
Cyclic trimer structure of $S{{O}_{3}}$contains:
(A) Six S=O bonds and three S-O-S bonds
(B) Three S=O bonds and six S-O-S bonds
(C) Three S=O bonds and two S-O-S bonds
(D) Six S=O bonds and two S-O-S bonds
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Sulphur has valency as 2 and oxygen as valency as 2. Sulphur trioxide has trigonal planar geometry. Sulphur has oxidation state +6. Structure of cyclic trimer of Sulphur trioxide is as following:
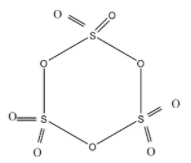
Complete step by step solution:
-Sulphur has atomic number 16. It belongs to group 16 of the periodic table. It is a p-block element. It has a valency as 2.
-Sulphur has electronic configuration as \[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{4}}\].
-oxygen has an atomic number 8. It belongs to group 16 of the periodic table. It has a valency of 2.
-Gaseous Sulphur trioxide has a trigonal planar structure.
-On condensation of gas, absolutely pure Sulphur trioxide undergoes condensation into a trimer.
-Sulphur atom has an oxidation state of +6.
-Sulphur trioxide is a strong Lewis acid.
-On direct oxidation of Sulphur dioxide produces Sulphur trioxide.
-Sulphur trioxide is hygroscopic.
-In sulfonation reactions, Sulphur trioxide is an essential reagent.
-Sulphur trioxide is an essential reagent in sulfonation reactions. Sulphur trioxide is generated in situ from sulphuric acid.
-The Lewis structure consists of S=O double bond and two S-O dative bonds without the utilization of d orbitals.
As shown in the diagram, the Cyclic trimer structure of $S{{O}_{3}}$contains (A) Six S=O bonds and three S-O-S bonds.
So, the correct option is (A).
Note: Pure Sulphur trioxide gas on condensation leads to the formation of the trimer. The Lewis structure consists of S=O double bond and two S-O dative bonds without the utilization of d orbitals. Gaseous Sulphur trioxide has a trigonal planar structure. On condensation of gas, absolutely pure Sulphur trioxide undergoes condensation into a trimer. Sulphur has an oxidation number of +6. The Valency of Sulphur is two.

Complete step by step solution:
-Sulphur has atomic number 16. It belongs to group 16 of the periodic table. It is a p-block element. It has a valency as 2.
-Sulphur has electronic configuration as \[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{4}}\].
-oxygen has an atomic number 8. It belongs to group 16 of the periodic table. It has a valency of 2.
-Gaseous Sulphur trioxide has a trigonal planar structure.
-On condensation of gas, absolutely pure Sulphur trioxide undergoes condensation into a trimer.
-Sulphur atom has an oxidation state of +6.
-Sulphur trioxide is a strong Lewis acid.
-On direct oxidation of Sulphur dioxide produces Sulphur trioxide.
-Sulphur trioxide is hygroscopic.
-In sulfonation reactions, Sulphur trioxide is an essential reagent.
-Sulphur trioxide is an essential reagent in sulfonation reactions. Sulphur trioxide is generated in situ from sulphuric acid.
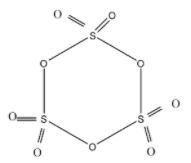
-The Lewis structure consists of S=O double bond and two S-O dative bonds without the utilization of d orbitals.

As shown in the diagram, the Cyclic trimer structure of $S{{O}_{3}}$contains (A) Six S=O bonds and three S-O-S bonds.
So, the correct option is (A).
Note: Pure Sulphur trioxide gas on condensation leads to the formation of the trimer. The Lewis structure consists of S=O double bond and two S-O dative bonds without the utilization of d orbitals. Gaseous Sulphur trioxide has a trigonal planar structure. On condensation of gas, absolutely pure Sulphur trioxide undergoes condensation into a trimer. Sulphur has an oxidation number of +6. The Valency of Sulphur is two.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




