
Among the following molecules which have the zero dipole moment?
A. \[B{F_3}\]
B. \[{H_2}O\]
C. \[N{F_3}\]
D. \[Cl{O_2}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Dipole moment is a vector quantity and is directed from a positive charge towards a negative charge. In molecules, the net dipole moment depends on their structure.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
A dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges within a system. It is a measure of the polarity of the system.
Since the atoms are very small, they can be considered point charges. If we have a positive point charge (+q) and a negative point charge (-q) separated by a distance d, the dipole moment between them (\[\overrightarrow p \]) is defined as \[\overrightarrow p = - q\overrightarrow d \]. The negative sign indicates that the dipole moment vector is directed from the positive charge to the negative charge. The SI unit of dipole moment is Coulomb meter (\[Cm\]). Another unit called Debye (\[D\]) is also commonly used in chemistry.
Since a dipole moment is a vector quantity, the addition of two dipole moments occurs according to the laws of vector addition. Because of this, two or more dipoles may add up to a net-zero dipole moment depending on their orientation.
Keeping all of this in mind, let’s look at Boron trifluoride (\[B{F_3}\]). Boron trifluoride has a trigonal planar structure with the Boron atom at the centre. Since Boron is more electropositive and Fluorine is more electronegative, \[B{F_3}\] the dipole moment is oriented towards the Fluorine atoms from the Boron atom as shown below:
Image: Structure of Boron Trifluoride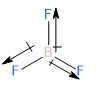
On summing up all the dipole moment vectors it can be observed that the resultant of any two dipole moment vectors will get cancelled out by the third one. Therefore, the net dipole moment on this molecule is zero.
The water molecule has a bent shape. The structure and dipole moments are shown below:
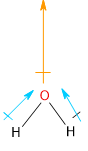
Image: Structure of Water Molecule and the Dipole moments within the molecule.
The two hydrogen-oxygen dipole moments (blue arrows) add up to a net non-zero resultant dipole moment (orange arrow).
Nitrogen trifluoride (\[N{F_3}\]) has a trigonal pyramidal structure as shown below. The three nitrogen-fluorine dipole moments do not cancel each other out. Thus, Nitrogen trifluoride has a net non-zero dipole moment.
Image: Structure and Dipole moment of Nitrogen Trifluoride molecule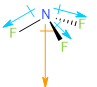
Chlorine dioxide (\[Cl{O_2}\]) has a structure similar to water. Thus, its dipole moments will add up like that of water.
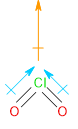
Image: Structure and Dipole moments of Chlorine Dioxide molecule
Thus, option A is correct.
Note: Knowledge of the structures of these molecules is crucial to solving these types of questions. It is also necessary to have at least an intuitive idea of how vector addition works without which students can make mistakes in predicting the net dipole moments of compounds.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
A dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges within a system. It is a measure of the polarity of the system.
Since the atoms are very small, they can be considered point charges. If we have a positive point charge (+q) and a negative point charge (-q) separated by a distance d, the dipole moment between them (\[\overrightarrow p \]) is defined as \[\overrightarrow p = - q\overrightarrow d \]. The negative sign indicates that the dipole moment vector is directed from the positive charge to the negative charge. The SI unit of dipole moment is Coulomb meter (\[Cm\]). Another unit called Debye (\[D\]) is also commonly used in chemistry.
Since a dipole moment is a vector quantity, the addition of two dipole moments occurs according to the laws of vector addition. Because of this, two or more dipoles may add up to a net-zero dipole moment depending on their orientation.
Keeping all of this in mind, let’s look at Boron trifluoride (\[B{F_3}\]). Boron trifluoride has a trigonal planar structure with the Boron atom at the centre. Since Boron is more electropositive and Fluorine is more electronegative, \[B{F_3}\] the dipole moment is oriented towards the Fluorine atoms from the Boron atom as shown below:
Image: Structure of Boron Trifluoride

On summing up all the dipole moment vectors it can be observed that the resultant of any two dipole moment vectors will get cancelled out by the third one. Therefore, the net dipole moment on this molecule is zero.
The water molecule has a bent shape. The structure and dipole moments are shown below:

Image: Structure of Water Molecule and the Dipole moments within the molecule.
The two hydrogen-oxygen dipole moments (blue arrows) add up to a net non-zero resultant dipole moment (orange arrow).
Nitrogen trifluoride (\[N{F_3}\]) has a trigonal pyramidal structure as shown below. The three nitrogen-fluorine dipole moments do not cancel each other out. Thus, Nitrogen trifluoride has a net non-zero dipole moment.
Image: Structure and Dipole moment of Nitrogen Trifluoride molecule

Chlorine dioxide (\[Cl{O_2}\]) has a structure similar to water. Thus, its dipole moments will add up like that of water.

Image: Structure and Dipole moments of Chlorine Dioxide molecule
Thus, option A is correct.
Note: Knowledge of the structures of these molecules is crucial to solving these types of questions. It is also necessary to have at least an intuitive idea of how vector addition works without which students can make mistakes in predicting the net dipole moments of compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




