
An inductor and resistor are connected in series with an AC source. In this circuit,
The current and the PD across resistance lead the PD across the inductance.
(A) The current and the PD across the resistance lag behind the PD across the inductance by angle $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
(B) The current and the PD across the resistance lag behind the PD across the inductance by an angle $\pi $
(C) The PD across the resistance lags behind the PD across the inductance by an angle (D)$\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ but the current in resistance leads the PD across the inductance by $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Answer
240k+ views
Hint Find the impedance for series resistance and inductor AC circuit then, draw the phasor diagram of series inductance and resistance series AC circuit. In the phasor diagram, draw the voltage across resistance and also draw the voltage across inductance. If the angle of voltage across inductance is greater then it leads the voltage across resistance.
Step by Step Solution
Let the resistance and inductance be R and L respectively
Construct a series L-R AC circuit
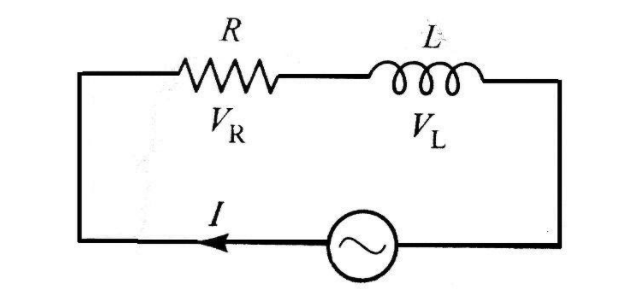
Now, we get
${V_{net}} = {\vec V_L} + {\vec V_R}$
By taking magnitude
\[
\left| {{{\vec V}_{net}}} \right| = \sqrt {({V^2}_L + {V^2}_R)} \\
\left| {{{\vec V}_{net}}} \right| = \sqrt {({i^2}{X^2}_L + {i^2}{R^2})} \\
\\
\]
By taking ${i^2}$ common
\[\left| {{{\vec V}_{net}}} \right| = i\sqrt {({X^2}_L + {R^2})} \]
To calculate the impedance let impedance be $Z$
$Z = \dfrac{V}{i} = \sqrt {({X_L}^2 + {R^2})} $
Because, ${X_L} = \omega L$ we get
$Z = \sqrt {({\omega ^2}{L^2} + {R^2})} $
This is the impedance for series L-R AC circuit
Now, draw the phasor diagram for series L-R AC circuit
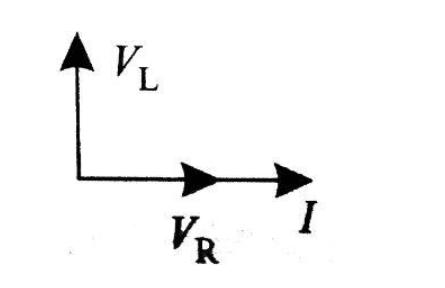
$
\tan \varphi = \dfrac{{{V_L}}}{{{V_R}}} \\
\tan \varphi = \dfrac{{i{X_L}}}{{iR}} \\
\\
$
Now, we get
$\varphi = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{X_L}}}{R}} \right)$
Therefore, after seeing the phasor diagram we can easily conclude that potential difference across inductance leads the current and potential difference across resistance by an angle $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Hence, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note resistance is the measure of the opposition of current in the circuit. It is denoted by R. It is measured in ohms $(\Omega )$.
Inductance is the property of a conductor to oppose the flow of electric current through it. The flow of current makes a magnetic field around the conductor. It is denoted by L. It is measured in Henry $(H)$.
Step by Step Solution
Let the resistance and inductance be R and L respectively
Construct a series L-R AC circuit

Now, we get
${V_{net}} = {\vec V_L} + {\vec V_R}$
By taking magnitude
\[
\left| {{{\vec V}_{net}}} \right| = \sqrt {({V^2}_L + {V^2}_R)} \\
\left| {{{\vec V}_{net}}} \right| = \sqrt {({i^2}{X^2}_L + {i^2}{R^2})} \\
\\
\]
By taking ${i^2}$ common
\[\left| {{{\vec V}_{net}}} \right| = i\sqrt {({X^2}_L + {R^2})} \]
To calculate the impedance let impedance be $Z$
$Z = \dfrac{V}{i} = \sqrt {({X_L}^2 + {R^2})} $
Because, ${X_L} = \omega L$ we get
$Z = \sqrt {({\omega ^2}{L^2} + {R^2})} $
This is the impedance for series L-R AC circuit
Now, draw the phasor diagram for series L-R AC circuit

$
\tan \varphi = \dfrac{{{V_L}}}{{{V_R}}} \\
\tan \varphi = \dfrac{{i{X_L}}}{{iR}} \\
\\
$
Now, we get
$\varphi = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{X_L}}}{R}} \right)$
Therefore, after seeing the phasor diagram we can easily conclude that potential difference across inductance leads the current and potential difference across resistance by an angle $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Hence, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note resistance is the measure of the opposition of current in the circuit. It is denoted by R. It is measured in ohms $(\Omega )$.
Inductance is the property of a conductor to oppose the flow of electric current through it. The flow of current makes a magnetic field around the conductor. It is denoted by L. It is measured in Henry $(H)$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 1 (55/1/1) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Marking Scheme




