
Consider the following reactions \[{\rm{A}} \to {{\rm{P}}_{\rm{1}}}{\rm{;B}} \to {{\rm{P}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{;C}} \to {{\rm{P}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{;D}} \to {{\rm{P}}_{\rm{4}}},\]
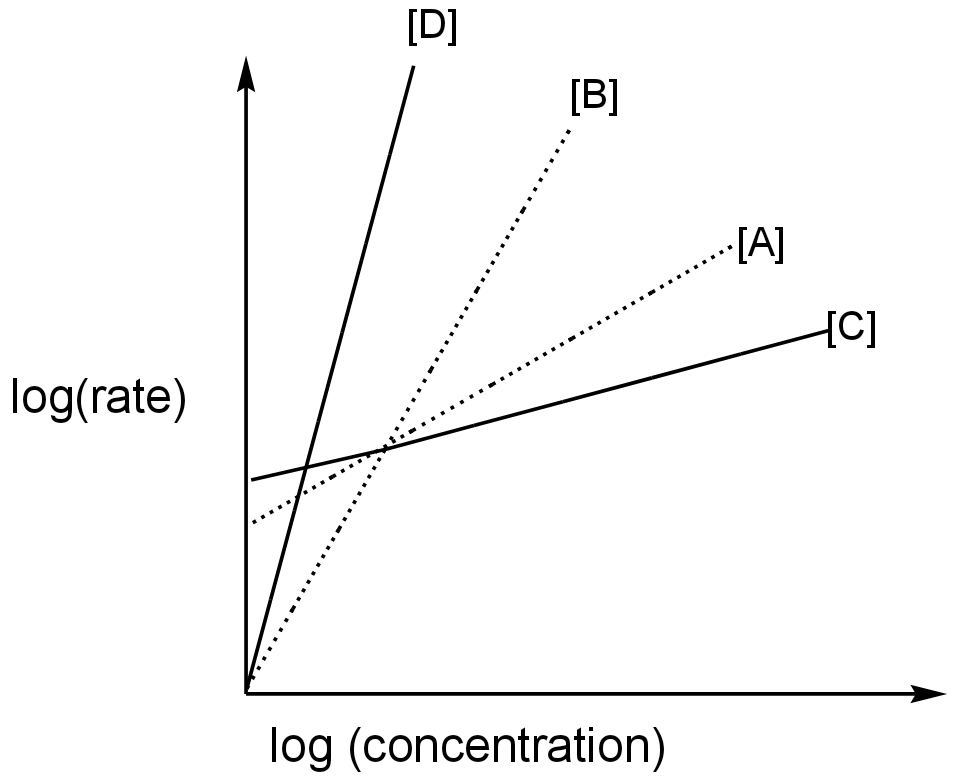
The order of the above reactions is a,b,c, and d, respectively. The following graph is obtained when log[rate] vs. log[conc.] are plotted.
Among the following the correct sequence for the order of the reactions is:
A. c > a > b > d
B. d > a > b > c
C. d > b > a > c
D. a > b > c > d
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We are given a graph of four reactions plotted log(rate) against log(concentration). To find which reaction has a higher-order, we have to compare the slope of each reaction.
Formula Used:
\[{\rm{log(rate) = nlog(concentration) + logk}}\]
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this graph log(rate) is plotted against log(concentration).
The graph is linear for all four reactions.
It means the rate changes with the concentration of the reactant.
Rate is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant.
Let us consider the order of the reactions to be n.
\[{\rm{Rate = k[A}}{{\rm{]}}^{\rm{n}}}\] for the first reaction.
\[{\rm{Rate = k[B}}{{\rm{]}}^{\rm{n}}}\]for the second reaction.
\[{\rm{Rate = k[C}}{{\rm{]}}^{\rm{n}}}\]for the third reaction.
\[{\rm{Rate = k[D}}{{\rm{]}}^{\rm{n}}}\]for the fourth reaction.
If we take the log for a rate law equation we get
\[{\rm{Rate = k(concentration}}{{\rm{)}}^{\rm{n}}}\]
\[{\rm{log(rate) = nlog(concentration) + logk}}\]
This equation resembles the mathematical expression \[{\rm{y = mx + c}}\].
Thus, comparing both the equations we get,
Slope or m is the order of the reaction.
Thus, the reaction having more slope will have more order.
