
Electrophilic addition reaction is not shown by:
(a) 2 methyl propene and bromine
(b) Acetylene and HOCl
(c) Propyne and MeMgBr
(d) Ethene and dilute sulphuric acid
Answer
232.5k+ views
Hint: An addition reaction, where a pi bond is broken and new sigma bonds are formed is called electrophilic addition reaction in organic chemistry. The reactant must contain a double bond or triple bond.
Complete step by step solution: The driving force of an electrophilic addition reaction is an electrophile (\[{{X}^{+}}\]) that can form covalent bonds with an electron-rich unsaturated bond. Mechanism of the reaction is that the positive charge on the electrophile is transferred to the carbon-carbon bond, forming a carbocation during the formation of the C-X bond. Then this positively charged intermediate combines with electron rich (usually an anion) to form a second covalent bond.
Let us consider each option given in the question.
-2 methyl propene and bromine react to give an additional product. Liquid bromine can react with alkenes to give additional products. The double bond is replaced with a sigma bond between the methylene group and one of the bromine.
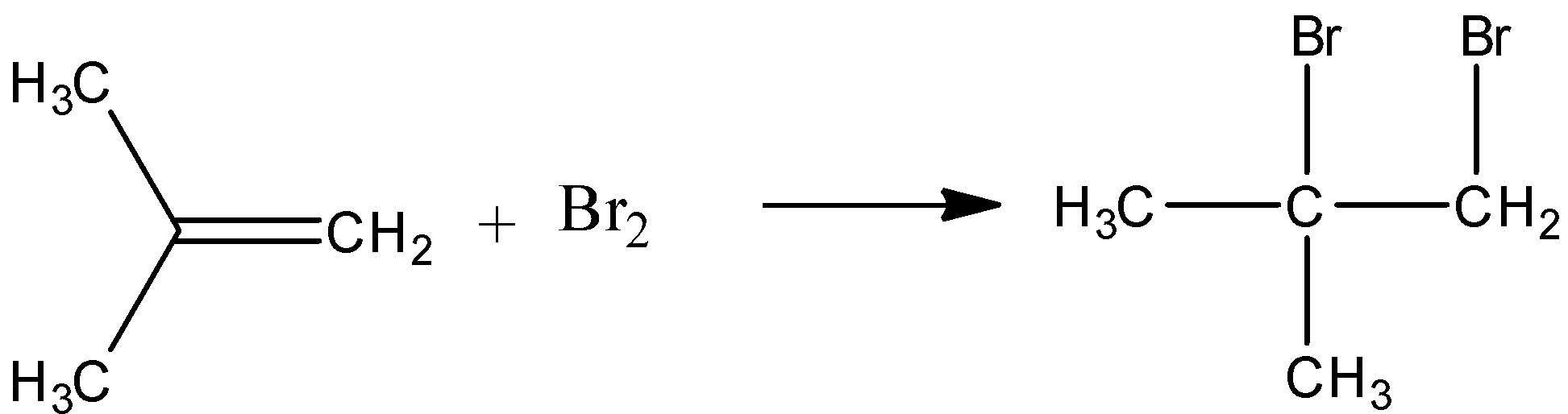
-When acetylene reacts with HOCl dichloro acetaldehyde is formed. Here oxidation addition of acetylene to aldehyde occurs. The reaction is as follows.
\[HC\equiv CH+2HOCl\to HCC{{l}_{2}}-C{{(OH)}_{2}}H\xrightarrow{-{{H}_{2}}O}HCC{{l}_{2}}-CHO\]
-In case of reaction between propyne and MeMgBr, the acidic proton of propyne is abstracted by \[CH_{3}^{-}\] group of the Grignard reagent methyl magnesium bromide. Thus, here additional products are not formed.
-When ethene reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid, it produces alkyl hydrogen sulfates. This is also an electrophilic addition product.
\[C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OS{{O}_{2}}OH\]
Thus, we can conclude that propyne and MeMgBr does not undergo electrophilic addition reaction and the correct option is (c).
