
An alkyl bromide (X) reacts with sodium in ether to form 4, 5-diethyl octane, the compound X is:
A. \[C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_3}Br\]
B. \[C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_5}Br\]
C. \[C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_3}CH\left( {Br} \right)C{H_3}\]
D. \[C{H_3} - {\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_2} - CH\left( {Br} \right) - C{H_2} - C{H_3}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: All alkyl halides undergo a coupling reaction with sodium in dry ether. The reaction is called the Wurtz Reaction. The product of this reaction is a higher alkane which is made of the alkyl groups of the reactant alkyl halides.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Alkyl halides (alkyl bromides in this case), in the presence of sodium in dry ether, undergo a reaction called the Wurtz Reaction. This is a coupling reaction between the alkyl halides in which their alkyl groups get attached via a carbon-carbon bond resulting in a higher alkane.
Wurtz reaction can occur between two molecules of the same alkyl halide. In this case, the corresponding higher alkane product will have twice the number of carbon atoms as the reactant alkyl halide. The general scheme is shown below:
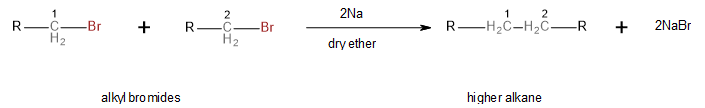
Image: General scheme of a Wurtz Reaction between two molecules of the same alkyl bromide
What is of note here, and what will help us solve this question, is that the new carbon-carbon bond of the higher alkane forms between the bromine-carrying carbons of the two alkyl bromides.
The higher alkane given in the question is 4, 5-diethyl octane.
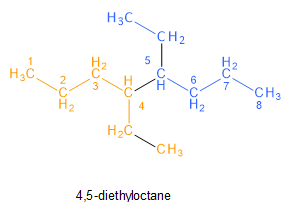
Image: Structure of 4,5-diethyloctane
From the structure, we can observe that 4,5-diethyloctane seems to be made of two identical hydrocarbon fragments (as shown in orange and blue colours), consisting of 6 carbon atoms in a straight chain, attached by a carbon-carbon bond between carbon 4 and carbon 5. Since the new carbon-carbon bond forms between the bromine-carrying carbons, we can deduce that carbons 4 and 5 are the bromine-carrying carbons of the reactant alkyl bromide.
Thus, the structure of the reactant alkyl bromide (X) is
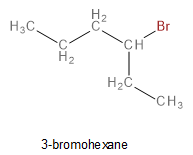
Image: Structure of X
Thus, option D is correct.
Note: To solve questions of this type, it is important to remember that the new carbon-carbon bond of the higher alkane will form between the halide-carrying carbons of the two alkyl halides. Drawing the structure of the given higher alkane will help us identify the alkyl fragments that were coupled in the Wurtz reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Alkyl halides (alkyl bromides in this case), in the presence of sodium in dry ether, undergo a reaction called the Wurtz Reaction. This is a coupling reaction between the alkyl halides in which their alkyl groups get attached via a carbon-carbon bond resulting in a higher alkane.
Wurtz reaction can occur between two molecules of the same alkyl halide. In this case, the corresponding higher alkane product will have twice the number of carbon atoms as the reactant alkyl halide. The general scheme is shown below:

Image: General scheme of a Wurtz Reaction between two molecules of the same alkyl bromide
What is of note here, and what will help us solve this question, is that the new carbon-carbon bond of the higher alkane forms between the bromine-carrying carbons of the two alkyl bromides.
The higher alkane given in the question is 4, 5-diethyl octane.

Image: Structure of 4,5-diethyloctane
From the structure, we can observe that 4,5-diethyloctane seems to be made of two identical hydrocarbon fragments (as shown in orange and blue colours), consisting of 6 carbon atoms in a straight chain, attached by a carbon-carbon bond between carbon 4 and carbon 5. Since the new carbon-carbon bond forms between the bromine-carrying carbons, we can deduce that carbons 4 and 5 are the bromine-carrying carbons of the reactant alkyl bromide.
Thus, the structure of the reactant alkyl bromide (X) is

Image: Structure of X
Thus, option D is correct.
Note: To solve questions of this type, it is important to remember that the new carbon-carbon bond of the higher alkane will form between the halide-carrying carbons of the two alkyl halides. Drawing the structure of the given higher alkane will help us identify the alkyl fragments that were coupled in the Wurtz reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




