
Can Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) reduce imine?
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: Sodium borohydride is a good reducing agent. It can reduce aldehydes and ketones into primary alcohols and secondary alcohols respectively.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
When ammonia is treated with aldehydes or ketones, the ammonia group gets added to the carbonyl group of aldehydes or ketones.
This is a reversible reaction and acid is used as a catalyst.
The product formed is called imine.
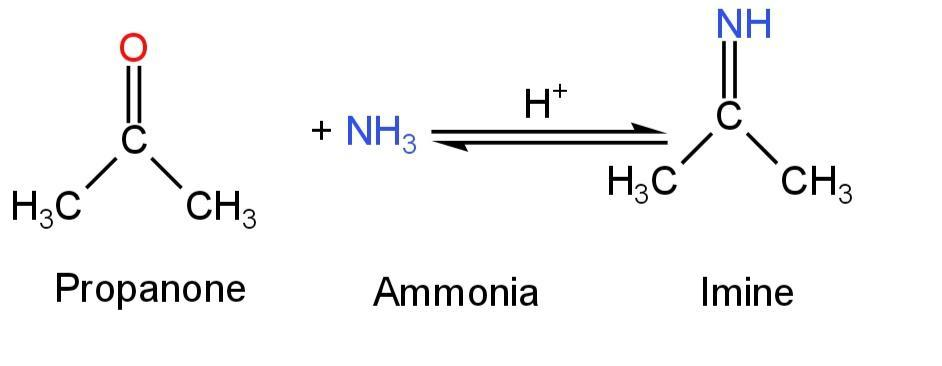
Image: Reaction of propanone with ammonia
Sodium borohydride is a good reducing agent that can reduce imines into secondary amines.
This reaction happens in the presence of alumina.
Here polar metal-hydrogen bond furnishes the hydride anion.
The mechanism of the reaction is of two steps.
Step-1
Nucleophilic attack by the hydride anion.
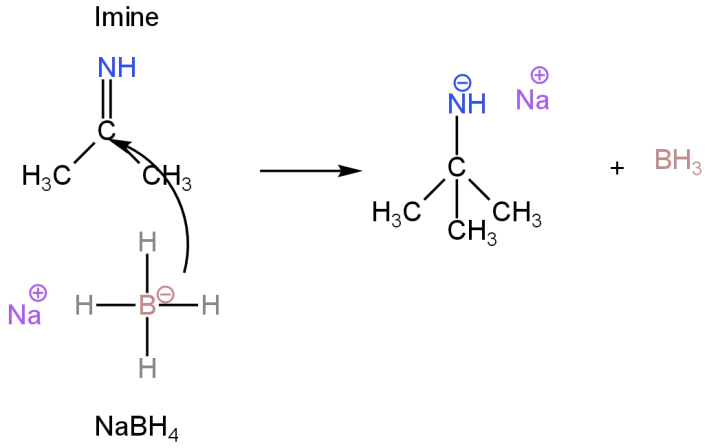
Image: Attack of the nucleophile
Step-2
Protonation leads to the formation of a secondary amine.
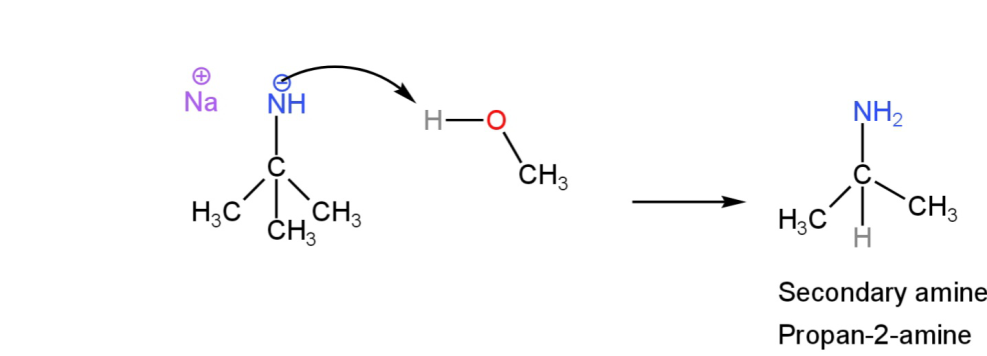
Image: Protonation in the presence of methanol.
Additional Information: Sodium borohydride is a lesser reducing agent than Lithium aluminium hydride. It can reduce aldehydes to primary alcohol and ketones, and acid chlorides to secondary alcohols. It cannot reduce esters, amides, acids, nitriles etc.
Note: Sodium borohydride is an inorganic compound and is a good reducing agent due to the existence of a polar metal-hydrogen bond. The hydrogen atom in the compound acts as a hydride and adds to the carbonyl carbon. The extremely familiar reducing agents in organic chemistry are lithium aluminium hydride and sodium borohydride. It is to be noted that the hydride anion does not directly exist during this reaction, rather a metal-hydrogen bond provides the hydride anion. This anion then acts as a nucleophile.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
When ammonia is treated with aldehydes or ketones, the ammonia group gets added to the carbonyl group of aldehydes or ketones.
This is a reversible reaction and acid is used as a catalyst.
The product formed is called imine.

Image: Reaction of propanone with ammonia
Sodium borohydride is a good reducing agent that can reduce imines into secondary amines.
This reaction happens in the presence of alumina.
Here polar metal-hydrogen bond furnishes the hydride anion.
The mechanism of the reaction is of two steps.
Step-1
Nucleophilic attack by the hydride anion.

Image: Attack of the nucleophile
Step-2
Protonation leads to the formation of a secondary amine.

Image: Protonation in the presence of methanol.
Additional Information: Sodium borohydride is a lesser reducing agent than Lithium aluminium hydride. It can reduce aldehydes to primary alcohol and ketones, and acid chlorides to secondary alcohols. It cannot reduce esters, amides, acids, nitriles etc.
Note: Sodium borohydride is an inorganic compound and is a good reducing agent due to the existence of a polar metal-hydrogen bond. The hydrogen atom in the compound acts as a hydride and adds to the carbonyl carbon. The extremely familiar reducing agents in organic chemistry are lithium aluminium hydride and sodium borohydride. It is to be noted that the hydride anion does not directly exist during this reaction, rather a metal-hydrogen bond provides the hydride anion. This anion then acts as a nucleophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




