
Consider the following reaction and identify (B)
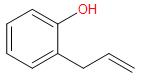 \[\underset{{{H}_{3}}O}{\overset{C{{H}_{3}}C{{O}_{3}}H}{\mathop{\to }}}\,\]\[(B)\]
\[\underset{{{H}_{3}}O}{\overset{C{{H}_{3}}C{{O}_{3}}H}{\mathop{\to }}}\,\]\[(B)\]
A. 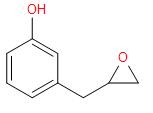
B. 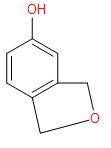
C. 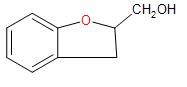
D. 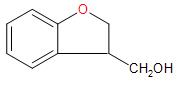
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The reaction given in the question is an epoxidation reaction where an alkene is subjected to a peroxyacid to convert it into an epoxide. We can also say that epoxidation is the electrophilic addition of oxygen to the double bond of the alkene. That is what actually happens here and we must keep that in mind while solving this reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
An epoxide is a 3-membered ring containing two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. We can consider it to be cyclic ether. It is interesting because it is easily opened due to small ring strain and due to the electronegativity of the oxygen atom.
The mechanism of this reaction is a little complex. While it is considered a single step reaction, it involves several changes. The double bond is our nucleophile and attacks the more electrophilic oxygen. This breaks the weak oxygen-oxygen bond and creates a new carbonyl. Once this carbonyl is formed, rearrangement occurs and the more electrophilic oxygen is released to become the oxygen of the epoxide.
The oxygen can only attack from one face of the alkene. This means that the stereochemistry of the alkene is retained. If we start with a cis alkene we will get a cis epoxide. If we start with a trans alkene, we will get a trans epoxide.
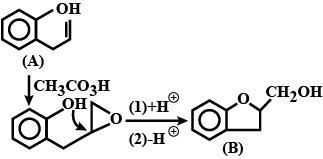
Hence, Option (C) is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Generally, we use peroxy acids in this electrophilic addition to the alkene. A peroxy acid is like a carboxylic acid, but has two oxygen atoms bonded to each other.
Note: This reaction is versatile, and works on many different alkenes. But we remember that the reaction will not work on the double bonds of an aromatic compound. Epoxides are essential from the examination point of view and we can expect at least one question on this.
Complete step by step answer:
An epoxide is a 3-membered ring containing two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. We can consider it to be cyclic ether. It is interesting because it is easily opened due to small ring strain and due to the electronegativity of the oxygen atom.
The mechanism of this reaction is a little complex. While it is considered a single step reaction, it involves several changes. The double bond is our nucleophile and attacks the more electrophilic oxygen. This breaks the weak oxygen-oxygen bond and creates a new carbonyl. Once this carbonyl is formed, rearrangement occurs and the more electrophilic oxygen is released to become the oxygen of the epoxide.
The oxygen can only attack from one face of the alkene. This means that the stereochemistry of the alkene is retained. If we start with a cis alkene we will get a cis epoxide. If we start with a trans alkene, we will get a trans epoxide.

Hence, Option (C) is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Generally, we use peroxy acids in this electrophilic addition to the alkene. A peroxy acid is like a carboxylic acid, but has two oxygen atoms bonded to each other.
Note: This reaction is versatile, and works on many different alkenes. But we remember that the reaction will not work on the double bonds of an aromatic compound. Epoxides are essential from the examination point of view and we can expect at least one question on this.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




