
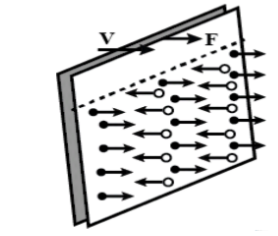
A thin heavy metal plate is being bombarded by a perpendicular beam of gas particles from both sides as shown in the figure. The solid dots are representing the molecules hitting from the left side and the faint dots are the molecules hitting from the right side. The mass of these gas particles is ${\text{m = 1}}{{\text{0}}^{{\text{ - 26}}}}{\text{kg}} $ and velocity before hitting is ${{\text{v}}_{\text{0}}}{\text{ = 5m/s}} $. Volume density of the gas particles on both sides is ${\text{n = 1}}{{\text{0}}^{{\text{25}}}}{\text{ per }}{{\text{m}}^3} $. Each beam has an area ${\text{A = 1}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}} $ and the collisions are perfectly elastic. What is the external force, F (in newton) required to move the plate with a constant velocity ${\text{v = 2m/s}} $
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint The given particles are in elastic collision. The initial and final velocities, mass of the particle, the area of the metal plate, and the volume density of the gas is provided. To solve this question we must know the concepts of elastic collision and the collision of particles in one and two dimensions. We know that force can be determined by change in momentum. Use these concepts to find the answer.
Complete step by step solution
The mass of gas particles is ${\text{m = 1}}{{\text{0}}^{{\text{ - 26}}}}{\text{kg}} $
Velocity before hitting the metal pate (before collision), ${{\text{v}}_{\text{0}}}{\text{ = 5m/s}} $
Velocity after collision, ${\text{v = 2m/s}} $
Volume density of the gas particles is ${\text{n = 1}}{{\text{0}}^{{\text{25}}}}{\text{ per }}{{\text{m}}^3} $
Area of the beam, ${\text{A = 1}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}} $
The external force, F=? (The force required to move the plate with a constant velocity, ${\text{v = 2m/s}} $)
Here the force required to move the plate is determined by the change in the momentum of the particle on the given area of the metal.
$ \Rightarrow {\text{F = }}\Delta {\text{PA }} \to {\text{1}} $
F is the force.
$\Delta P $ is the change in the momentum
We know that Momentum is the product of mass and velocity.
Then, the equation 1 becomes,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{F = m}}\dfrac{{d{v_0}}}{{dt}}{\text{nA}} - {\text{m}}\dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}{\text{nA}} $ (mass is constant)
$ \Rightarrow {\text{F = mnA}}\left( {\dfrac{{d{v_0}}}{{dt}} - \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}} \right) $
Differentiate
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = mnA}}\left( {{v_0}^2 - {v^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = mnA}}{\left( {{v_0} + v} \right)^2} - {\left( {{v_0} - v} \right)^2}\]
m is the mass
${v_0} $ is the initial velocity
v is the final velocity
n is the volume density of the gas particles
The external force, F=?
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = 2}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 26}} \times {10^{25}} \times 1 \times \left( {{{\left( {5 + 2} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {5 - 2} \right)}^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = 2}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 26}} \times {10^{25}} \times 1 \times \left( {49 - 9} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = 2}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 26}} \times {10^{25}} \times 1 \times 40\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = 8N}}\]
The external force, F required to move the plate is \[{\text{F = 8N}}\]
Hint Collision occurs when two objects hit one another. When the object collides with each other its momentum is conserved for an isolated system. The principle of conservation of momentum says that the momentum before collision is equal to the momentum after the collision. The difference between a one dimensional and two dimensional collision is in one dimensional collision, change in velocities of the particles occurs only in one direction so, conservation of momentum is in one direction only whereas in two dimensional, change in velocities of the particles occurs in two direction so, conservation of momentum is in two direction.
Complete step by step solution
The mass of gas particles is ${\text{m = 1}}{{\text{0}}^{{\text{ - 26}}}}{\text{kg}} $
Velocity before hitting the metal pate (before collision), ${{\text{v}}_{\text{0}}}{\text{ = 5m/s}} $
Velocity after collision, ${\text{v = 2m/s}} $
Volume density of the gas particles is ${\text{n = 1}}{{\text{0}}^{{\text{25}}}}{\text{ per }}{{\text{m}}^3} $
Area of the beam, ${\text{A = 1}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}} $
The external force, F=? (The force required to move the plate with a constant velocity, ${\text{v = 2m/s}} $)
Here the force required to move the plate is determined by the change in the momentum of the particle on the given area of the metal.
$ \Rightarrow {\text{F = }}\Delta {\text{PA }} \to {\text{1}} $
F is the force.
$\Delta P $ is the change in the momentum
We know that Momentum is the product of mass and velocity.
Then, the equation 1 becomes,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{F = m}}\dfrac{{d{v_0}}}{{dt}}{\text{nA}} - {\text{m}}\dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}{\text{nA}} $ (mass is constant)
$ \Rightarrow {\text{F = mnA}}\left( {\dfrac{{d{v_0}}}{{dt}} - \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}} \right) $
Differentiate
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = mnA}}\left( {{v_0}^2 - {v^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = mnA}}{\left( {{v_0} + v} \right)^2} - {\left( {{v_0} - v} \right)^2}\]
m is the mass
${v_0} $ is the initial velocity
v is the final velocity
n is the volume density of the gas particles
The external force, F=?
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = 2}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 26}} \times {10^{25}} \times 1 \times \left( {{{\left( {5 + 2} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {5 - 2} \right)}^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = 2}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 26}} \times {10^{25}} \times 1 \times \left( {49 - 9} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = 2}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 26}} \times {10^{25}} \times 1 \times 40\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{F = 8N}}\]
The external force, F required to move the plate is \[{\text{F = 8N}}\]
Hint Collision occurs when two objects hit one another. When the object collides with each other its momentum is conserved for an isolated system. The principle of conservation of momentum says that the momentum before collision is equal to the momentum after the collision. The difference between a one dimensional and two dimensional collision is in one dimensional collision, change in velocities of the particles occurs only in one direction so, conservation of momentum is in one direction only whereas in two dimensional, change in velocities of the particles occurs in two direction so, conservation of momentum is in two direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26




