
When a stone is dropped in a pool of water, circular ripples are produced. These are:
A) Surface waves
B) Transverse waves
C) Elastic waves
D) All the above
Answer
240.9k+ views
Hint: The nature of ripples in the water are all in accordance with the transmission properties of transverse waves. in addition, they just move the top few inches of the water surface.
Complete step by step solution:
A transverse wave is a manner of particle displacement where the particles oscillate in a direction to the direction of travel. Simply put, the particles move up and down while moving in a particular direction. These oscillations are about each particle’s equilibrium positions.
The properties of the transverse wave are:
1. Reflection:
Transverse wave, when struck with an obstruction, “bounce back” and starts traveling through the same path it was initially traveling in, but in the opposite direction.
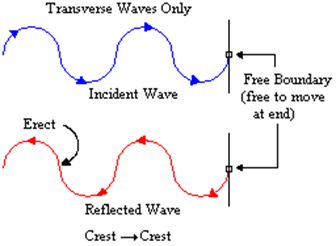
2. Superposition:
The phenomenon of waves that causes them to increase in amplitude who two with the same phase difference meet is called wave superposition.
The exact opposite thing happens when their phases do not match at the moment of interception, the amplitude is reduced in the resulting wave.

3. Elasticity:
Transverse wave oscillations are also elastic oscillations as the particles are displaced away from their relaxed positions.
When a stone is thrown into the water, it causes ripples on the water surface. These ripples travel radially in all directions with a to-and-fro motion. They bounce back when hit with a wall or any object in its path and they either g.
In addition, during ripples, only a few top inches of the water surface is displaced. This means that the trajectory is large, but the amplitude is small. This is the property of surface waves.
row in height or size down when met with other waves.
Therefore, it is safe to say that ripples in water are transverse, surface, and elastic waves.
The correct option is (D).
Note: Transverse waves are not supposed to be confused with longitudinal waves. They might have the same top view, but the basic difference between them is the direction of particle displacement. Transverse waves displace particles in a direction with respect to the direction of motion, whereas longitudinal waves displace them parallel to the direction of motion.
Complete step by step solution:
A transverse wave is a manner of particle displacement where the particles oscillate in a direction to the direction of travel. Simply put, the particles move up and down while moving in a particular direction. These oscillations are about each particle’s equilibrium positions.
The properties of the transverse wave are:
1. Reflection:
Transverse wave, when struck with an obstruction, “bounce back” and starts traveling through the same path it was initially traveling in, but in the opposite direction.

2. Superposition:
The phenomenon of waves that causes them to increase in amplitude who two with the same phase difference meet is called wave superposition.
The exact opposite thing happens when their phases do not match at the moment of interception, the amplitude is reduced in the resulting wave.

3. Elasticity:
Transverse wave oscillations are also elastic oscillations as the particles are displaced away from their relaxed positions.
When a stone is thrown into the water, it causes ripples on the water surface. These ripples travel radially in all directions with a to-and-fro motion. They bounce back when hit with a wall or any object in its path and they either g.
In addition, during ripples, only a few top inches of the water surface is displaced. This means that the trajectory is large, but the amplitude is small. This is the property of surface waves.
row in height or size down when met with other waves.
Therefore, it is safe to say that ripples in water are transverse, surface, and elastic waves.
The correct option is (D).
Note: Transverse waves are not supposed to be confused with longitudinal waves. They might have the same top view, but the basic difference between them is the direction of particle displacement. Transverse waves displace particles in a direction with respect to the direction of motion, whereas longitudinal waves displace them parallel to the direction of motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




