
A small bulb is placed at the focal point of a converging lens. When the bulb is switched on, the lens produces:
A) a convergent beam of light
B) a divergent beam of light
C) a parallel beam of light
D) a patch of coloured
Answer
242.4k+ views
Hint: In general, there are two types of lens, they are converging lens and diverging lens. Both lenses are used for transmitting the light rays and also used for human eye lenses for correcting the eye disorder. Converging lens is also called a positive lens and the diverging lens is also called a negative lens.
Complete step by step solution:
Converging lens:
Converging lens is a lens which is used for transmitting the light to the focus area. The converging lens is also known as convex lens. This lens is thicker at the centre of the lens than the edge of the lens. The function of the convex lens is, when the parallel rays of light are allowed to pass through the lens, the refracted rays converge which means the refracted light rays will meet in the same point, that point is called the principal focus point. And the function of the converging lens or convex lens is reversed also. For example, when the bulb is placed near the convex lens or converging lens, it will refract the light rays, and the refracted light rays are parallel to each other.
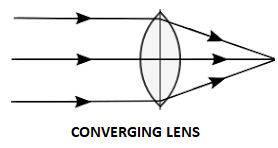
Thus, a small bulb is placed near the converging lens, and the bulb is switched on, which produces the parallel beam of light.
Hence, the option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: If the lens is very thicker at the centre than the both edges of the lens, then it is a converging lens or convex lens. And it is also called a positive lens because it is having a positive focal length. If the lens is thin at the centre than the both edges of the lens, then it is a diverging lens or concave lens. And it is also called a negative lens because it is having negative focal length.
Complete step by step solution:
Converging lens:
Converging lens is a lens which is used for transmitting the light to the focus area. The converging lens is also known as convex lens. This lens is thicker at the centre of the lens than the edge of the lens. The function of the convex lens is, when the parallel rays of light are allowed to pass through the lens, the refracted rays converge which means the refracted light rays will meet in the same point, that point is called the principal focus point. And the function of the converging lens or convex lens is reversed also. For example, when the bulb is placed near the convex lens or converging lens, it will refract the light rays, and the refracted light rays are parallel to each other.

Thus, a small bulb is placed near the converging lens, and the bulb is switched on, which produces the parallel beam of light.
Hence, the option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: If the lens is very thicker at the centre than the both edges of the lens, then it is a converging lens or convex lens. And it is also called a positive lens because it is having a positive focal length. If the lens is thin at the centre than the both edges of the lens, then it is a diverging lens or concave lens. And it is also called a negative lens because it is having negative focal length.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

CBSE Class 10 Sanskrit Set 4 52 Question Paper 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




