
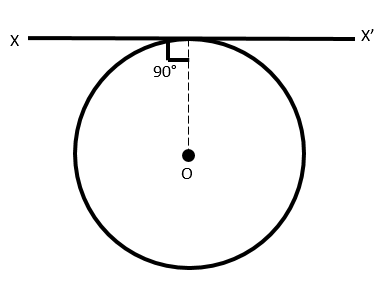
A wire of length L and uniform mass density \[\rho \] is bent into a circular loop with center at O as shown. The moment of inertia of the loop about the axis XX’ is:
A. \[\dfrac{{\rho {L^3}}}{{8{\pi ^2}}} \\ \]
B. \[\dfrac{{\rho {L^3}}}{{16{\pi ^2}}} \\ \]
C. \[\dfrac{{5\rho {L^3}}}{{16{\pi ^2}}} \\ \]
D. \[\dfrac{{3\rho {L^3}}}{{8{\pi ^2}}}\]
Answer
240.9k+ views
Hint:To find the moment of inertia of a body about an axis parallel to another axis of rotation when the moment of inertia about the known axis of rotation is known, we use the parallel axis theorem.
Formula used:
\[I = {I_{cm}} + m{d^2}\]
Here, I is the moment inertia about the required axis of rotation, \[{I_{cm}}\] is the moment of inertia of about center of mass, m is the mass of the body and d is the distance of the required axis of rotation from the center of mass.
The moment of inertia of circular loop of mass m and radius r about diameter is given as,
\[{I_O} = \dfrac{{m{r^2}}}{2}\],
Here m is the mass of the loop and r is the radius of the loop.
Complete step by step solution:
The given axis of rotation XX’ is parallel to the diameter of the loop.
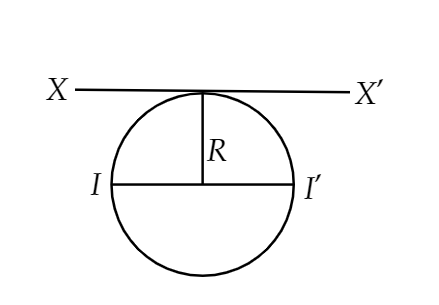
Image: Wire of length L in circular form
The distance of the axis of rotation from the center of mass is \[d = r\]
The moment of inertia of the circular loop about the diameter is \[{I_{cm}} = \dfrac{{m{r^2}}}{2}\]
The mass of the circular loop of length L having linear mass density \[\rho \]is,
\[m = \rho L\]
If the radius of the circular loop is r then the circumference of the loop will be equal to the total length of loop, i.e. L.
\[2\pi r = L \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{L}{{2\pi }}\]
Putting in the expression for the moment of inertia about the axis of rotation XX’, we get
\[{I_{XX'}} = {I_{cm}} + m{d^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {I_{XX'}} = \dfrac{{\rho L{{\left( {\dfrac{L}{{2\pi }}} \right)}^2}}}{2} + \rho L{\left( {\dfrac{L}{{2\pi }}} \right)^2}\]
\[{I_{XX'}} = \dfrac{{\rho {L^3}}}{{8{\pi ^2}}} + \dfrac{{\rho {L^3}}}{{4{\pi ^2}}}\]
\[\therefore {I_{XX'}} = \dfrac{{\rho {L^3} + 2\rho {L^3}}}{{8{\pi ^2}}} = \dfrac{{3\rho {L^3}}}{{8{\pi ^2}}}\]
Hence, the moment of inertia of the given circular loop about the axis of rotation XX’ is \[\dfrac{{3\rho {L^3}}}{{8{\pi ^2}}}\].
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: The moment of inertia of the circular loop about the diameter is calculated using perpendicular axis theorem. The perpendicular axis theorem is applied where the mass distribution is uniform along the plane of the body.
Formula used:
\[I = {I_{cm}} + m{d^2}\]
Here, I is the moment inertia about the required axis of rotation, \[{I_{cm}}\] is the moment of inertia of about center of mass, m is the mass of the body and d is the distance of the required axis of rotation from the center of mass.
The moment of inertia of circular loop of mass m and radius r about diameter is given as,
\[{I_O} = \dfrac{{m{r^2}}}{2}\],
Here m is the mass of the loop and r is the radius of the loop.
Complete step by step solution:
The given axis of rotation XX’ is parallel to the diameter of the loop.

Image: Wire of length L in circular form
The distance of the axis of rotation from the center of mass is \[d = r\]
The moment of inertia of the circular loop about the diameter is \[{I_{cm}} = \dfrac{{m{r^2}}}{2}\]
The mass of the circular loop of length L having linear mass density \[\rho \]is,
\[m = \rho L\]
If the radius of the circular loop is r then the circumference of the loop will be equal to the total length of loop, i.e. L.
\[2\pi r = L \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{L}{{2\pi }}\]
Putting in the expression for the moment of inertia about the axis of rotation XX’, we get
\[{I_{XX'}} = {I_{cm}} + m{d^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {I_{XX'}} = \dfrac{{\rho L{{\left( {\dfrac{L}{{2\pi }}} \right)}^2}}}{2} + \rho L{\left( {\dfrac{L}{{2\pi }}} \right)^2}\]
\[{I_{XX'}} = \dfrac{{\rho {L^3}}}{{8{\pi ^2}}} + \dfrac{{\rho {L^3}}}{{4{\pi ^2}}}\]
\[\therefore {I_{XX'}} = \dfrac{{\rho {L^3} + 2\rho {L^3}}}{{8{\pi ^2}}} = \dfrac{{3\rho {L^3}}}{{8{\pi ^2}}}\]
Hence, the moment of inertia of the given circular loop about the axis of rotation XX’ is \[\dfrac{{3\rho {L^3}}}{{8{\pi ^2}}}\].
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: The moment of inertia of the circular loop about the diameter is calculated using perpendicular axis theorem. The perpendicular axis theorem is applied where the mass distribution is uniform along the plane of the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

JEE Main Correction Window 2026 Session 1 Dates Announced - Edit Form Details, Dates and Link

Other Pages
JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Free Radical Substitution and Its Stepwise Mechanism

How Does Fusion Reaction Happen Inside the Sun?

JEE Main 2026 Helpline Numbers for Aspiring Candidates




