that rapidly interconvert. In one structure, there is $\left( \text{Co}-\text{Co} \right)$ and eight $\left( \text{Co}-\text{CO} \right)$ ligands. Other structure has there is two bridging $\left( \text{Co}-\text{CO}-\text{Co} \right)$ ligand and there is six $\left( \text{Co}-\text{CO} \right)$ ligands.
Complete step by step solution:
The EAN value of period 4 will be the atomic number of the last element present in this period. The last element of this period is Krypton $\left( \text{Kr} \right)$ with atomic number 36. The last element is taken because it is a noble gas and its configuration is noble gas configuration.
Let us solve this question step by step to find the final compound:
Step (1)- The EAN value of $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{\text{x}}}$ will be 36.
Because cobalt also belongs to period 4.
Step (2)- The formula of EAN is the atomic number of central metal atom added to the number of electrons donated by ligands attached minus with its oxidation state. Mathematically, written as Atomic number – oxidation state + electrons by ligands.
We have done this question by considering only one cobalt and solving accordingly.
The atomic number of cobalt is 27.
The oxidation state of Co will be zero.
It is because the carbonyl compound has zero charge and overall charge on the compound is also.
The electrons donated by $\text{CO}$ ligand will be $\left( 2\times \text{no}\text{. of ligands} \right)$.
The EAN of $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{\text{x}}}$ will be $\left[ 27-0+1+\dfrac{\left( \text{2}\times \text{x} \right)}{2} \right]=36$.
Step (3)- Find the value of x.
The value of x will be $\left[ 28+\text{x} \right]=36$ or x = 8.
The compound formed will be $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{8}}$. The IUPAC name of the compound is dicobalt octacarbonyl.
Following Sidgwick’s rule of EAN, $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{\text{x}}}$ will be $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{8}}$.
The correct option is option (C).
Additional Information:
Dicobalt octacarbonyl compound or $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{8}}$ compound is used as a reagent and catalyst in organic synthesis and organometallic chemistry.
Note: Each molecule consists of two cobalt atoms and eight carbon monoxide ligands. The structure of $\text{C}{{\text{o}}_{2}}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{8}}$ is

The compound exists in several isomeric forms. In solution, there are two isomers known that rapidly interconvert. In one structure, there is $\left( \text{Co}-\text{Co} \right)$ and eight $\left( \text{Co}-\text{CO} \right)$ ligands. Other structure has there is two bridging $\left( \text{Co}-\text{CO}-\text{Co} \right)$ ligand and there is six $\left( \text{Co}-\text{CO} \right)$ ligands.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

For pure water A pH increases while pOH decreases with class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Which of the following is most stable A Sn2+ B Ge2+ class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages




