
Equivalent conductance for strong electrolyte on dilution _____.
Answer
238.8k+ views
Hint: The conducting power of the ions present in the solution which is formed by dissolving , electrolyte of 1 gram equivalent in a particular solvent is called equivalent conductance.
The equivalent conductance is denoted by \[{\Lambda _e}\].
Complete step by step solution:
Dilution is defined as a process where the solute concentration is decreased with the addition of solvent.
The variations in the value of equivalent conductance depend on the type of electrolyte.
Strong electrolytes dissociate completely into its substituent ions when dissolved in solvent forming a solution. On increasing the dilution (decreasing the concentration of solute), there is the decline in the attractive force present between the cation and anion which further affect there mobility towards each other. This is known as ionic interference. Due to the increase in dilution, the equivalent conductance increases and at infinite dilution, the value of equivalent conductance is highest and it is termed as equivalent conductance at infinite dilution.
Therefore, the equivalent conductance for strong electrolyte on dilution increases.
The effect of electrolyte concentration on the equivalent conductance is observed by the graph plotted between the equivalent conductance value and square root of concentration.
The graph for strong electrolyte is shown below.
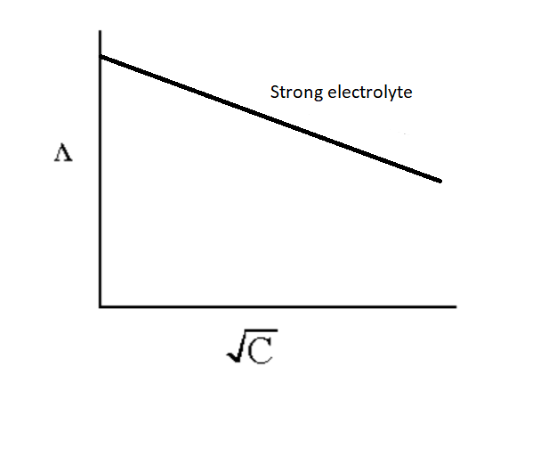
Image: Effect of dilution in the value of equivalent conductance
Note: For strong electrolyte, the number of ions remains the same in the solution at all dilutions, the only change observed is the mobility of ions due to the effect of interionic attraction but in the case of weak electrolyte, the increase in the value of equivalent conductance is due to the increase in the number of ions as weak electrolyte possess a low concentration of ions, so the interionic interaction is negligible.
The equivalent conductance is denoted by \[{\Lambda _e}\].
Complete step by step solution:
Dilution is defined as a process where the solute concentration is decreased with the addition of solvent.
The variations in the value of equivalent conductance depend on the type of electrolyte.
Strong electrolytes dissociate completely into its substituent ions when dissolved in solvent forming a solution. On increasing the dilution (decreasing the concentration of solute), there is the decline in the attractive force present between the cation and anion which further affect there mobility towards each other. This is known as ionic interference. Due to the increase in dilution, the equivalent conductance increases and at infinite dilution, the value of equivalent conductance is highest and it is termed as equivalent conductance at infinite dilution.
Therefore, the equivalent conductance for strong electrolyte on dilution increases.
The effect of electrolyte concentration on the equivalent conductance is observed by the graph plotted between the equivalent conductance value and square root of concentration.
The graph for strong electrolyte is shown below.

Image: Effect of dilution in the value of equivalent conductance
Note: For strong electrolyte, the number of ions remains the same in the solution at all dilutions, the only change observed is the mobility of ions due to the effect of interionic attraction but in the case of weak electrolyte, the increase in the value of equivalent conductance is due to the increase in the number of ions as weak electrolyte possess a low concentration of ions, so the interionic interaction is negligible.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 - Solutions - 2025-26




