
Baeyer's reagent is:
A. Alkaline $KMn{O_4}$ solution
B. Acidic $KMn{O_4}$ solution
C. Neutral $KMn{O_4}$ solution
D. Aqueous bromine solution
Answer
232.5k+ views
Hint: Try to recall that Bayer’s reagent is used to test unsaturation in organic compounds. Also, on dissolving in water it gives intensely pink or purple solutions. Now by using this you can easily answer the given question.
Complete step by step solution:
As it is known to you that Bayer’s reagent is used in the qualitative organic analysis to test for the presence of unsaturation.
Also, when Bayer’s reagent reacts with double bonds or triple bonds it causes discharge of color of Bayer’s reagent from pink/purple to brown color due to the formation of $Mn{O_2}$.
By observing color change, you can easily say that Bayer’s reagent is a dilute alkaline solution of cold potassium permanganate ($KMn{O_4}$).
It is already known to you that $KMn{O_4}$ act as oxidizing agent in acidic medium, alkaline as well as neutral medium but dilute alkaline $KMn{O_4}$ will act as mild oxidizing agent and get reduced
The general reaction of Baeyer's reagent with double or triple bond is as follows:
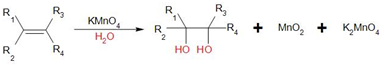
In this case, hydroxyl groups are added across the double bond and syn diols are formed. Hence, it is also known as hydroxylation reaction.
Therefore, from above we can say that option A is the correct option to the given question.
Note: It should be remembered to you that alkenes form syn diols and alkynes form dicarbonyl compounds on reaction with Baeyer's reagent.
Aldehydes and formic acid also give positive tests to Bayer’s reagent i.e. changes color from purple to brown.
Also, it should be remembered that ketones do not give positive tests to Baeyer’s reagent.
Complete step by step solution:
As it is known to you that Bayer’s reagent is used in the qualitative organic analysis to test for the presence of unsaturation.
Also, when Bayer’s reagent reacts with double bonds or triple bonds it causes discharge of color of Bayer’s reagent from pink/purple to brown color due to the formation of $Mn{O_2}$.
By observing color change, you can easily say that Bayer’s reagent is a dilute alkaline solution of cold potassium permanganate ($KMn{O_4}$).
It is already known to you that $KMn{O_4}$ act as oxidizing agent in acidic medium, alkaline as well as neutral medium but dilute alkaline $KMn{O_4}$ will act as mild oxidizing agent and get reduced
The general reaction of Baeyer's reagent with double or triple bond is as follows:

In this case, hydroxyl groups are added across the double bond and syn diols are formed. Hence, it is also known as hydroxylation reaction.
Therefore, from above we can say that option A is the correct option to the given question.
Note: It should be remembered to you that alkenes form syn diols and alkynes form dicarbonyl compounds on reaction with Baeyer's reagent.
Aldehydes and formic acid also give positive tests to Bayer’s reagent i.e. changes color from purple to brown.
Also, it should be remembered that ketones do not give positive tests to Baeyer’s reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




