
A stone is dropped from the top of a building. When it crosses a point 5m below the top, another stone starts to fall from a point 25m below the top, both stones reach the bottom of the building simultaneously. The height of the building is: [Take g = 10 m/s\[^2\]]
A. 45 m
B. 35 m
C. 25 m
D. 50 m
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Gravity is a fundamental interaction between two objects having a certain mass. It is a form of mutual attraction force between the interacting objects. The force of this mutual attraction depends on the size of the objects and the square of the distance separating them. So far, as known in Physics, Gravitational pull is the weakest known force existing in nature.
Complete step by step solution:
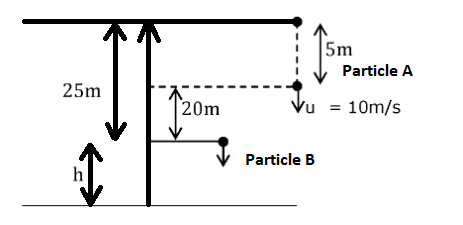
Image: Figure to explain the question
The velocity of the particle (A) at 5m below top
\[{u_1} = \sqrt {2gh} \\ \Rightarrow {u_1} = \sqrt {(2 \times 10 \times 5)} \\ \Rightarrow {u_1} = 10\,m{s^{ - 1}} \\ \]
The second law of motion is denoted by:
\[S = ut + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)a{t^2}\]
where, S = Distance Travelled, u = Initial Velocity, t = time taken and a = acceleration.
For a particle (A), using \[{2^{nd}}\] the equation of motion, we get:
\[20 + h = 10t + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)g{t^2} - - - - (1)\]
For a particle (B), using \[{2^{nd}}\] the equation of motion
\[h = \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)g{t^2}\]
Put equation (2) in equation (1), and we get,
\[20 + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)g{t^2} = 10t + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)g{t^2} \\ \Rightarrow t = 2\,\sec \\ \]
Putting the time value in equation (2), we get:
\[h = \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)g{t^2} \\ \Rightarrow h = \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) \times 10 \times {2^2} \\ \therefore h = 20m \]
Hence, the total height of the building is \[\;25 + 20 = 45m\].
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Note: The most fundamental principles of an object's motion are described by the equations of motion used in kinematics. In 1D, 2D, and 3D, these equations control how an object moves. Expressions like the position, velocity, or acceleration of an object at different times can be simply calculated using them.
Complete step by step solution:

Image: Figure to explain the question
The velocity of the particle (A) at 5m below top
\[{u_1} = \sqrt {2gh} \\ \Rightarrow {u_1} = \sqrt {(2 \times 10 \times 5)} \\ \Rightarrow {u_1} = 10\,m{s^{ - 1}} \\ \]
The second law of motion is denoted by:
\[S = ut + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)a{t^2}\]
where, S = Distance Travelled, u = Initial Velocity, t = time taken and a = acceleration.
For a particle (A), using \[{2^{nd}}\] the equation of motion, we get:
\[20 + h = 10t + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)g{t^2} - - - - (1)\]
For a particle (B), using \[{2^{nd}}\] the equation of motion
\[h = \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)g{t^2}\]
Put equation (2) in equation (1), and we get,
\[20 + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)g{t^2} = 10t + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)g{t^2} \\ \Rightarrow t = 2\,\sec \\ \]
Putting the time value in equation (2), we get:
\[h = \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)g{t^2} \\ \Rightarrow h = \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) \times 10 \times {2^2} \\ \therefore h = 20m \]
Hence, the total height of the building is \[\;25 + 20 = 45m\].
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Note: The most fundamental principles of an object's motion are described by the equations of motion used in kinematics. In 1D, 2D, and 3D, these equations control how an object moves. Expressions like the position, velocity, or acceleration of an object at different times can be simply calculated using them.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




