
Consider the following transformations of a compound P.
Choose the correct option(s).
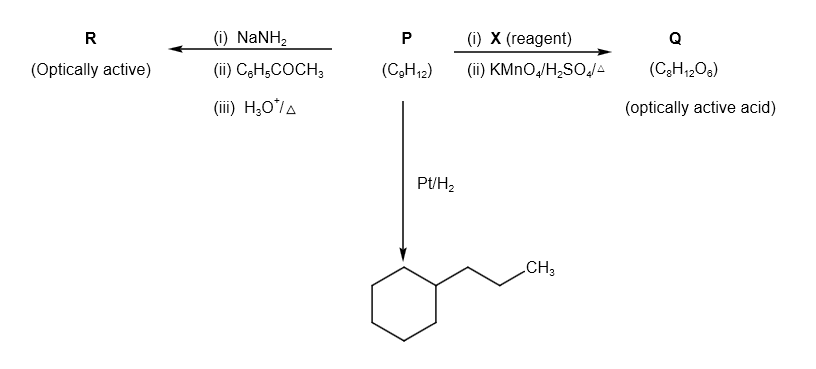
A. P is
B. X is \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\]
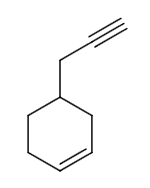
C. P is
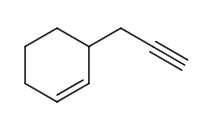
D.R is
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: \[NaN{H_2}\] is a potent nucleophile and strong base. It is employed in elimination reactions as well as the deprotonation of weak acids. Alkenes can be reduced to alkanes with \[{H_2}\] in the presence of metal catalysts such as \[Pt\] .
Complete Step by Step Solution:
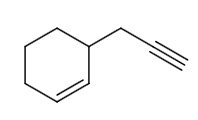
From the options, let us assume the structure of P is as follows:
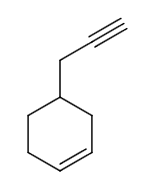
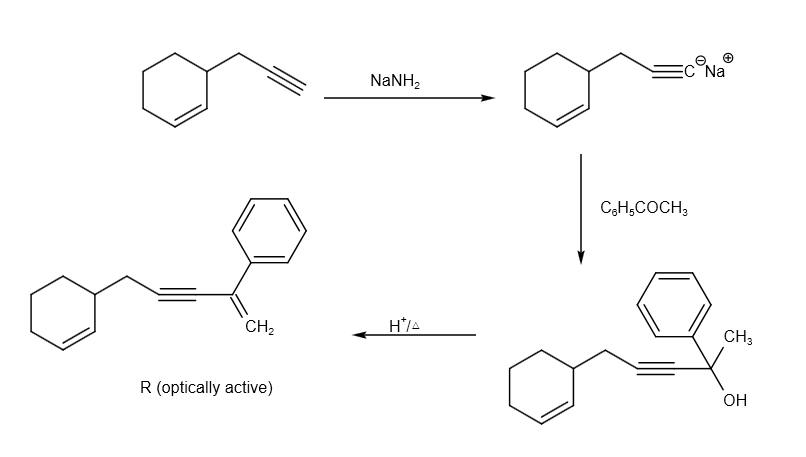
The reaction of P to R can be written as follows:
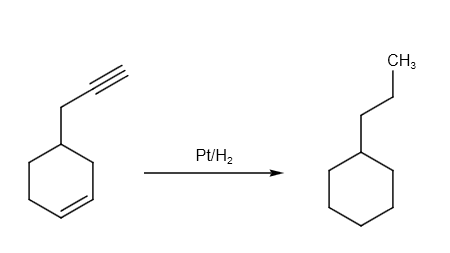
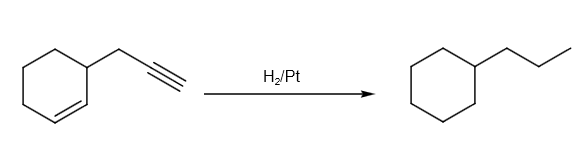
Hydrogenation can be written as follows:
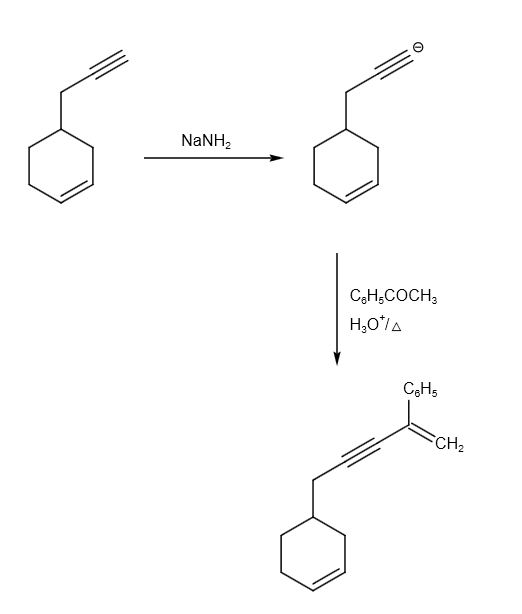
From the options, let us take \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] as reagent X. \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] is Lindlar’s catalyst. The reaction can be written as follows:
Therefore, option A is not the correct answer.
From the options, let us assume the structure of P is as follows:
Let us assume \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] as reagent X. The reaction of P to Q can be written as follows:
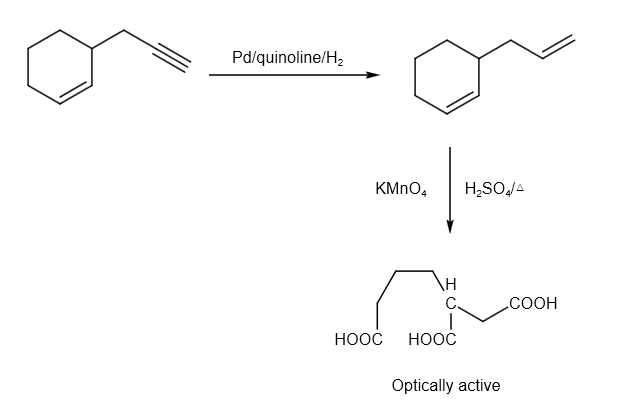
The hydrogenation reaction can be written as follows:
The reaction from P to R can be written as follows:
Therefore, option B and C are correct answer.
Additional Information:
• A heterogeneous catalyst called Lindlar is made of palladium that was created on calcium carbonate and treated with various forms of lead. A heterogeneous catalyst is one that constantly exists in a distinct state from the reactant solution (solid, liquid, or gas solution).
