
An example of homopolysaccharides is/are: (This question contains multiple correct answers)
(A) Sucrose
(B) Cellulose
(C) Mannose
(D) Starch
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The monomers of Sucrose are glucose and fructose. The monomer of Cellulose is glucose. The mannose is an aldohexose. The monomer of starch is glucose.
Complete step by step solution:
Homopolysaccharides are those polymers that are made up of only one type of monomer. Polysaccharides are those compounds in which the number of monomers is greater than 100 or even thousand.
Let us study all the options one by one:
(a)- Sucrose: Sucrose is a disaccharide. It is also known as cane-sugar or table sugar. The formula of sucrose is ${{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}$. It is the most common disaccharide and is widely distributed in the plants. It is manufactured from beetroot and sugarcane. When the sucrose is hydrolyzed it forms D-Glucose and D-Fructose.
$\underset{sucrose}{\mathop {{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}}\,+{{H}_{2}}O\to \underset{D-Glu\cos e}{\mathop {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}}\,+\underset{D-Fructose}{\mathop {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}}\,$
(b)- Cellulose: It is a polysaccharide that is made up of only one type of monomer. The monomer in the cellulose is glucose. The number of monomers varies from 300 to 3000 units per cellulose molecule. It is widely distributed in plants. The linkage in cellulose is $\beta -gly\cos idic\,linkage$.
(c)- Mannose: Mannose is an Aldohexose. The formula of mannose is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$. It is a monomer unit.