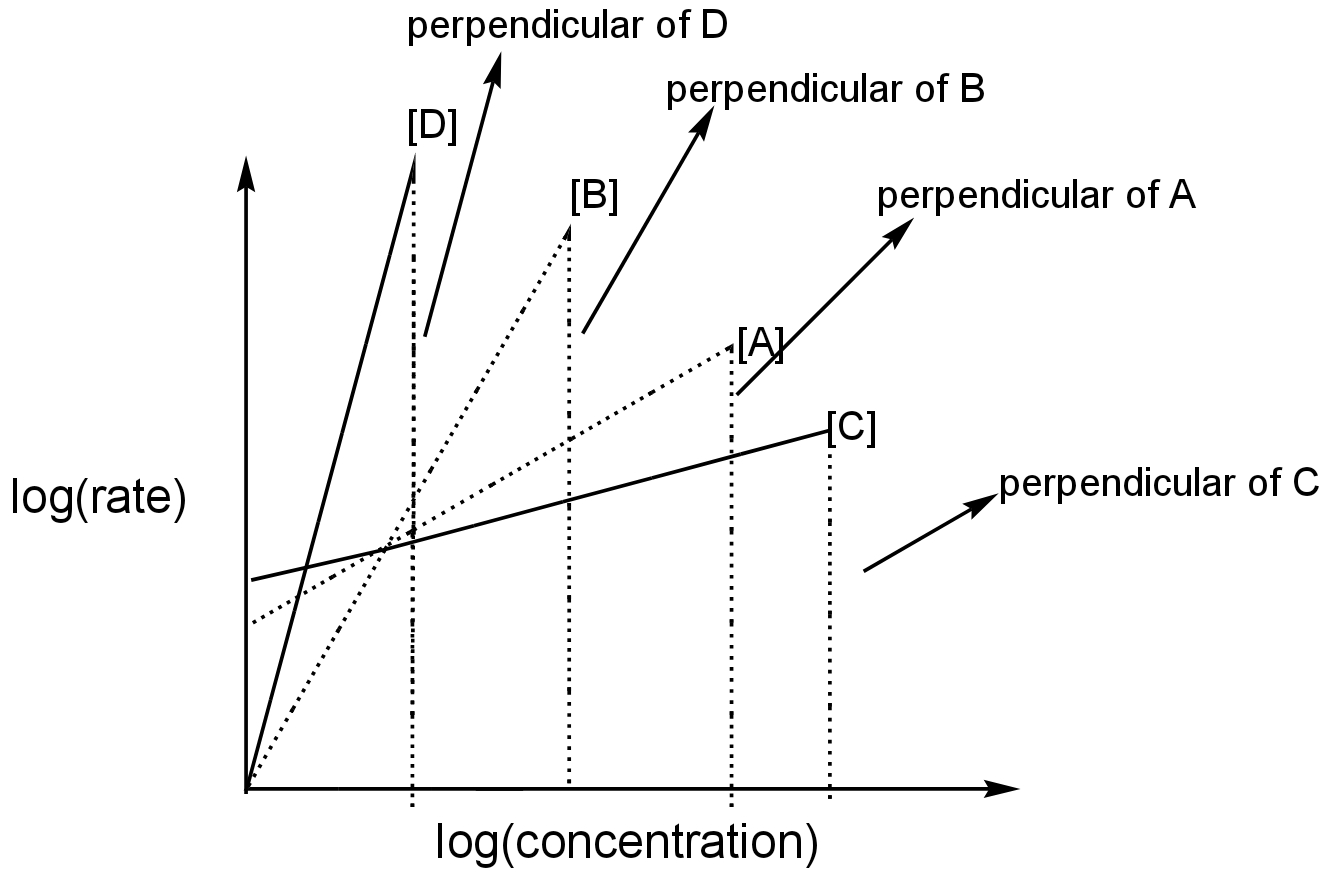
Image: perpendiculars of the slopes of different reactions.
The line which has a higher length of perpendicular has a higher slope.
D has the highest length of perpendicular, so has the highest slope and hence, the highest order.
B has a perpendicular less than D but more than A and C.
A has a higher length of perpendicular than C.
C has the least length of perpendicular as compared to others. Hence, C has the lowest order.
Thus, the correct sequence for the order of the reactions is d>b>a>c
So, option C is correct.
Note: We know that the tangent of an angle gives the slope. The tangent of an angle is the ratio of its perpendicular to the base. So, if the line has a higher length perpendicular, then it will have more slope. So, by observing the graph we can see whose perpendicular has a higher length and higher slope.
Formula Used:
\[{\rm{log(rate) = nlog(concentration) + logk}}\]
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this graph log(rate) is plotted against log(concentration).
The graph is linear for all four reactions.
It means the rate changes with the concentration of the reactant.
Rate is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant.
Let us consider the order of the reactions to be n.
\[{\rm{Rate = k[A}}{{\rm{]}}^{\rm{n}}}\] for the first reaction.
\[{\rm{Rate = k[B}}{{\rm{]}}^{\rm{n}}}\]for the second reaction.
\[{\rm{Rate = k[C}}{{\rm{]}}^{\rm{n}}}\]for the third reaction.
\[{\rm{Rate = k[D}}{{\rm{]}}^{\rm{n}}}\]for the fourth reaction.
If we take the log for a rate law equation we get
\[{\rm{Rate = k(concentration}}{{\rm{)}}^{\rm{n}}}\]
\[{\rm{log(rate) = nlog(concentration) + logk}}\]
This equation resembles the mathematical expression \[{\rm{y = mx + c}}\].
Thus, comparing both the equations we get,
Slope or m is the order of the reaction.
Thus, the reaction having more slope will have more order.

Image: perpendiculars of the slopes of different reactions.
The line which has a higher length of perpendicular has a higher slope.
D has the highest length of perpendicular, so has the highest slope and hence, the highest order.
B has a perpendicular less than D but more than A and C.
A has a higher length of perpendicular than C.
C has the least length of perpendicular as compared to others. Hence, C has the lowest order.
Thus, the correct sequence for the order of the reactions is d>b>a>c
So, option C is correct.
Note: We know that the tangent of an angle gives the slope. The tangent of an angle is the ratio of its perpendicular to the base. So, if the line has a higher length perpendicular, then it will have more slope. So, by observing the graph we can see whose perpendicular has a higher length and higher slope.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




