
What is the direction of angular velocity for the second hand of a clock going from 0 to 30 seconds?
(A) Outward from the clock face
(B) Inward towards the clock face
(C) Upward
(D) Downward
(E) To the right
Answer
242.1k+ views
Hint:Since angular velocity is in rotational motion and a vector quantity the right hand rule tells its direction. Curl the fingers in the direction of rotation along the axis and the thumb indicates the direction of angular velocity
Complete step by step answer:
Angular velocity is a vector quantity having both magnitude and direction.
To find out the direction of angular velocity we need to use the right-hand rule. The direction of angular velocity is always perpendicular to the plane of rotation. According to this right-hand rule, the fingers curl in the direction of rotation and the thumb pointing is the direction of the angular velocity.
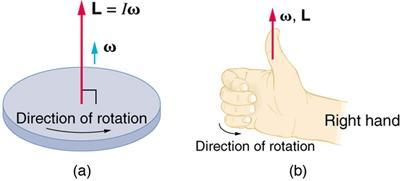
In this case the fingers are pointing at zero seconds and curl the fingers as it changes to 30 seconds along the axis of rotation now the thumb is pointing towards the clock which is the direction of angular velocity.
Hence, the direction of angular velocity is inwards towards the clock face and the correct option is B.
Note This right-hand rule is basically used to define the direction of the cross product of 2 vectors. It points in the direction which is perpendicular to both of these vectors. In this case angular velocity is defined as the cross product of the radius of the circle with the linear velocity of the particle. Its direction is also pointed mutually perpendicular to both of these vectors.
Complete step by step answer:
Angular velocity is a vector quantity having both magnitude and direction.
To find out the direction of angular velocity we need to use the right-hand rule. The direction of angular velocity is always perpendicular to the plane of rotation. According to this right-hand rule, the fingers curl in the direction of rotation and the thumb pointing is the direction of the angular velocity.

In this case the fingers are pointing at zero seconds and curl the fingers as it changes to 30 seconds along the axis of rotation now the thumb is pointing towards the clock which is the direction of angular velocity.
Hence, the direction of angular velocity is inwards towards the clock face and the correct option is B.
Note This right-hand rule is basically used to define the direction of the cross product of 2 vectors. It points in the direction which is perpendicular to both of these vectors. In this case angular velocity is defined as the cross product of the radius of the circle with the linear velocity of the particle. Its direction is also pointed mutually perpendicular to both of these vectors.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