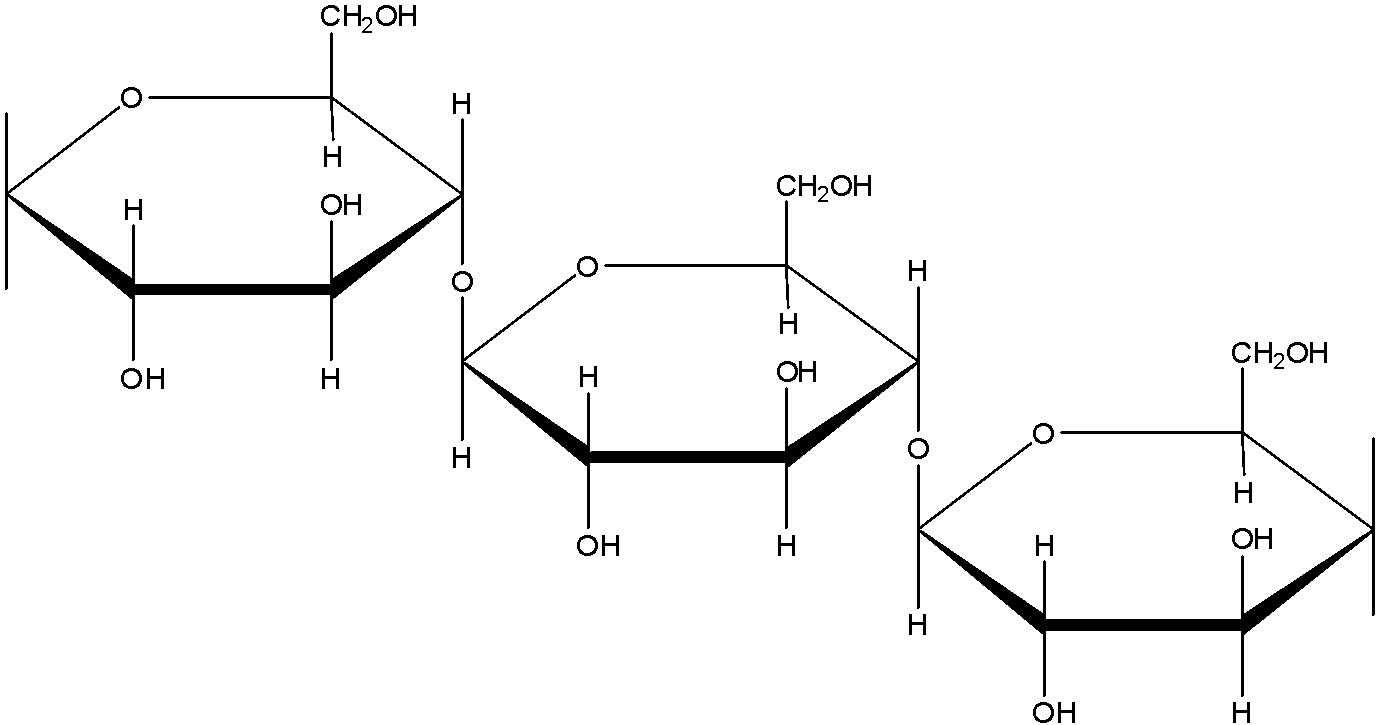
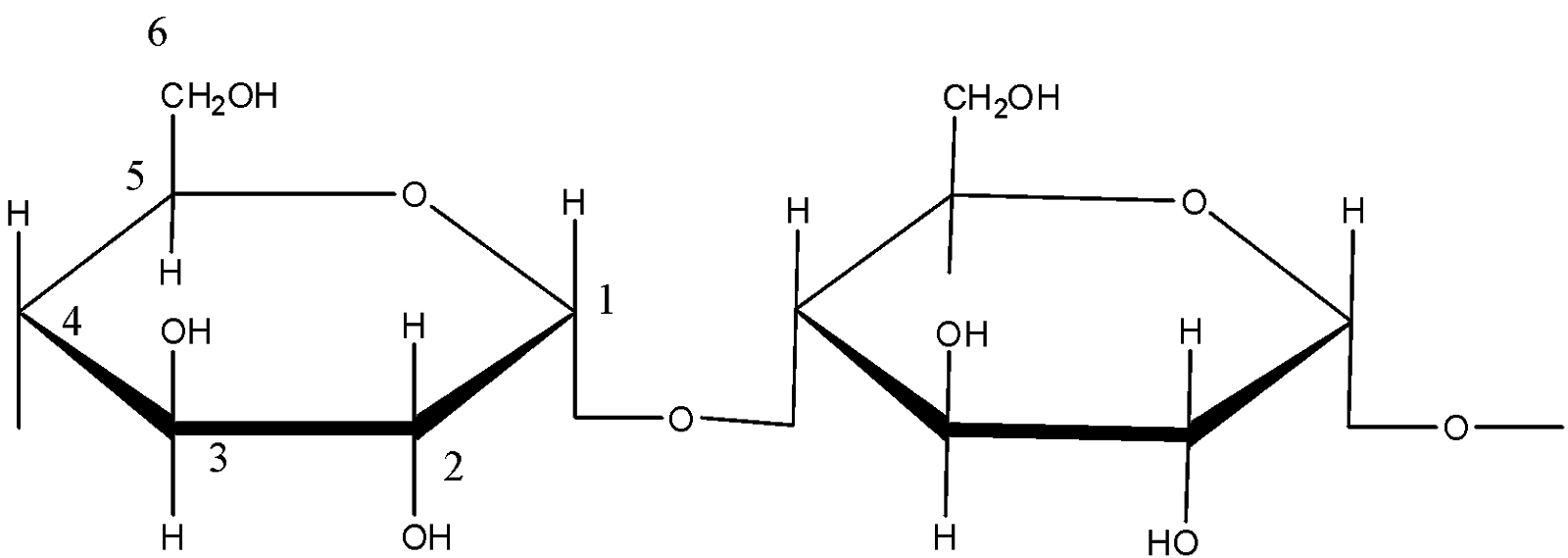
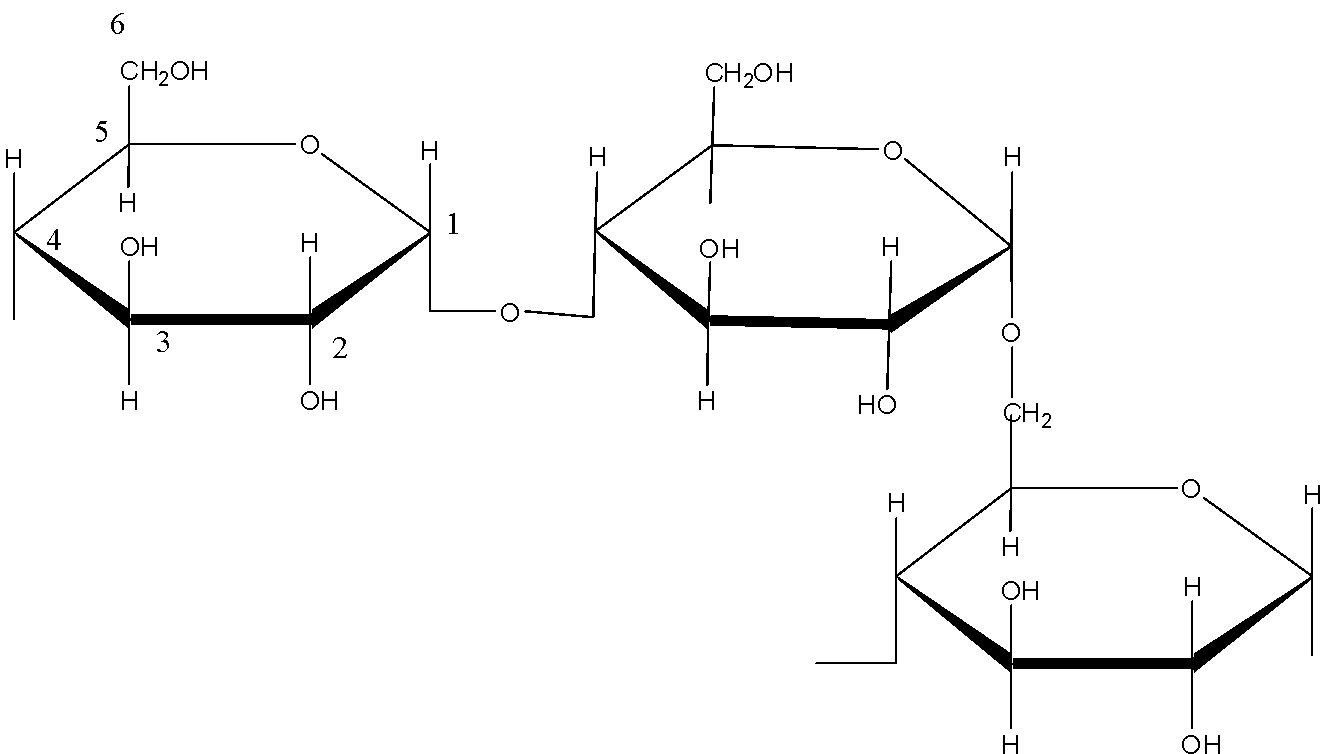
(d)- Starch: Starch is a polysaccharide which is made up of only one type of monomer. The monomer of Starch is glucose. It is a food reserve in plants Amylose, and amylopectin are two components of Starch. In amylose, the linkage is ${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{4}}\text{ }\alpha -gly\cos idic\,linkage$. In amylopectin there are 2 linkages: ${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{4}}\text{ }\alpha -gly\cos idic\,linkage$ and ${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{6}}\text{ }\alpha -gly\cos idic\,linkage$.
The structure of amylose is:
The structure of amylopectin is:
So, the correct answer is options (B) and (D).
Note: Aldohexose refers to the carbohydrate which has 6 carbons in the ring structure and the main functional group is aldehydes. Cellulose and starch on hydrolysis will form only glucose.
Complete step by step solution:
Homopolysaccharides are those polymers that are made up of only one type of monomer. Polysaccharides are those compounds in which the number of monomers is greater than 100 or even thousand.
Let us study all the options one by one:
(a)- Sucrose: Sucrose is a disaccharide. It is also known as cane-sugar or table sugar. The formula of sucrose is ${{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}$. It is the most common disaccharide and is widely distributed in the plants. It is manufactured from beetroot and sugarcane. When the sucrose is hydrolyzed it forms D-Glucose and D-Fructose.
