
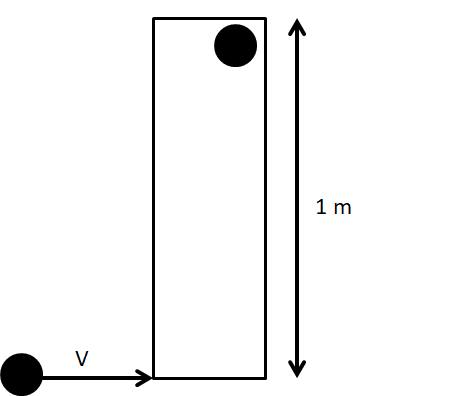
A thin rod of mass \[\;0.9kg,\] and length \[1{\text{ }}m\] is suspended, at rest, from one end so that it can freely oscillate in the vertical plane. A particle of mass \[0.1{\text{ }}kg\] moving in a straight line with velocity \[80{\text{ }}m/s\] hits the rod at its bottom most point and sticks to it (see figure). The angular speed \[\left( {in{\text{ }}rad/s} \right)\] of the rod immediately after the collision will be __________.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We can say that to determine the angular speed of a body, we need to apply the conservation of angular momentum to it. Here, the kinematics of the oscillation mode are governed by the equation. We have to use the given figure for the reference.
Complete step by step solution:
The rod of mass \[0.9{\text{ }}kg\] and length \[1{\text{ }}m\] is suspended, at rest, from one end so that it can freely oscillate in the vertical plane. We know that when an object is touching a flat surface, there are no stresses on the surface. This means that the surface will not transmit any forces to the object below it but allow free sliding.
The mass of the rod is\[\;0.9kg,\] the length of the rod is \[1m\], the mass of the particle is \[0.1kg\], and the particle's velocity is \[20\,rad/s\]. To Determine: The rod's angular speed. When the particle collides with the rod, make a schematic diagram. Before and after the collision, use the conservation of angular momentum. Find the angular speed of the rod by substituting the supplied value into the equation \[mbv = \left( {m{L^3}/3{\text{ }} + mp{L^2}} \right)\]
Applying COAM about the Pivot,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{L_i}\; = {\text{ }}{L_f}} \\ \Rightarrow {0.1{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}80{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}1{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\{ [0.9{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}{1^2}]{\text{ }}/{\text{ }}3\} {\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}\omega {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\left( {0.1} \right){\text{ }}{1^2}\;\omega } \\ \Rightarrow {8{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\left( {0.3{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}0.1} \right){\text{ }}\omega } \\ \Rightarrow {8{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\left( {0.4} \right){\text{ }}\omega } \\ \therefore {\omega {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}80{\text{ }}/{\text{ }}4{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}20} \end{array}\]
The angular speed is \[20\,rad/s\].
Note: This case is about a thin rod at rest and oscillating horizontally. The thin rod could be either in equilibrium or unstable. In equilibrium, the force on the rod must be zero so that it would not accelerate. But if the force on one end of this thin rod was stronger than that on the other, then it will accelerate and move to a point where force is zero. On instability, it will oscillate back and forth between these two points with a constant acceleration.
Complete step by step solution:
The rod of mass \[0.9{\text{ }}kg\] and length \[1{\text{ }}m\] is suspended, at rest, from one end so that it can freely oscillate in the vertical plane. We know that when an object is touching a flat surface, there are no stresses on the surface. This means that the surface will not transmit any forces to the object below it but allow free sliding.
The mass of the rod is\[\;0.9kg,\] the length of the rod is \[1m\], the mass of the particle is \[0.1kg\], and the particle's velocity is \[20\,rad/s\]. To Determine: The rod's angular speed. When the particle collides with the rod, make a schematic diagram. Before and after the collision, use the conservation of angular momentum. Find the angular speed of the rod by substituting the supplied value into the equation \[mbv = \left( {m{L^3}/3{\text{ }} + mp{L^2}} \right)\]
Applying COAM about the Pivot,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{L_i}\; = {\text{ }}{L_f}} \\ \Rightarrow {0.1{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}80{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}1{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\{ [0.9{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}{1^2}]{\text{ }}/{\text{ }}3\} {\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}\omega {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\left( {0.1} \right){\text{ }}{1^2}\;\omega } \\ \Rightarrow {8{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\left( {0.3{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}0.1} \right){\text{ }}\omega } \\ \Rightarrow {8{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\left( {0.4} \right){\text{ }}\omega } \\ \therefore {\omega {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}80{\text{ }}/{\text{ }}4{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}20} \end{array}\]
The angular speed is \[20\,rad/s\].
Note: This case is about a thin rod at rest and oscillating horizontally. The thin rod could be either in equilibrium or unstable. In equilibrium, the force on the rod must be zero so that it would not accelerate. But if the force on one end of this thin rod was stronger than that on the other, then it will accelerate and move to a point where force is zero. On instability, it will oscillate back and forth between these two points with a constant acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




