
Area bounded by the curves $y=\left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{64}+2 \right],y=x-1$and \[\]\[x=0\] av0ve x-axis ($\left[ . \right]$ denotes the greatest integer function)
A. 2 sq unit
B. 3 sq unit
C. 4 sq unit
D. None of this
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:In the given question we need to find the bounded curve formed by two given equation of line such as $y=\left[ \frac{{{x}^{2}}}{64}+2 \right]$ and $y=x-1$at point x = 0. As soon as the bounded curved is formed we need to integrate the whole area under the curve from starting point bounded curve (lower limit of integration) to the last point of the bounded point (upper limit of integration if the curve has no definite shape otherwise we can apply the formula of definite shapes (rectangle, circle, triangle and so on). In this question, we got a bounded curve in a triangle shape. Before proceeding into the question, you should have a general idea of coordinate geometry, and how to make a graph of the given equations. And also know about the concept of coordinate geometry in which pair of straight lines cuts the parabola at two points on the y-axis.
Formula Used: $\int {{x}^{n+1}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}$
Area of triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height$
Complete step-by-step solution:
As we have two equations of lines such as $y=\left[ \frac{{{x}^{2}}}{64}+2 \right],y=x-1$so firstly draw both lines on axis graph by putting different valve of x such as
Taking account the first equation of line such as
$y=\left[ \frac{{{x}^{2}}}{64}+2 \right]$
As we put the different values of x and putting in the given equation we will get different values of y corresponding to different values of x.
If we put \[x\text{ }=\text{ }1\]we get
\[\begin{align}
& y=\left[ \frac{{{1}^{2}}}{64}+2 \right] \\
& y=\left[ \frac{1}{64}+2 \right] \\
& y=\left[ 0.0156+2 \right] \\
& y=\left[ 2.0156 \right] \\
\end{align}\]
By greatest function as given in the question, we get the approx value of y 2 corresponding to the value of x, 1 such as \[Y=2\]. Similarly, if we put values of x in between 0 to 7 it always get
\[Y=2\]
Only \[\text{Y }=\text{ }3\]if we put value in between 8 to 15 and so on such as
Plotting a graph of given equation
$y=\left[ \frac{{{x}^{2}}}{64}+2 \right],y=x-1$And\[x=0\]
Taking account the second equation of line such as
$y=x-1$
As we put the different values of x and putting in given equation we will get different values of y corresponding to different values of x.
If we put \[x\text{ }=\text{ }1\]we get
$y=1-1=0$,
For \[x\text{ }=\text{ }2\], value of y will be equal to 1 and similarly when we put value of
\[x\text{ }=\text{ }3\]
\[x\text{ }=\text{ }3\] value of y will be 2 such as
As both lines are cutting each other at (3, 2) so the curve under the both line and \[x\text{ }=\text{ }0\]is given as
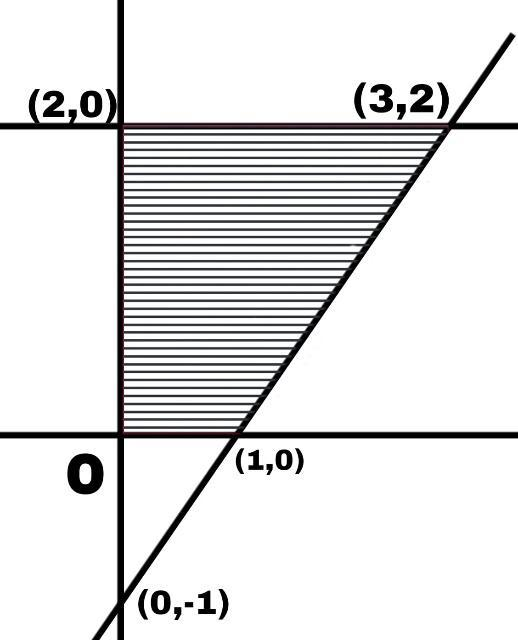
We need to find the area of shaded portion
Area of shaded portion = Area of big triangle – area of small triangle
Here from the big triangle we conclude that
Base of triangle =3 unit
Height of triangle =3 unit
Area of triangle = $\frac{1}{2}\times base\times height$
\[\begin{align}
& \frac{1}{2}\times base\times height \\
& \frac{1}{2}\times 3\times 3 \\
& \frac{9}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Similarly for small triangle
Base of small triangle=1 unit
Height of small triangle =1 unit
Area of triangle = $\frac{1}{2}\times base\times height$
\[\begin{align}
& \frac{1}{2}\times base\times height \\
& \frac{1}{2}\times 1\times 1 \\
& \frac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Area of shaded portion = Area of big triangle – area of small triangle
Area of shaded portion=$\begin{align}
& \frac{9}{2}-\frac{1}{2} \\
& \frac{8}{2} \\
& 4 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note: In finding the area of the big triangle we have covered the unbounded area and to get the bounded curve we need to cut the unbounded curve from the big triangle which is a small triangle. We expended the curve in a negative direction also but as we need to curve when the curve cut out at x = 0 thus we need to cut the expended curve (small triangle) from the whole curve (big triangle).
