
A stone of $1 \mathrm{kg}$ is thrown with a velocity $20m{{s}^{-1}}$across the frozen surface of a lake and comes to rest after travelling a distance of $50 \mathrm{m}$. What is the force of friction between the stone and the ice?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We should know that velocity is defined as the rate change of displacement per unit time. Speed in a specific direction is also known as velocity. Velocity is equal to displacement divided by time. Speed, being a scalar quantity, is the rate at which an object covers distance. The average speed is the distance which is a scalar quantity per time ratio. On the other hand, velocity is a vector quantity; it is direction-aware. An object which moves in the negative direction has a negative velocity. If the object is slowing down then its acceleration vector is directed in the opposite direction as its motion in this case. Based on this we have to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer
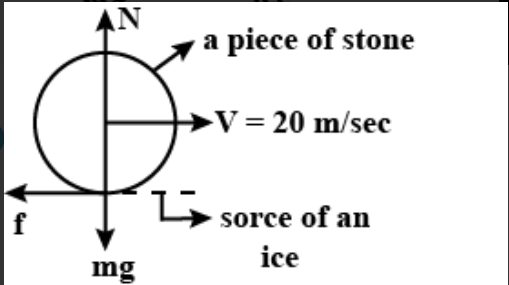
Before we proceed, we have to make a free body diagram of the stone-ice system. In the figure, we are seeing that frictional force acting in leftward while the stone is moving rightward direction. One thing we have to fix in our mind that frictional force will always act opposite to the direction of motion of the body. Now on resolving the forces, $\mathrm{f}-\mathrm{ma} = 0$ or $\mathrm{f}=\mathrm{ma}$ also form the equation of motion $\mathrm{v}^{2}=\mathrm{u}^{2}+2as$ as, here final velocity is zero, so $\mathrm{v}=0$
$\mathrm{u}^{2}=-2 \mathrm{as}$
$\mathrm{u}^{2}=-2 \mathrm{as}$
$\mathrm{a}=\dfrac{-\mathrm{u}^{2}}{2 \mathrm{s}}=-\dfrac{20^{2}}{2 \times 50}=-4 \dfrac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{sec}^{2}}$
On substituting the given data in equation (1) $\mathrm{f}=1 \times(-4)=-4 \mathrm{N}$
Note: We should know that if an object's speed or velocity is increasing at a constant rate then we say it has uniform acceleration. The rate of acceleration is constant. If a car speeds up then slows down then speeds up it doesn't have uniform acceleration. The instantaneous acceleration, or simply acceleration, is defined as the limit of the average acceleration when the interval of time considered approaches 0. It is also defined in a similar manner as the derivative of velocity with respect to time. If an object begins acceleration from rest or a standstill, its initial time is 0. If we get a negative value for acceleration, it means the object is slowing down. The acceleration of an object is its change in velocity over an increment of time. This can mean a change in the object's speed or direction. Average acceleration is the change of velocity over a period of time. Constant or uniform acceleration is when the velocity changes the same amount in every equal time period.
Complete step by step answer
Before we proceed, we have to make a free body diagram of the stone-ice system. In the figure, we are seeing that frictional force acting in leftward while the stone is moving rightward direction. One thing we have to fix in our mind that frictional force will always act opposite to the direction of motion of the body. Now on resolving the forces, $\mathrm{f}-\mathrm{ma} = 0$ or $\mathrm{f}=\mathrm{ma}$ also form the equation of motion $\mathrm{v}^{2}=\mathrm{u}^{2}+2as$ as, here final velocity is zero, so $\mathrm{v}=0$

$\mathrm{u}^{2}=-2 \mathrm{as}$
$\mathrm{u}^{2}=-2 \mathrm{as}$
$\mathrm{a}=\dfrac{-\mathrm{u}^{2}}{2 \mathrm{s}}=-\dfrac{20^{2}}{2 \times 50}=-4 \dfrac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{sec}^{2}}$
On substituting the given data in equation (1) $\mathrm{f}=1 \times(-4)=-4 \mathrm{N}$
Note: We should know that if an object's speed or velocity is increasing at a constant rate then we say it has uniform acceleration. The rate of acceleration is constant. If a car speeds up then slows down then speeds up it doesn't have uniform acceleration. The instantaneous acceleration, or simply acceleration, is defined as the limit of the average acceleration when the interval of time considered approaches 0. It is also defined in a similar manner as the derivative of velocity with respect to time. If an object begins acceleration from rest or a standstill, its initial time is 0. If we get a negative value for acceleration, it means the object is slowing down. The acceleration of an object is its change in velocity over an increment of time. This can mean a change in the object's speed or direction. Average acceleration is the change of velocity over a period of time. Constant or uniform acceleration is when the velocity changes the same amount in every equal time period.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