$\underset{sucrose}{\mathop {{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}}\,+{{H}_{2}}O\to \underset{D-Glu\cos e}{\mathop {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}}\,+\underset{D-Fructose}{\mathop {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}}\,$
(b)- Cellulose: It is a polysaccharide that is made up of only one type of monomer. The monomer in the cellulose is glucose. The number of monomers varies from 300 to 3000 units per cellulose molecule. It is widely distributed in plants. The linkage in cellulose is $\beta -gly\cos idic\,linkage$.

(c)- Mannose: Mannose is an Aldohexose. The formula of mannose is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$. It is a monomer unit.
(d)- Starch: Starch is a polysaccharide which is made up of only one type of monomer. The monomer of Starch is glucose. It is a food reserve in plants Amylose, and amylopectin are two components of Starch. In amylose, the linkage is ${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{4}}\text{ }\alpha -gly\cos idic\,linkage$. In amylopectin there are 2 linkages: ${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{4}}\text{ }\alpha -gly\cos idic\,linkage$ and ${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{6}}\text{ }\alpha -gly\cos idic\,linkage$.
The structure of amylose is:

The structure of amylopectin is:

So, the correct answer is options (B) and (D).
Note: Aldohexose refers to the carbohydrate which has 6 carbons in the ring structure and the main functional group is aldehydes. Cellulose and starch on hydrolysis will form only glucose.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