Formula Used: $\int {{x}^{n+1}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}$
Area of triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height$
Complete step-by-step solution:
As we have two equations of lines such as $y=\left[ \frac{{{x}^{2}}}{64}+2 \right],y=x-1$so firstly draw both lines on axis graph by putting different valve of x such as
Taking account the first equation of line such as
$y=\left[ \frac{{{x}^{2}}}{64}+2 \right]$
As we put the different values of x and putting in the given equation we will get different values of y corresponding to different values of x.
If we put \[x\text{ }=\text{ }1\]we get
\[\begin{align}
& y=\left[ \frac{{{1}^{2}}}{64}+2 \right] \\
& y=\left[ \frac{1}{64}+2 \right] \\
& y=\left[ 0.0156+2 \right] \\
& y=\left[ 2.0156 \right] \\
\end{align}\]
By greatest function as given in the question, we get the approx value of y 2 corresponding to the value of x, 1 such as \[Y=2\]. Similarly, if we put values of x in between 0 to 7 it always get
\[Y=2\]
Only \[\text{Y }=\text{ }3\]if we put value in between 8 to 15 and so on such as
| Value of x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | So on |
| Value of y | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
Plotting a graph of given equation
$y=\left[ \frac{{{x}^{2}}}{64}+2 \right],y=x-1$And\[x=0\]
Taking account the second equation of line such as
$y=x-1$
As we put the different values of x and putting in given equation we will get different values of y corresponding to different values of x.
If we put \[x\text{ }=\text{ }1\]we get
$y=1-1=0$,
For \[x\text{ }=\text{ }2\], value of y will be equal to 1 and similarly when we put value of
\[x\text{ }=\text{ }3\]
\[x\text{ }=\text{ }3\] value of y will be 2 such as
| Value of X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Value of Y (X – 1) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
As both lines are cutting each other at (3, 2) so the curve under the both line and \[x\text{ }=\text{ }0\]is given as

We need to find the area of shaded portion
Area of shaded portion = Area of big triangle – area of small triangle
Here from the big triangle we conclude that
Base of triangle =3 unit
Height of triangle =3 unit
Area of triangle = $\frac{1}{2}\times base\times height$
\[\begin{align}
& \frac{1}{2}\times base\times height \\
& \frac{1}{2}\times 3\times 3 \\
& \frac{9}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Similarly for small triangle
Base of small triangle=1 unit
Height of small triangle =1 unit
Area of triangle = $\frac{1}{2}\times base\times height$
\[\begin{align}
& \frac{1}{2}\times base\times height \\
& \frac{1}{2}\times 1\times 1 \\
& \frac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Area of shaded portion = Area of big triangle – area of small triangle
Area of shaded portion=$\begin{align}
& \frac{9}{2}-\frac{1}{2} \\
& \frac{8}{2} \\
& 4 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note: In finding the area of the big triangle we have covered the unbounded area and to get the bounded curve we need to cut the unbounded curve from the big triangle which is a small triangle. We expended the curve in a negative direction also but as we need to curve when the curve cut out at x = 0 thus we need to cut the expended curve (small triangle) from the whole curve (big triangle).
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole




