
How does phenol react with conc. Nitric acid? Give an equation.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The reaction taking place between phenol and concentrated nitric acid is a nitration reaction. Nitration is a chemical reaction where the replacement of a Hydrogen atom present in a chemical compound is done with a nitro group.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Phenol is an aromatic hydrocarbon where a hydroxyl group is present in a benzene ring. The molecular formula of phenol is \[{C_6}{H_5}OH\]. Phenol is a white crystalline solid which is volatile in nature.
Nitric acid is a strong acid having a molecular formula \[HN{O_3}\].
The nitration reaction is a type of electrophilic aromatic substitution where a hydrogen atom present in an aromatic hydrocarbon is displaced by an electrophile.
In the reaction between phenol and conc. Nitric acid, the nitro group is the electrophile.
In phenol, the hydroxyl group ease the delocalisation of the charge present in the aromatic compound.
When phenol reacts with concentrated nitric acid, 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol is formed as the main product.
2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol is commonly known as Picric acid.
The reaction taking place between phenol and nitric acid is shown below.
Image: Nitration of phenol
Therefore, the product formed on the reaction of phenol and nitric acid is 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol.
Note: When phenol is reacted with a dilute nitric acid solution at a temperature of 298K, it give a mixture of ortho and para derivative of nitrophenol as a main product. This mixture can be further separated by the distillation process due to their difference in boiling point. The ortho derivative is less volatile as compared to the para derivative due to hydrogen bonding.
The reaction is shown below.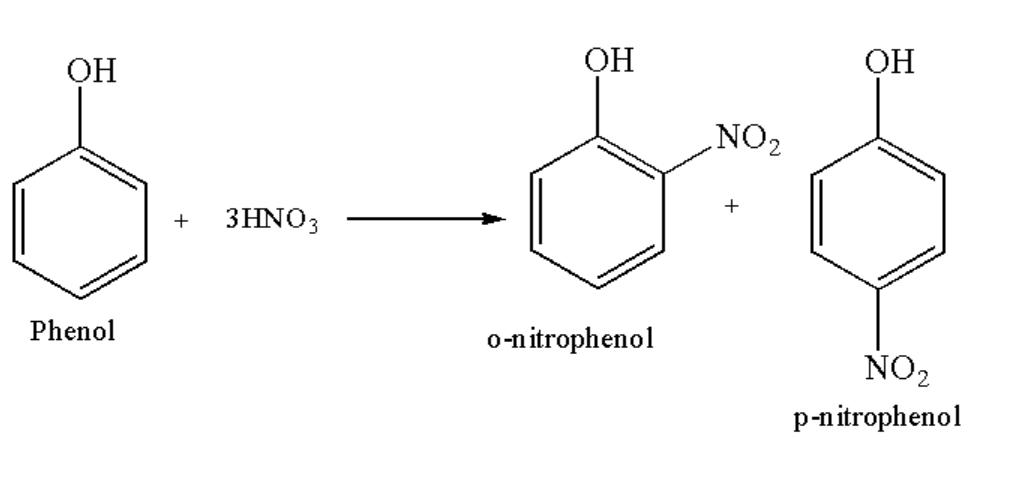
Image: Nitration of phenol
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Phenol is an aromatic hydrocarbon where a hydroxyl group is present in a benzene ring. The molecular formula of phenol is \[{C_6}{H_5}OH\]. Phenol is a white crystalline solid which is volatile in nature.
Nitric acid is a strong acid having a molecular formula \[HN{O_3}\].
The nitration reaction is a type of electrophilic aromatic substitution where a hydrogen atom present in an aromatic hydrocarbon is displaced by an electrophile.
In the reaction between phenol and conc. Nitric acid, the nitro group is the electrophile.
In phenol, the hydroxyl group ease the delocalisation of the charge present in the aromatic compound.
When phenol reacts with concentrated nitric acid, 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol is formed as the main product.
2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol is commonly known as Picric acid.
The reaction taking place between phenol and nitric acid is shown below.
Image: Nitration of phenol
Therefore, the product formed on the reaction of phenol and nitric acid is 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol.
Note: When phenol is reacted with a dilute nitric acid solution at a temperature of 298K, it give a mixture of ortho and para derivative of nitrophenol as a main product. This mixture can be further separated by the distillation process due to their difference in boiling point. The ortho derivative is less volatile as compared to the para derivative due to hydrogen bonding.
The reaction is shown below.

Image: Nitration of phenol
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




