
A transverse sine wave of amplitude 10cm and wavelength 200cm travels from left to right along a long horizontal stretched string with a speed of 100cm/s. Take the origin at the left end of the string. At time t=0, the left end of the string is at the origin and is moving downward. Then the equation of the wave will be (in C. G. S. system)
(a) \[10\sin (0.01\pi x - \pi t)\]
(b) \[10\sin (0.02\pi x - \pi t)\]
(c) \[10\sin (0.01x - \pi t)\]
(d) \[10\sin (0.02x - \pi t)\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Waves can be of two types longitudinal and transverse. In transverse waves, the particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. If we take the velocity of the wave along the x axis then the displacement of the particles will be along y axis. In longitudinal waves, the particles vibrate along the direction of the propagation of the wave.
Formula Used:
1. Wave number: $k = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }$ ……(1)
Where,
$\lambda $is the wavelength of the wave
2. Velocity of the wave: $v = \lambda \upsilon $ ……(2)
Where,
$\upsilon $ is the frequency of the wave.
3. Angular frequency: $\omega = 2\pi \upsilon $ ……(3)
4. Equation of the wave travelling in positive x direction:
$y(x,t) = A\sin (kx - \omega t + \phi )$ ……(4)
Where,
$y(x,t)$ is the displacement along y direction when the wave is at x point and at time t
$\phi $ is the phase angle
Diagram:
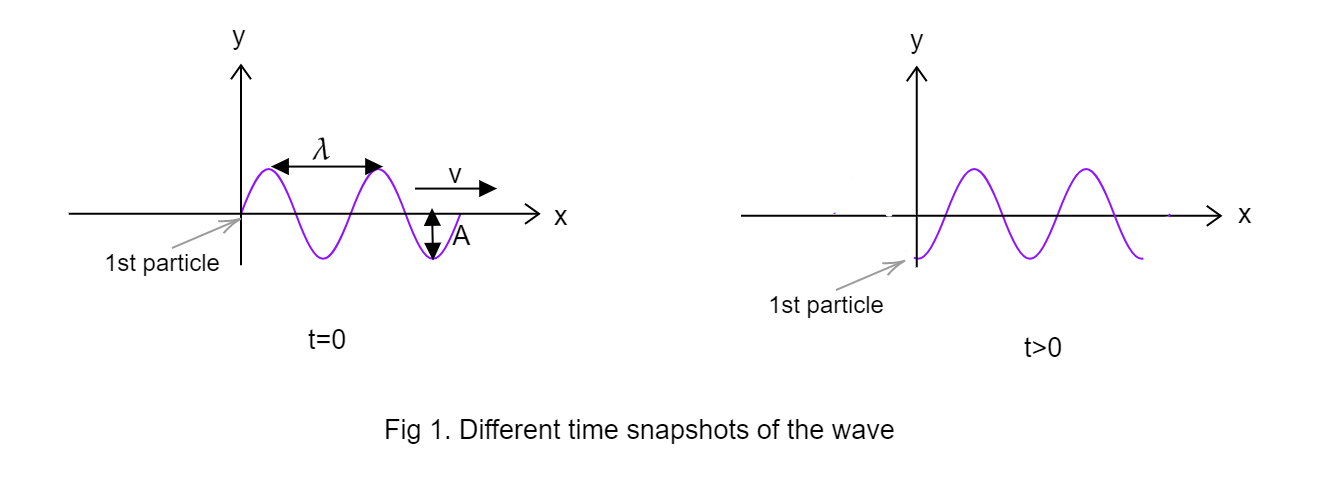
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
1. Amplitude of the wave A = 10cm
2. Wavelength of the wave $\lambda = 200cm$
3. Speed of the wave v = 100cm/s
To find: The equation of the wave in the C.G.S system.
