
Chiral carbon is:
(A) carbon in which all four valencies are satisfied with four different atoms or group of atoms
(B) carbon in which at least two of their valency are satisfied with four different atoms or group of atoms
(C) carbon in which all four valencies satisfied with same atoms
(D) none of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: A chiral carbon indicates the presence of optical activity around the central carbon. The mirror image of an optically active compound should not superimpose over the original image. So, if the same groups or atoms are attached the mirror image will not be unique.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The word “isomer” is derived from the Greek words "isos" and "mers". "Isos" means equal and "mers" means parts, so "isomers" means equal parts.
Isomerism is the phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formulas but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers i.e. they exhibit isomerism.
Isomerism is of two types namely, Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
In stereoisomerism, the compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in their respective orientations of the atoms belonging to the compound in a 3D space.
The types of stereoisomerism are:
- Geometrical
- Optical
Optical isomers are two compounds having the same molecular formula but differ in their spatial arrangements of atoms, which have non-superimposable mirror images.
Since the mirror images are not the same, the groups around the chiral carbon must be different in order to satisfy the above condition. So Chiral carbon is carbon in which all four valencies are satisfied with four different atoms or groups of atoms.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
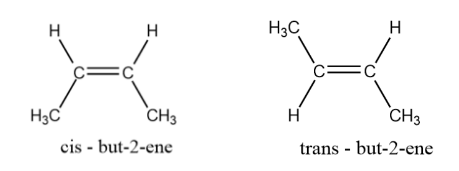
Note: Geometrical isomerism is popularly known as cis-trans isomerism.
Geometrical isomers have different spatial arrangements of atoms present in the compound in a 3D space. Given below is an example of pair of isomers exhibiting geometrical isomerism:
Complete step-by-step answer:
The word “isomer” is derived from the Greek words "isos" and "mers". "Isos" means equal and "mers" means parts, so "isomers" means equal parts.
Isomerism is the phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formulas but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers i.e. they exhibit isomerism.
Isomerism is of two types namely, Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
In stereoisomerism, the compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in their respective orientations of the atoms belonging to the compound in a 3D space.
The types of stereoisomerism are:
- Geometrical
- Optical
Optical isomers are two compounds having the same molecular formula but differ in their spatial arrangements of atoms, which have non-superimposable mirror images.
Since the mirror images are not the same, the groups around the chiral carbon must be different in order to satisfy the above condition. So Chiral carbon is carbon in which all four valencies are satisfied with four different atoms or groups of atoms.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Geometrical isomerism is popularly known as cis-trans isomerism.
Geometrical isomers have different spatial arrangements of atoms present in the compound in a 3D space. Given below is an example of pair of isomers exhibiting geometrical isomerism:

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




