
An organic compound ‘A’ on treatment with ${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$gives ‘B’ which on heating gives ‘C’, ‘C’ when treated with ${\rm{B}}{{\rm{r}}_{\rm{2}}}$in the presence of ${\rm{KOH}}$produces ethylamine. Compound ‘A’ is:
A. ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}}$
B. ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{COOH}}$
C. 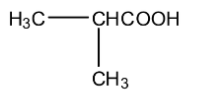
D. ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{COOH}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We know that Hoffmann bromamide reaction is the reaction which produces alkyl amine on reaction of amide with bromine in presence of ethanolic solution of sodium or potassium hydroxide.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, it is given that reaction ‘C’ with bromine in presence of potassium hydroxide solution gives ethaylamine that means, the reaction is Hoffmann Bromoamide reaction. Then, C must be an amide. ‘C’ forms by heating of B. Then, ‘B’ must be a carboxylate ion. Then ‘A’ must be a carboxylic acid. Now, we have to determine, which carboxylic acid among the given options is correct. We know that, in Hoffmann Bromamide degradation reaction, the loss of one carbon atom takes place. In the question product formed is ethylamine, that means, the amide composed of three carbon atoms, which indicates that the carboxylic acid ‘A’ also contains three carbon atoms, that is propanoic acid.
Now, we write the whole reaction.
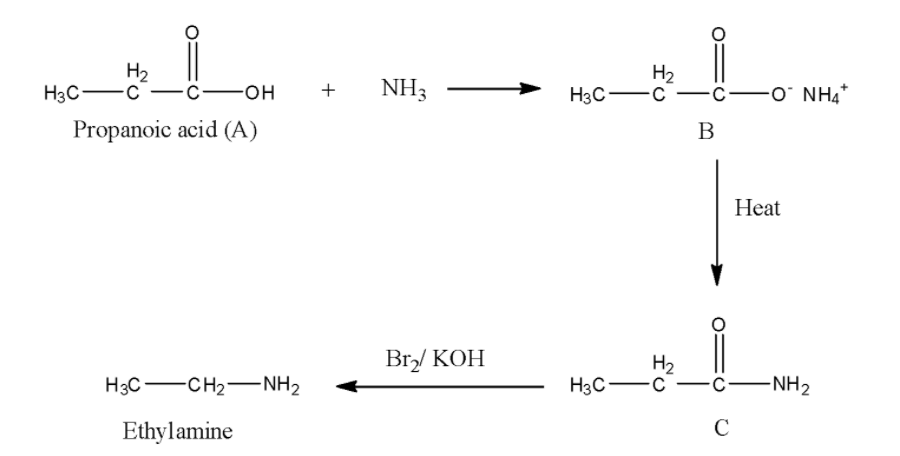
Thus, the correct answer is option D, i.e., ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{COOH}}$..
Additional Information:
Hoffmann bromoamide reaction is a degradation reaction, where migration of an aryl or alkyl group from carbonyl carbon of amide to nitrogen atom takes place. So, the amine forms in the reaction contain one less carbon atom than that of the amide.
Note:
Students might get confused in choosing the correct carboxylic acid from the given options. They might think that, as the product of the reaction (ethylamine) consists of two carbon atoms, so the carboxylic acid also has two carbon atoms. But they must not forget that Hoffmann bromoamide reaction is a degradation reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, it is given that reaction ‘C’ with bromine in presence of potassium hydroxide solution gives ethaylamine that means, the reaction is Hoffmann Bromoamide reaction. Then, C must be an amide. ‘C’ forms by heating of B. Then, ‘B’ must be a carboxylate ion. Then ‘A’ must be a carboxylic acid. Now, we have to determine, which carboxylic acid among the given options is correct. We know that, in Hoffmann Bromamide degradation reaction, the loss of one carbon atom takes place. In the question product formed is ethylamine, that means, the amide composed of three carbon atoms, which indicates that the carboxylic acid ‘A’ also contains three carbon atoms, that is propanoic acid.
Now, we write the whole reaction.

Thus, the correct answer is option D, i.e., ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{COOH}}$..
Additional Information:
Hoffmann bromoamide reaction is a degradation reaction, where migration of an aryl or alkyl group from carbonyl carbon of amide to nitrogen atom takes place. So, the amine forms in the reaction contain one less carbon atom than that of the amide.
Note:
Students might get confused in choosing the correct carboxylic acid from the given options. They might think that, as the product of the reaction (ethylamine) consists of two carbon atoms, so the carboxylic acid also has two carbon atoms. But they must not forget that Hoffmann bromoamide reaction is a degradation reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




