
An oxidizing agent is a substance which can
A.Accept electrons
B.Donate electrons
C.Accept protons
D.Donate protons
Answer
243k+ views
Hint: Basically, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that tends to oxidize other substances. It causes an increase in the oxidation state of the substance by making it lose electrons. Generally, it takes the electrons towards itself and thus it gains electrons and gets reduced.
Complete step by step answer:
An oxidizing agent, also known as an oxidizer or oxidant is a chemical compound that readily transfers oxygen atoms in a redox reaction. Basically, it helps in the oxidation while getting reduced by gaining hydrogen and giving oxygen or gaining electrons form the other reactants. Some of the common examples of oxidizing agents are halogens such as chlorine and fluorine, oxygen and hydrogen peroxide.
Now, oxidizing agents can be defined in two different ways:
1.As an electron acceptor- These are the chemical substances whose atoms remove at least one electron from another atom in a chemical reaction. Basically, oxidizing agents are the reactants that undergo reduction in redox reactions. An illustration is as shown:
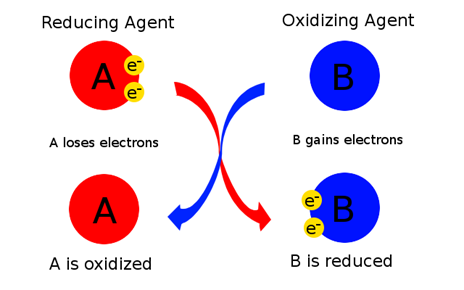
We can see that substance A undergoes oxidation, resulting in an increase in oxidation number whereas substance B becomes smaller as it gains electrons by undergoing reduction.
2.As an atom transferring substance- It is a substance that transfers at least one electronegative atom to a chemical species in a chemical reaction and the transferred atom is typically an oxygen atom. The example is as shown:
\[F{e_2}{O_3} + 3CO \to 2Fe + 3C{O_2}\]
In this case, the $F{e_2}{O_3}$ molecule acts as an oxidizer by transferring the electronegative oxygen atom to carbon monoxide molecule.
Therefore, an oxidizing agent is a substance which can accept electrons.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:Oxidizing agents have various commercial and industrial applications. They are used in bleaching of fabrics, purification of water, storage of energy in batteries, vulcanization of rubber. Moreover, they are also vital to many biological processes such as metabolism and photosynthesis.
Complete step by step answer:
An oxidizing agent, also known as an oxidizer or oxidant is a chemical compound that readily transfers oxygen atoms in a redox reaction. Basically, it helps in the oxidation while getting reduced by gaining hydrogen and giving oxygen or gaining electrons form the other reactants. Some of the common examples of oxidizing agents are halogens such as chlorine and fluorine, oxygen and hydrogen peroxide.
Now, oxidizing agents can be defined in two different ways:
1.As an electron acceptor- These are the chemical substances whose atoms remove at least one electron from another atom in a chemical reaction. Basically, oxidizing agents are the reactants that undergo reduction in redox reactions. An illustration is as shown:

We can see that substance A undergoes oxidation, resulting in an increase in oxidation number whereas substance B becomes smaller as it gains electrons by undergoing reduction.
2.As an atom transferring substance- It is a substance that transfers at least one electronegative atom to a chemical species in a chemical reaction and the transferred atom is typically an oxygen atom. The example is as shown:
\[F{e_2}{O_3} + 3CO \to 2Fe + 3C{O_2}\]
In this case, the $F{e_2}{O_3}$ molecule acts as an oxidizer by transferring the electronegative oxygen atom to carbon monoxide molecule.
Therefore, an oxidizing agent is a substance which can accept electrons.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:Oxidizing agents have various commercial and industrial applications. They are used in bleaching of fabrics, purification of water, storage of energy in batteries, vulcanization of rubber. Moreover, they are also vital to many biological processes such as metabolism and photosynthesis.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




