
Add the following algebraic expression using both horizontal and vertical methods.
Did you get the same answer with both methods?
$2{x^2} - 6x + 3; - 3{x^2} - x + 4;1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The horizontal method and the vertical method of adding the expression are two different ways to add the expression but the resultant answer is the same in both the cases.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given algebraic expressions are $2{x^2} - 6x + 3; - 3{x^2} - x + 4;1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$
Assume the given algebraic expression as the functions:
$f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} - 6x + 3$ ,
$g\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} - x + 4$
$h\left( x \right) = 1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$
First, we add these expressions using the horizontal method. In the horizontal method of adding the expression, we first need to write all the expression in a horizontal line and then make groups of like terms, after that add all the like terms together.
$S\left( x \right) = f\left( x \right) + g\left( x \right) + h\left( x \right)$
Substitute $2{x^2} - 6x + 3$as the value of$f\left( x \right)$, $ - 3{x^2} - x + 4$as the value of$g\left( x \right)$and $1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$as the value of $h\left( x \right)$in the above expression:
$S\left( x \right) = \left( {2{x^2} - 6x + 3} \right) + \left( { - 3{x^2} - x + 4} \right) + \left( {1 + 2x - 3{x^2}} \right)$
Open the braces and express the terms:
$S\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} - 6x + 3 - 3{x^2} - x + 4 + 1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$
Now, collect all the like terms together and add them.
$S\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} - 3{x^2} - 3{x^2} - 6x - x + 2x + 3 + 4 + 1$
$S\left( x \right) = 4{x^2} - 5x + 8$
The sum of the given expression using the horizontal method is$4{x^2} - 5x + 8$.
Now, add the functions in the vertical method. In this method of adding expression, we first need to arrange the expressions in a vertical line in such a manner that the like terms and their signs are one below the other, and then add them.
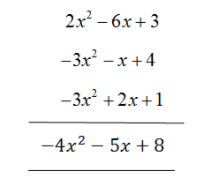
The sum of the given expression using the vertical method is$4{x^2} - 5x + 8$.
When we added the given expression using the horizontal method, then we have the solution:
$4{x^2} - 5x + 8$
And when we added the given expression using the vertical method, then we have the solution:
$4{x^2} - 5x + 8$
It can be seen that both solutions are the same. The conclusion is that we get the same answer using horizontal and vertical methods both.
Note: The like terms are the terms of the expression that have the same variables raised to the same power. In the given expressions, $2{x^2} - 6x + 3; - 3{x^2} - x + 4;1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$, the like terms are $\left( {2{x^2}, - 3{x^2}, - 3{x^2}} \right),\left( { - 6x, - x,2x} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3,4,1} \right)$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given algebraic expressions are $2{x^2} - 6x + 3; - 3{x^2} - x + 4;1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$
Assume the given algebraic expression as the functions:
$f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} - 6x + 3$ ,
$g\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} - x + 4$
$h\left( x \right) = 1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$
First, we add these expressions using the horizontal method. In the horizontal method of adding the expression, we first need to write all the expression in a horizontal line and then make groups of like terms, after that add all the like terms together.
$S\left( x \right) = f\left( x \right) + g\left( x \right) + h\left( x \right)$
Substitute $2{x^2} - 6x + 3$as the value of$f\left( x \right)$, $ - 3{x^2} - x + 4$as the value of$g\left( x \right)$and $1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$as the value of $h\left( x \right)$in the above expression:
$S\left( x \right) = \left( {2{x^2} - 6x + 3} \right) + \left( { - 3{x^2} - x + 4} \right) + \left( {1 + 2x - 3{x^2}} \right)$
Open the braces and express the terms:
$S\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} - 6x + 3 - 3{x^2} - x + 4 + 1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$
Now, collect all the like terms together and add them.
$S\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} - 3{x^2} - 3{x^2} - 6x - x + 2x + 3 + 4 + 1$
$S\left( x \right) = 4{x^2} - 5x + 8$
The sum of the given expression using the horizontal method is$4{x^2} - 5x + 8$.
Now, add the functions in the vertical method. In this method of adding expression, we first need to arrange the expressions in a vertical line in such a manner that the like terms and their signs are one below the other, and then add them.
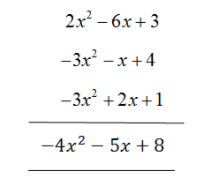
The sum of the given expression using the vertical method is$4{x^2} - 5x + 8$.
When we added the given expression using the horizontal method, then we have the solution:
$4{x^2} - 5x + 8$
And when we added the given expression using the vertical method, then we have the solution:
$4{x^2} - 5x + 8$
It can be seen that both solutions are the same. The conclusion is that we get the same answer using horizontal and vertical methods both.
Note: The like terms are the terms of the expression that have the same variables raised to the same power. In the given expressions, $2{x^2} - 6x + 3; - 3{x^2} - x + 4;1 + 2x - 3{x^2}$, the like terms are $\left( {2{x^2}, - 3{x^2}, - 3{x^2}} \right),\left( { - 6x, - x,2x} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3,4,1} \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

Area vs Volume: Key Differences Explained for Students

Area of an Octagon Formula Explained Simply

Absolute Pressure Formula Explained: Key Equation & Examples

Central Angle of a Circle Formula Explained Quickly

Difference Between Vapor and Gas: JEE Main 2026

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Main Response Sheet 2026 Released – Key Dates and Official Updates by NTA

JEE Main 2026 Answer Key OUT – Download Session 1 PDF, Response Sheet & Challenge Link

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 1 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Circles (2025-26)

Fuel Cost Calculator – Estimate Your Journey Expenses Easily

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Surface Areas and Volumes (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Surface Areas And Volumes Exercise 11.3 (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Heron's Formula (2025-26)





