
When does an Avalanche breakdown happen in a diode?
(A) the potential barrier is reduced to zero.
(B) the forward current exceeds a certain value.
(C) reverse bias exceeds a certain value.
(D) none of these.
Answer
528.8k+ views
Hint: Breakdown happens when the electric field enhances strongly enough so that it can pull electrons from the molecules of a material and ionizes them. The free electrons are increased in speed by the field which strike other atoms which results in creating more free electrons.
Complete answer:
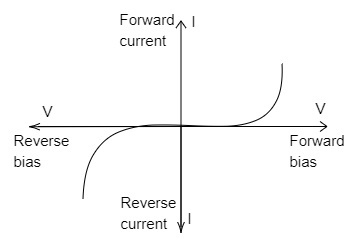
Break down of a diode usually occurs in the reverse biased state. Under the reverse biased state of a PN diode, the positive end of the battery is connected to the n-side of the diode and the negative end is connected to the p-side of the diode. As an outcome of this, electrons will be drawn in respect to the off-side and the holes will be drawn in respect to the side of the p-side. There are two types of breakdown that happen in a diode. They are Zener breakdown and Avalanche breakdown.
Zener diode:
The phenomena of Zener breakdown that happens in a pn junction diode of heavy doping and a thin junction, that is in a way that the size of the depletion layer is very small. Zener breakdown is not that the diode is damaged. As the current is only because of drifting of electrons, there are certain limitations to the increase in current.
Avalanche breakdown:
The phenomenon of Avalanche breaks down that happens in a pn junction diode which is averagely doped that has the thickest junction, that is the thickness of the depletion section is high. This phenomenon normally takes place when there is a greater reverse voltage. Which is evidently greater than that of the Zener breakdown voltage. That is when we increase the applied reverse voltage, the electric field over the junction will keep on rising.
Therefore, Avalanche breakdown in a diode occurs when the reverse bias exceeds a certain value.
Hence, the option (C), reverse bias exceeds certain value is the correct.
Note: In a Zener the current that is essential to split the electrons from the covalent bonds can be obtained with the help of lower voltage than that of the avalanche, which is due to the thin layer of the pn junction. Since the thickness of the depletion in the avalanche is higher than that of the Zener the required electrons to split the covalent bond is greater.
Complete answer:
Break down of a diode usually occurs in the reverse biased state. Under the reverse biased state of a PN diode, the positive end of the battery is connected to the n-side of the diode and the negative end is connected to the p-side of the diode. As an outcome of this, electrons will be drawn in respect to the off-side and the holes will be drawn in respect to the side of the p-side. There are two types of breakdown that happen in a diode. They are Zener breakdown and Avalanche breakdown.

Zener diode:
The phenomena of Zener breakdown that happens in a pn junction diode of heavy doping and a thin junction, that is in a way that the size of the depletion layer is very small. Zener breakdown is not that the diode is damaged. As the current is only because of drifting of electrons, there are certain limitations to the increase in current.
Avalanche breakdown:
The phenomenon of Avalanche breaks down that happens in a pn junction diode which is averagely doped that has the thickest junction, that is the thickness of the depletion section is high. This phenomenon normally takes place when there is a greater reverse voltage. Which is evidently greater than that of the Zener breakdown voltage. That is when we increase the applied reverse voltage, the electric field over the junction will keep on rising.
Therefore, Avalanche breakdown in a diode occurs when the reverse bias exceeds a certain value.
Hence, the option (C), reverse bias exceeds certain value is the correct.
Note: In a Zener the current that is essential to split the electrons from the covalent bonds can be obtained with the help of lower voltage than that of the avalanche, which is due to the thin layer of the pn junction. Since the thickness of the depletion in the avalanche is higher than that of the Zener the required electrons to split the covalent bond is greater.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




