
Benzaldehyde condenses with N, N-dimethylaniline in presence of anhydrous \[ZnC{l_2}\] to give
A. Michler’s ketone
B. Azo dye
C. Malachite green
D. Buffer yellow
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: The chemical formula of benzaldehyde is \[{C_6}{H_5}CH = O\]. In N, N-dimethylaniline and hydrogen of the amine group are replaced by two methyl groups. In the given reaction dehydration takes place as a water molecule is removed. It is a type of condensation reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Benzaldehyde in reaction with N,N-dimethyl aniline in presence of anhydrous zinc chloride gives malachite green. Anhydrous means free from water. Here, the two hydrogen atoms from two molecules of N, N-dimethylaniline are removed along with one oxygen atom of benzaldehyde forming a malachite green and removing the water molecule.
The complete reaction between benzaldehyde and N, N-dimethylaniline in presence of anhydrous \[ZnC{l_2}\]is shown below.
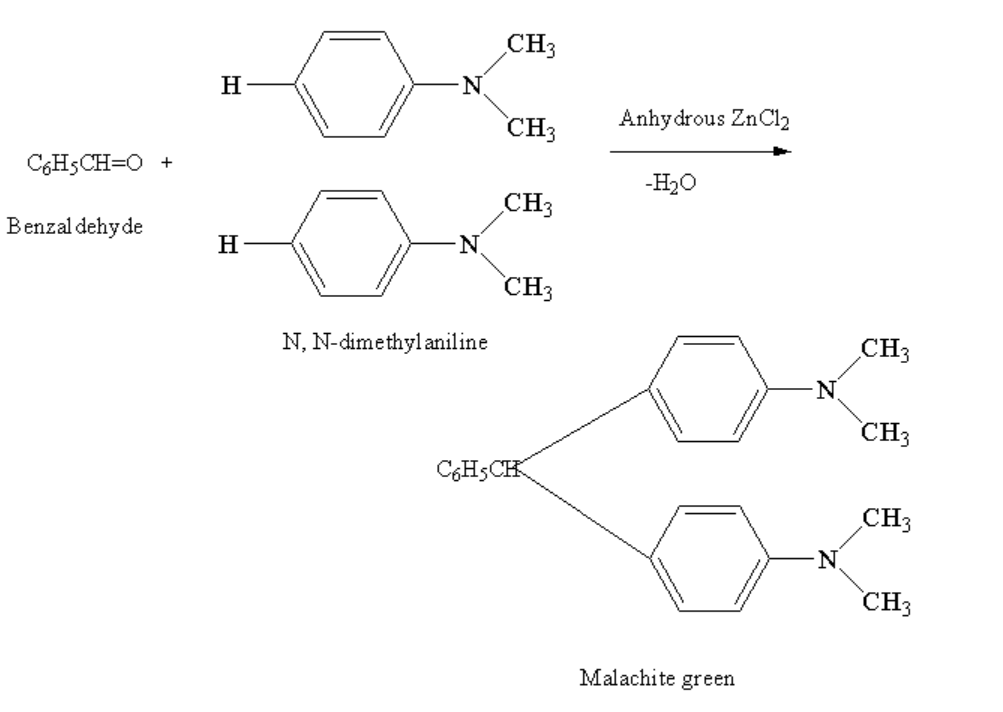
Image: Reaction of benzaldehyde and N, N-Dimethylaniline
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Additional information: Hermann Fisher was the first scientist to prepare Leuco malachite green in the year 1877. Malachite green is generally used in the dyestuff industry as triarylmethane and in the pigment industry. The term malachite green is used due to its coloured green cation. Malachite green is very hard to detect as it does not give any fluorescence in an aqueous solution.
Note: It should be noted that two molecules of N, N-dimethylaniline are reacted not one molecule with benzaldehyde to give malachite green. First when benzaldehyde reacts with N, N-dimethylaniline it gives leuco malachite green which is a colourless compound which further on reacting gives hydrogen chloride and oxidation forms malachite green.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Benzaldehyde in reaction with N,N-dimethyl aniline in presence of anhydrous zinc chloride gives malachite green. Anhydrous means free from water. Here, the two hydrogen atoms from two molecules of N, N-dimethylaniline are removed along with one oxygen atom of benzaldehyde forming a malachite green and removing the water molecule.
The complete reaction between benzaldehyde and N, N-dimethylaniline in presence of anhydrous \[ZnC{l_2}\]is shown below.

Image: Reaction of benzaldehyde and N, N-Dimethylaniline
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Additional information: Hermann Fisher was the first scientist to prepare Leuco malachite green in the year 1877. Malachite green is generally used in the dyestuff industry as triarylmethane and in the pigment industry. The term malachite green is used due to its coloured green cation. Malachite green is very hard to detect as it does not give any fluorescence in an aqueous solution.
Note: It should be noted that two molecules of N, N-dimethylaniline are reacted not one molecule with benzaldehyde to give malachite green. First when benzaldehyde reacts with N, N-dimethylaniline it gives leuco malachite green which is a colourless compound which further on reacting gives hydrogen chloride and oxidation forms malachite green.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




