
Explain the industrial method of preparation of bleaching powder with a neat diagram.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:Bleaching powder is extensively used as a disinfectant and in bleaching of paper. Bleaching powder is known by calcium hypochlorite as its chemical name. The chemical formula of bleaching powder is $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$.
Complete step by step solution:
> Let’s look at the process of production of bleaching powder:
- The raw material required in its production are:
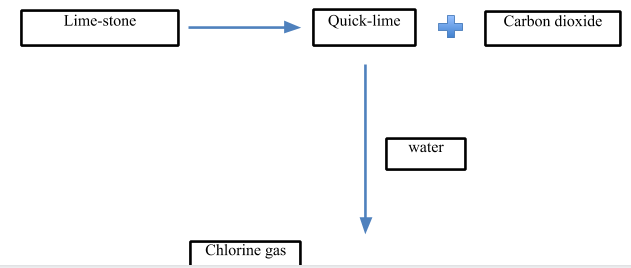
1) Lime-stone
2) \[C{{l}_{2}}\]gas
> Now, let’s look at the process:
- In the first step, quick lime is produced. It is produced from limestone. The limestone is heated at a very high temperature at about $898{}^\circ C$ to decompose it into quicklime and carbon dioxide gas.
\[CaC{{O}_{3}}\,\xrightarrow{898{}^\circ C}\,CaO\,+\,C{{O}_{2}}\]
- In the next step, the quick lime is treated with water to give slaked lime which is the major raw material for the production of bleaching powder.
\[CaO\,+\,{{H}_{2}}O\,\to \,Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}\]
- In the last step, the slaked lime is treated with $C{{l}_{2}}$ gas to give bleaching powder.
- The chlorine gas is passed through the slaked lime in chlorine chambers where solid bleaching powder is collected as the product. The temperature is kept below $35{}^\circ C$.
- The slaked lime is poured from above while the chlorine gas is passed from a lower level.
\[Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}\,+\,C{{l}_{2}}\,\to \,Ca{{(ClO)}_{2}}CaC{{l}_{2}}Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}.2{{H}_{2}}O\]
Note: Students can get confused in the chemical formula of bleaching powder. $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$is the representation of bleaching powder while the actual formula is $Ca{{(ClO)}_{2}}CaC{{l}_{2}}Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}.2{{H}_{2}}O$. So, if the formula is asked then students must choose the second one.
The bleaching action is due to hypochlorite ion and it is permanent.
Complete step by step solution:
> Let’s look at the process of production of bleaching powder:
- The raw material required in its production are:
1) Lime-stone
2) \[C{{l}_{2}}\]gas
> Now, let’s look at the process:
- In the first step, quick lime is produced. It is produced from limestone. The limestone is heated at a very high temperature at about $898{}^\circ C$ to decompose it into quicklime and carbon dioxide gas.
\[CaC{{O}_{3}}\,\xrightarrow{898{}^\circ C}\,CaO\,+\,C{{O}_{2}}\]
- In the next step, the quick lime is treated with water to give slaked lime which is the major raw material for the production of bleaching powder.
\[CaO\,+\,{{H}_{2}}O\,\to \,Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}\]
- In the last step, the slaked lime is treated with $C{{l}_{2}}$ gas to give bleaching powder.
- The chlorine gas is passed through the slaked lime in chlorine chambers where solid bleaching powder is collected as the product. The temperature is kept below $35{}^\circ C$.
- The slaked lime is poured from above while the chlorine gas is passed from a lower level.
\[Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}\,+\,C{{l}_{2}}\,\to \,Ca{{(ClO)}_{2}}CaC{{l}_{2}}Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}.2{{H}_{2}}O\]

Note: Students can get confused in the chemical formula of bleaching powder. $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$is the representation of bleaching powder while the actual formula is $Ca{{(ClO)}_{2}}CaC{{l}_{2}}Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}.2{{H}_{2}}O$. So, if the formula is asked then students must choose the second one.
The bleaching action is due to hypochlorite ion and it is permanent.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