Note: Only when there is a double or triple bond is present electrophilic addition occurs. Here an electrophile attacks the unsaturated part of the compound and forms sigma bonds.
Complete step by step solution: The driving force of an electrophilic addition reaction is an electrophile (\[{{X}^{+}}\]) that can form covalent bonds with an electron-rich unsaturated bond. Mechanism of the reaction is that the positive charge on the electrophile is transferred to the carbon-carbon bond, forming a carbocation during the formation of the C-X bond. Then this positively charged intermediate combines with electron rich (usually an anion) to form a second covalent bond.
Let us consider each option given in the question.
-2 methyl propene and bromine react to give an additional product. Liquid bromine can react with alkenes to give additional products. The double bond is replaced with a sigma bond between the methylene group and one of the bromine.
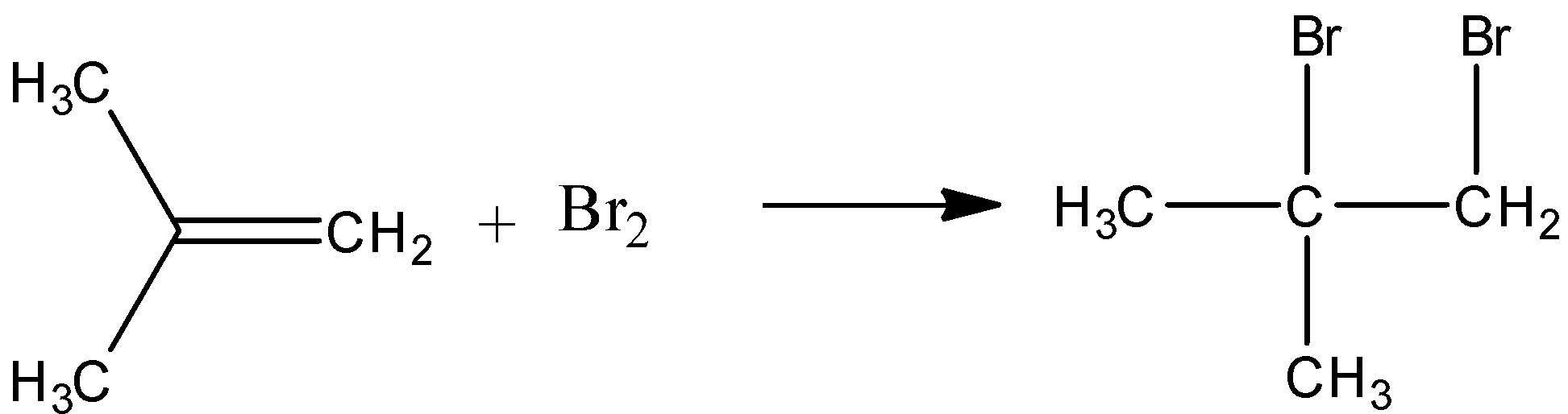
-When acetylene reacts with HOCl dichloro acetaldehyde is formed. Here oxidation addition of acetylene to aldehyde occurs. The reaction is as follows.
\[HC\equiv CH+2HOCl\to HCC{{l}_{2}}-C{{(OH)}_{2}}H\xrightarrow{-{{H}_{2}}O}HCC{{l}_{2}}-CHO\]
-In case of reaction between propyne and MeMgBr, the acidic proton of propyne is abstracted by \[CH_{3}^{-}\] group of the Grignard reagent methyl magnesium bromide. Thus, here additional products are not formed.
-When ethene reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid, it produces alkyl hydrogen sulfates. This is also an electrophilic addition product.
\[C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OS{{O}_{2}}OH\]
Thus, we can conclude that propyne and MeMgBr does not undergo electrophilic addition reaction and the correct option is (c).
Note: Only when there is a double or triple bond is present electrophilic addition occurs. Here an electrophile attacks the unsaturated part of the compound and forms sigma bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




