
Drops of water fall from the roof of a building $9m$ high at regular intervals of time, the first drop reaching the ground at the same instant fourth drop starts to fall. What are the distances of the second and third drops from the roof?
(A) $6m$ and $2m$
(B) $6m$ and $3m$
(C) $4m$ and $1m$
(D) $4m$ and $2m$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Since the drops fall at a regular interval of time, the time taken by all of the drops to reach the ground will be the same. If the first drop reaches the ground at the same time when the fourth drop starts to fall then the time taken by this drop can be assumed to be four times of a uniform time interval. This could be put into the equations of motion, which gives the required quantities.
Complete step by step answer: When the first drop reaches the ground, the fourth drop starts to fall, this means that by the time the first drop reaches the ground, three more drops have formed. The time taken by the first drop to reach the ground is $3t$.
Where $t$ is the time taken by each drop to get generated.
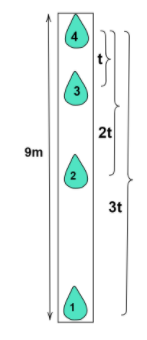
The height of the roof from which the drops fall is given as $h = 9m$
It is known that the drops fall under the action of gravity. Thus the acceleration of the drops would be taken as $g = 10m/{s^2}$
For the first drop,
We have the initial velocity of drop 1, $u = 0$
Putting these values in the second equation of motion,
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9 = 0 \times 3t + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10{(3t)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9{t^2} = 1.8$
$ \Rightarrow {t^2} = 0.2$
$ \Rightarrow t = \sqrt {0.2} $seconds..
We get the time interval between the releasing of each drop as $t = 1.8\sec $.
Now to calculate the distance travelled by the second drop-
The second drop takes a time interval equal to $2t$to cover this given distance.
Putting these values in the equation of motion again,
We have-
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {s_2} = 0 \times {\kern 1pt} \sqrt {0.2} + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times {\left( {2 \times \sqrt {0.2} } \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow s = 5 \times 4 \times 0.2 = 4$
The distance covered by the second drop is,${s_2} = 4m$
To calculate the distance travelled by the third drop-
The third drop takes a time interval equal to $t$to cover the given distance.
We have,
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
\[ \Rightarrow {s_3} = 0 \times \sqrt {0.2} + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times {\left( {\sqrt {0.2} } \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {s_3} = 5 \times 0.2 = 1\]
The distance covered by the third drop is, \[{s_3} = 1\]
Therefore the option, (C) is correct.
Note: It is given that the time taken by all drops to reach the ground is the same. But this does not imply that the distance covered by them in each second is also the same. Since the gravitational force causes the acceleration, the distance covered in each second is more than the previous second.
Complete step by step answer: When the first drop reaches the ground, the fourth drop starts to fall, this means that by the time the first drop reaches the ground, three more drops have formed. The time taken by the first drop to reach the ground is $3t$.
Where $t$ is the time taken by each drop to get generated.

The height of the roof from which the drops fall is given as $h = 9m$
It is known that the drops fall under the action of gravity. Thus the acceleration of the drops would be taken as $g = 10m/{s^2}$
For the first drop,
We have the initial velocity of drop 1, $u = 0$
Putting these values in the second equation of motion,
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9 = 0 \times 3t + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10{(3t)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9{t^2} = 1.8$
$ \Rightarrow {t^2} = 0.2$
$ \Rightarrow t = \sqrt {0.2} $seconds..
We get the time interval between the releasing of each drop as $t = 1.8\sec $.
Now to calculate the distance travelled by the second drop-
The second drop takes a time interval equal to $2t$to cover this given distance.
Putting these values in the equation of motion again,
We have-
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {s_2} = 0 \times {\kern 1pt} \sqrt {0.2} + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times {\left( {2 \times \sqrt {0.2} } \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow s = 5 \times 4 \times 0.2 = 4$
The distance covered by the second drop is,${s_2} = 4m$
To calculate the distance travelled by the third drop-
The third drop takes a time interval equal to $t$to cover the given distance.
We have,
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
\[ \Rightarrow {s_3} = 0 \times \sqrt {0.2} + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times {\left( {\sqrt {0.2} } \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {s_3} = 5 \times 0.2 = 1\]
The distance covered by the third drop is, \[{s_3} = 1\]
Therefore the option, (C) is correct.
Note: It is given that the time taken by all drops to reach the ground is the same. But this does not imply that the distance covered by them in each second is also the same. Since the gravitational force causes the acceleration, the distance covered in each second is more than the previous second.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




