
An acidified solution of potassium chromate was layered with an equal volume of amyl alcohol. When it was shaken after the addition of 1 mL of 3% \[{{\mathop{\rm H}\nolimits} _2}{O_2}\], a blue alcohol layer was obtained. The blue colour is due to the formation of a chromium (VI) compound 'X'. What is the number of oxygen atoms bonded to chromium through only single bonds in a molecule of X?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Potassium dichromate is a powerful oxidising agent. It reacts with Hydrogen peroxide to give a deep blue colouration due to the formation of the Peroxo compound.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Chromium is a transition metal of the 3d-series.
Its atomic number is 25.
Its electronic configuration is \[\left[ {{\rm{Ar}}} \right]{\rm{3}}{{\rm{d}}^{\rm{5}}}{\rm{4}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}\].
It shows a variable oxidation state.
The most common oxidation states are +3 and +6.
Potassium dichromate is an important compound of Chromium used as an oxidising agent.
Potassium dichromate is in the form of orange crystals.
The oxidation state of Chromium in this compound is +6.
When an acidified solution of Potassium reacts with Hydrogen peroxide, it gives a blue colouration.
This is due to the formation of peroxo compound, \[{\rm{Cr}}{\left( {{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}\].
.\[{{\mathop{\rm Cr}\nolimits} _2}{O_7}^{2 - } + 2{H^ + } + 4{H_2}{O_2} \to 2Cr{O_5} + 5{H_2}O\].
The structure of the product formed is
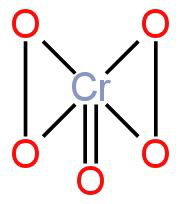
Image: Chromium pentoxide
The oxidation state of Chromium in this compound is +6.
It has a trigonal bipyramidal structure.
The number of oxygen atoms bonded to chromium only through single bonds in Chromium pentoxide is 4.
So,the number of oxygen atoms bonded to chromium only through single bonds in Chromium pentoxide is 4.
Additional Information: Chromium pentoxide decomposes to Cr3+ ions and oxygen which leads to the discoloration of the blue colour solution. It is a very good oxidising agent due to the presence of two reactive peroxo ligands. Ketones and primary alcohols when treated with it get oxidised to aldehydes and carboxylic acids.
Note: Chromium pentoxide is formed as a product when Potassium dichromate reacts with Hydrogen peroxide. This compound is a peroxo compound having one double bond and four single bonds attached to oxygen atoms. The structure of this compound is also called butterfly structure.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Chromium is a transition metal of the 3d-series.
Its atomic number is 25.
Its electronic configuration is \[\left[ {{\rm{Ar}}} \right]{\rm{3}}{{\rm{d}}^{\rm{5}}}{\rm{4}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}\].
It shows a variable oxidation state.
The most common oxidation states are +3 and +6.
Potassium dichromate is an important compound of Chromium used as an oxidising agent.
Potassium dichromate is in the form of orange crystals.
The oxidation state of Chromium in this compound is +6.
When an acidified solution of Potassium reacts with Hydrogen peroxide, it gives a blue colouration.
This is due to the formation of peroxo compound, \[{\rm{Cr}}{\left( {{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}\].
.\[{{\mathop{\rm Cr}\nolimits} _2}{O_7}^{2 - } + 2{H^ + } + 4{H_2}{O_2} \to 2Cr{O_5} + 5{H_2}O\].
The structure of the product formed is

Image: Chromium pentoxide
The oxidation state of Chromium in this compound is +6.
It has a trigonal bipyramidal structure.
The number of oxygen atoms bonded to chromium only through single bonds in Chromium pentoxide is 4.
So,the number of oxygen atoms bonded to chromium only through single bonds in Chromium pentoxide is 4.
Additional Information: Chromium pentoxide decomposes to Cr3+ ions and oxygen which leads to the discoloration of the blue colour solution. It is a very good oxidising agent due to the presence of two reactive peroxo ligands. Ketones and primary alcohols when treated with it get oxidised to aldehydes and carboxylic acids.
Note: Chromium pentoxide is formed as a product when Potassium dichromate reacts with Hydrogen peroxide. This compound is a peroxo compound having one double bond and four single bonds attached to oxygen atoms. The structure of this compound is also called butterfly structure.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




