
Earth’s magnetic strength is __________ near the geographical poles.
(A) Strongest
(B) Weakest
(C) Zero
(D) None of the above
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint Magnetic lines in a magnet start from the north magnetic pole to the south magnetic pole. You can think of the earth’s pole as the pole of a magnet. Thus, the higher the flux of the magnetic field can be observed near the pole as compared to anywhere else on the planet.
Complete Step by step solution
Earth’s magnetic strength is strongest near the geographical poles. Like a magnet bar, the earth’s magnetic lines loops going from the north magnetic pole to south magnetic. The magnetic field lines are closer near the poles comparatively and it goes into space and back to the south pole of the earth. The field is comparatively weaker near the equator.
Geographically, it is accepted that the origin of the earth’s magnetic field is the electric current that flows in the molten outer core of Earth.
Thus, Option (A) is correct.
Additional Information The magnetic field can be calculated. It has been approximated correctly centuries ago. However, now we can represent the earth’s magnetic field by the following diagram:
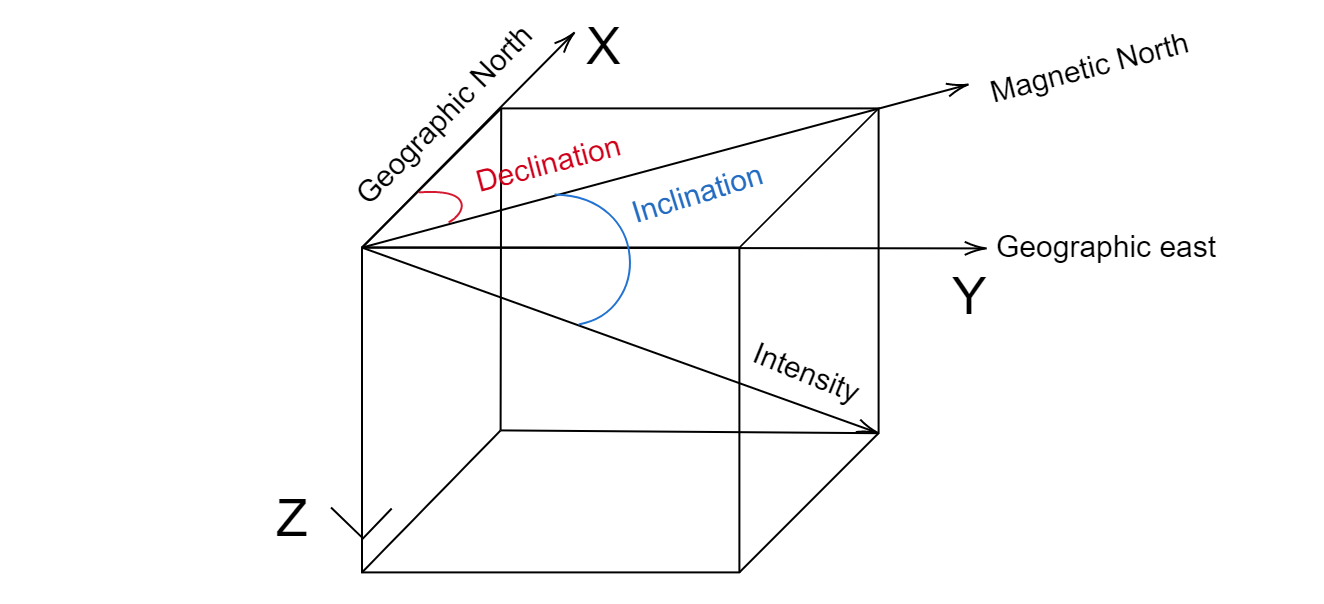
Here, the X-axis represents the geographic north while the Y-axis represents the geographic east.
The Z-axis points towards the downward direction.
The inclination or magnetic inclination is the angle between horizontal and earth’s magnetic field. The way it is measured is that positive values suggest that the magnetic field is pointing downwards while the negative value means the magnetic field is pointing upwards. This angle varies with the position of the observer on earth.
Declination of Magnetic declination is the angle between geographic north and true (magnetic) north. Like the magnetic inclination, this angle also varies with the position of the observer.
Note Take care of the fact that the geographic North pole of the earth is the magnetic south pole. In the case of compasses, the opposites attract, and thus the north end of the compass needle points towards the magnetic south. While approaching such a question, take care of what has been asked, geographic north/south pole, or magnetic north/south pole.
Complete Step by step solution
Earth’s magnetic strength is strongest near the geographical poles. Like a magnet bar, the earth’s magnetic lines loops going from the north magnetic pole to south magnetic. The magnetic field lines are closer near the poles comparatively and it goes into space and back to the south pole of the earth. The field is comparatively weaker near the equator.
Geographically, it is accepted that the origin of the earth’s magnetic field is the electric current that flows in the molten outer core of Earth.
Thus, Option (A) is correct.
Additional Information The magnetic field can be calculated. It has been approximated correctly centuries ago. However, now we can represent the earth’s magnetic field by the following diagram:

Here, the X-axis represents the geographic north while the Y-axis represents the geographic east.
The Z-axis points towards the downward direction.
The inclination or magnetic inclination is the angle between horizontal and earth’s magnetic field. The way it is measured is that positive values suggest that the magnetic field is pointing downwards while the negative value means the magnetic field is pointing upwards. This angle varies with the position of the observer on earth.
Declination of Magnetic declination is the angle between geographic north and true (magnetic) north. Like the magnetic inclination, this angle also varies with the position of the observer.
Note Take care of the fact that the geographic North pole of the earth is the magnetic south pole. In the case of compasses, the opposites attract, and thus the north end of the compass needle points towards the magnetic south. While approaching such a question, take care of what has been asked, geographic north/south pole, or magnetic north/south pole.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