• After Herbert Lindlar, the company's founder, the name "Lindlar" was given. In some places, lead will be required to deactivate the palladium. Lead is present; hence this is frequently referred to as a "poisoned catalyst." When a catalyst's potency starts to decline, it becomes toxic.
Note: Different chemical pollutants, including lead acetate and lead oxide, are utilised to poison the palladium. Normally, just 5% of the weight of the catalyst is made up of the palladium element. Alkenes are subjected to the catalyst in order to hydrogenate alkynes.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
From the options, let us assume the structure of P is as follows:

The reaction of P to R can be written as follows:

Hydrogenation can be written as follows:

From the options, let us take \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] as reagent X. \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] is Lindlar’s catalyst. The reaction can be written as follows:
Therefore, option A is not the correct answer.
From the options, let us assume the structure of P is as follows:

Let us assume \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] as reagent X. The reaction of P to Q can be written as follows:

The hydrogenation reaction can be written as follows:

The reaction from P to R can be written as follows:

Therefore, option B and C are correct answer.
Additional Information:
- • A catalyst is a material that modifies or speeds up any chemical reaction without causing any change on its own. Typically, a catalyst is utilised in smaller quantities than the reactants or other reaction participants.
Note: Different chemical pollutants, including lead acetate and lead oxide, are utilised to poison the palladium. Normally, just 5% of the weight of the catalyst is made up of the palladium element. Alkenes are subjected to the catalyst in order to hydrogenate alkynes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




