
Describe the motion as shown by the following velocity time graphs.
A)
B)
Answer
242.1k+ views
Hint: The slope of the velocity-time graph gives the acceleration of the body. When the line describing motion of the particle is parallel to the X-axis, the velocity of the particle is considered to be 0. The motion of the body can be defined using acceleration, velocity and the displacement of the body. The slope of any velocity-time graph is the acceleration and the area of the graph is the displacement.
Complete step by step answer:
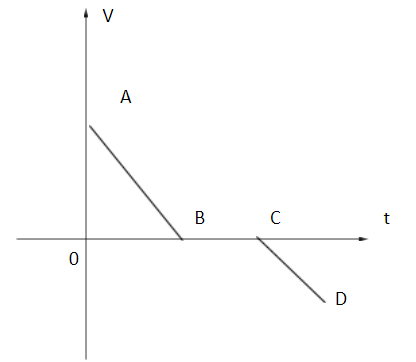
(A)
As we can see from the above figure, the point A is in the positive Y axis that means, the velocity of the particle is positive.
We know, Slope of the velocity-time graph gives us the acceleration. In the region AB, we see a slope which is decreasing, therefore, we can say the acceleration is in the negative direction, also termed as deceleration.When the line describing motion of the particle is parallel to the X-axis, the velocity of the particle is considered to be 0. Thus, the region BC is constant zero velocity.
Further, in region CD, we observe a negative slope, that means the body again decelerates at a constant rate.
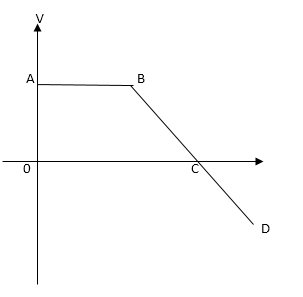
(B)
In the above figure, we can observe the following:
Region AB has a constant velocity of some magnitude, as the line of motion is parallel to the x axis.
Region BC, it is seen that the slope of the curve proceeds towards the negative axis, as it has a negative slope. Thus the body decelerates.
In the region CD, the body continues moving further towards the negative axis, due to constant deceleration.
Note: When velocity of a particle is 0, the curve in velocity-time graph coincides with the X axis. Acceleration refers to the increase in speed of a body with respect to time and deceleration refers to decrease in speed of a body with respect to time. Deceleration is also referred to as negative acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
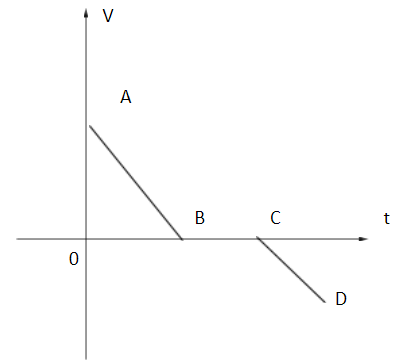
(A)

As we can see from the above figure, the point A is in the positive Y axis that means, the velocity of the particle is positive.
We know, Slope of the velocity-time graph gives us the acceleration. In the region AB, we see a slope which is decreasing, therefore, we can say the acceleration is in the negative direction, also termed as deceleration.When the line describing motion of the particle is parallel to the X-axis, the velocity of the particle is considered to be 0. Thus, the region BC is constant zero velocity.
Further, in region CD, we observe a negative slope, that means the body again decelerates at a constant rate.
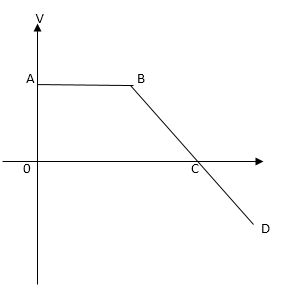
(B)

In the above figure, we can observe the following:
Region AB has a constant velocity of some magnitude, as the line of motion is parallel to the x axis.
Region BC, it is seen that the slope of the curve proceeds towards the negative axis, as it has a negative slope. Thus the body decelerates.
In the region CD, the body continues moving further towards the negative axis, due to constant deceleration.
Note: When velocity of a particle is 0, the curve in velocity-time graph coincides with the X axis. Acceleration refers to the increase in speed of a body with respect to time and deceleration refers to decrease in speed of a body with respect to time. Deceleration is also referred to as negative acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