Step 1:
Calculate k using to eq. (1):
$
\Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{200}} \\
\Rightarrow k = 0.01\pi c{m^{ - 1}} \\
$
Rearrange the terms in eq (2) to find $\upsilon $:
$\upsilon = \dfrac{v}{\lambda }$ ……(5)
Step 2:
Find frequency using eq (5):
$
\Rightarrow \upsilon = \dfrac{{100}}{{200}} \\
\Rightarrow \upsilon = 0.5Hz \\
$
Find angular frequency using eq (3):
$
\omega = 2\pi (0.5) \\
\omega = \pi Hz \\
$
Step 3:
Phase angle determines how much the 1st particle is initially displaced when t=0. When t=0, the 1st particle of the string is at origin. This means the 1st particle(x=0) is at displacement y=0 for t=0. Hence, the phase angle $\phi $ is 0.
If the point at x=0 is moving down in a negative y direction, it means that the wave has moved forward in x direction (left to right). So, it is a wave travelling in +x direction. Use eq (4) to find the equation:
$
\Rightarrow y(x,t) = 10\sin (0.01\pi x - \pi t + 0) \\
\Rightarrow y(x,t) = 10\sin (0.01\pi x - \pi t) \\
$
Final Answer
The equation of the wave is (a) \[10\sin (0.01\pi x - \pi t)\] in the C.G.S system.
Note: Try to remember the general equation of a wave propagating along the x axis. In this equation x and t are variables, the rest of the unknown quantities can be found using their definitions. For example, phase angle is the angle by which the origin of the wave has displaced with respect to the origin of the sin wave.
Formula Used:
1. Wave number: $k = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }$ ……(1)
Where,
$\lambda $is the wavelength of the wave
2. Velocity of the wave: $v = \lambda \upsilon $ ……(2)
Where,
$\upsilon $ is the frequency of the wave.
3. Angular frequency: $\omega = 2\pi \upsilon $ ……(3)
4. Equation of the wave travelling in positive x direction:
$y(x,t) = A\sin (kx - \omega t + \phi )$ ……(4)
Where,
$y(x,t)$ is the displacement along y direction when the wave is at x point and at time t
$\phi $ is the phase angle
Diagram:

Complete step by step answer:
Given:
1. Amplitude of the wave A = 10cm
2. Wavelength of the wave $\lambda = 200cm$
3. Speed of the wave v = 100cm/s
To find: The equation of the wave in the C.G.S system.
Step 1:
Calculate k using to eq. (1):
$
\Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{200}} \\
\Rightarrow k = 0.01\pi c{m^{ - 1}} \\
$
Rearrange the terms in eq (2) to find $\upsilon $:
$\upsilon = \dfrac{v}{\lambda }$ ……(5)
Step 2:
Find frequency using eq (5):
$
\Rightarrow \upsilon = \dfrac{{100}}{{200}} \\
\Rightarrow \upsilon = 0.5Hz \\
$
Find angular frequency using eq (3):
$
\omega = 2\pi (0.5) \\
\omega = \pi Hz \\
$
Step 3:
Phase angle determines how much the 1st particle is initially displaced when t=0. When t=0, the 1st particle of the string is at origin. This means the 1st particle(x=0) is at displacement y=0 for t=0. Hence, the phase angle $\phi $ is 0.
If the point at x=0 is moving down in a negative y direction, it means that the wave has moved forward in x direction (left to right). So, it is a wave travelling in +x direction. Use eq (4) to find the equation:
$
\Rightarrow y(x,t) = 10\sin (0.01\pi x - \pi t + 0) \\
\Rightarrow y(x,t) = 10\sin (0.01\pi x - \pi t) \\
$
Final Answer
The equation of the wave is (a) \[10\sin (0.01\pi x - \pi t)\] in the C.G.S system.
Note: Try to remember the general equation of a wave propagating along the x axis. In this equation x and t are variables, the rest of the unknown quantities can be found using their definitions. For example, phase angle is the angle by which the origin of the wave has displaced with respect to the origin of the sin wave.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




