
Displacement between maximum potential energy position and maximum kinetic energy position for a particle executing simple harmonic motion is.
Answer
239.1k+ views
Hint: According to the law of conservation of energy, the system's overall energy will never change. For straightforward harmonic motion, the displacement of the particle from the mean location determines the exchange of kinetic and potential energy.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to know that the expression of the kinetic energy is:
\[K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{\omega ^2}({a^2} - {x^2})\]..…. (1)
where m is the mass of the body, ω is the angular frequency, a is the amplitude and x is the position of the particle.
And, the expression of potential energy is:
\[U = \dfrac{1}{2}m{\omega ^2}{x^2}\]…… (2)
where m is the mass of the body, ω is the angular frequency, a is the amplitude and x is the position of the particle.
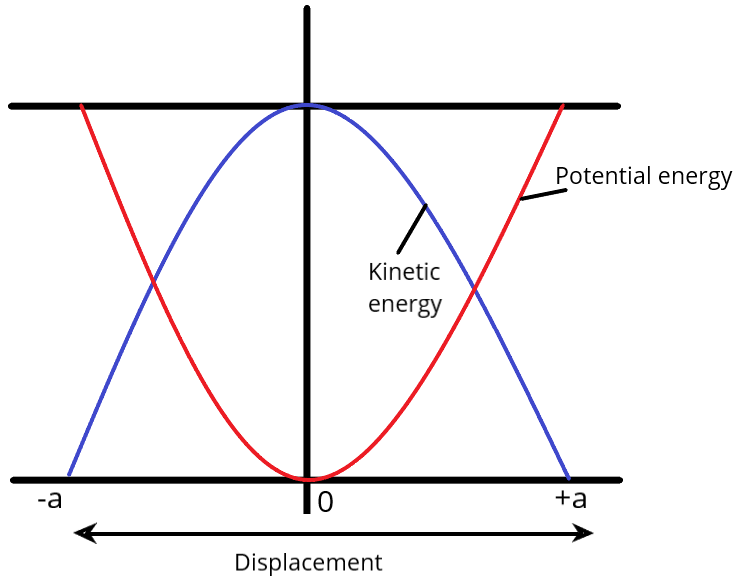
We observe that at the mean position \[(x = 0)\], kinetic energy is maximum \[\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}m{\omega ^2}{a^2}} \right)\] and potential energy is minimum or zero.
Also, at extreme positions \[(x = \pm a)\], kinetic energy is zero and potential energy is maximum \[\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}m{\omega ^2}{a^2}} \right)\].
Thus, the displacement between positions of maximum potential energy and maximum kinetic energy is \[ \pm a\].
Note:Here, it's important to keep in mind that the system's overall energy should not change. The answer will then be aided by the fact that the energy of the Simple Harmonic Oscillator only totally transforms from one form to another.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to know that the expression of the kinetic energy is:
\[K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{\omega ^2}({a^2} - {x^2})\]..…. (1)
where m is the mass of the body, ω is the angular frequency, a is the amplitude and x is the position of the particle.
And, the expression of potential energy is:
\[U = \dfrac{1}{2}m{\omega ^2}{x^2}\]…… (2)
where m is the mass of the body, ω is the angular frequency, a is the amplitude and x is the position of the particle.

We observe that at the mean position \[(x = 0)\], kinetic energy is maximum \[\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}m{\omega ^2}{a^2}} \right)\] and potential energy is minimum or zero.
Also, at extreme positions \[(x = \pm a)\], kinetic energy is zero and potential energy is maximum \[\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}m{\omega ^2}{a^2}} \right)\].
Thus, the displacement between positions of maximum potential energy and maximum kinetic energy is \[ \pm a\].
Note:Here, it's important to keep in mind that the system's overall energy should not change. The answer will then be aided by the fact that the energy of the Simple Harmonic Oscillator only totally transforms from one form to another.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26




