
Ethylamine $({C}_{2}{H}_{5}N{H}_{2})$ can be obtained from N-ethylphthalimide on treatment with:
(A) $NaB{H}_{4}$
(B) $Ca{H}_{2}$
(C) ${H}_{2}O$
(D) $N{H}_{2}N{H}_{2}$
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: The Gabriel synthesis is a chemical reaction that transforms primary alkyl halides into primary amines. In this process only pure primary amines are formed and not secondary or tertiary amines.
Complete step by step answer: This synthesis is used to get primary amines from primary alkyl halides. The reaction has been generalized for applications in the alkylation of sulfonamides and imides & their deprotection in order to obtain amines. Alkylation of ammonia is quite inefficient, therefore it is substituted with phthalimide anion in the Gabriel synthesis.In this reaction N-ethylphthalimide reacts with $N{H}_{2}N{H}_{2}$ in order to form phthalhydrazide and N-ethylamine.
The following is the reaction that is included in this process.
N-ethylphthalimide is made to react with hydrazine $N{H}_{2}N{H}_{2}$. In this N-ethylphthalimide is heated with hydrazine in order to form phthalhydrazide and n-ethylamine.
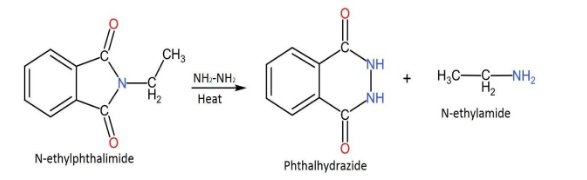
In this, the hydrazine gets attached to the carbonyl group and through a sequence of steps, the amine ends up leaving the group.
Note: N-ethyphthlamide can also be produced through a different approach also. That is with the use of an alkali KOH. Phthalimide is made to react with KOH. A good nucleophile in the form of an imide ion is formed when potassium hydroxide reacts with the phthalimide. The imide ion executes a nucleophilic substitution reaction on the alkyl halide and creates an intermediate – N-alkyl phthalimide. Then further hydrolysis of this phthalimide yields a primary alkyl amine. However, aryl amines cannot be prepared via Gabriel synthesis as aryl halides don’t undergo simple nucleophilic substitution.
Complete step by step answer: This synthesis is used to get primary amines from primary alkyl halides. The reaction has been generalized for applications in the alkylation of sulfonamides and imides & their deprotection in order to obtain amines. Alkylation of ammonia is quite inefficient, therefore it is substituted with phthalimide anion in the Gabriel synthesis.In this reaction N-ethylphthalimide reacts with $N{H}_{2}N{H}_{2}$ in order to form phthalhydrazide and N-ethylamine.
The following is the reaction that is included in this process.
N-ethylphthalimide is made to react with hydrazine $N{H}_{2}N{H}_{2}$. In this N-ethylphthalimide is heated with hydrazine in order to form phthalhydrazide and n-ethylamine.

In this, the hydrazine gets attached to the carbonyl group and through a sequence of steps, the amine ends up leaving the group.
Note: N-ethyphthlamide can also be produced through a different approach also. That is with the use of an alkali KOH. Phthalimide is made to react with KOH. A good nucleophile in the form of an imide ion is formed when potassium hydroxide reacts with the phthalimide. The imide ion executes a nucleophilic substitution reaction on the alkyl halide and creates an intermediate – N-alkyl phthalimide. Then further hydrolysis of this phthalimide yields a primary alkyl amine. However, aryl amines cannot be prepared via Gabriel synthesis as aryl halides don’t undergo simple nucleophilic substitution.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




