
A single slit of width $0.1mm$ is illuminated by a parallel beam of light of wavelength and diffraction bands are observed on a screen $0.5m$ from the slit. The distance of the third dark band from the central bright band is:
(A) $3mm$
(B) $4.5mm$
(C) $1.5mm$
(D) $9mm$
Answer
242.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question the concept of single slit experiment and all the formulas related to the experiment should be known. The technical terms and the meaning of each term should be thoroughly understood by the students then only they can understand this problem.
Complete step by step answer
Single slit diffraction: Single slit diffraction occurs in a single slit experiment where light waves from a source passes through a single slit of width ‘w’ which is in the order of the wavelength of the light wave passing through it to get a distinctive pattern called diffraction pattern.
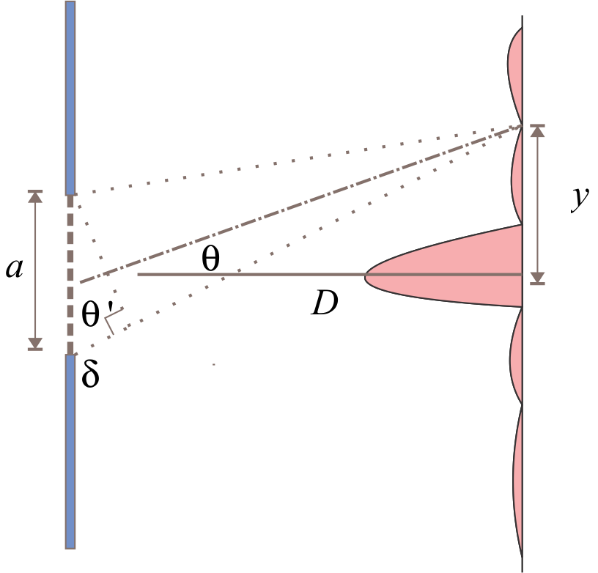
In the diagram
a is the width of the slit
D is the distance of the screen from the slit.
Y is the central minima
Given,
The single slit of width $0.1mm$ is illuminated by a parallel beam of light of wavelength and diffraction bands are observed on a screen $0.5m$ from the slit we have to find the The distance of the third dark band from the central bright band.
The condition for the nth minima is given by
${\text{a sin}}\theta {\text{ = n}}\lambda $
Minima for the single slit is given by the formula,
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{n\lambda }}{a}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{n\lambda }}{a} = \dfrac{x}{D}{\text{ }} \to {\text{1}}$
Where,
n is the number of fringe
a is the width of the slit
$\lambda $ is the wavelength
$\theta $ is the angle of deviation
D id the distance of the screen from the slit
X is the distance of the nth dark band from the central bright band
Given,
The number of dark fringe n is $3$
The wavelength of light $\lambda $ is
The width of the screen a is $0.1mm = 0.1 \times {10^{ - 3}}m$
Substitute these values in the formula
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{3 \times 6000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}}{{0.1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
One angstrom is equal to ${10^{ - 10}}m$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{3 \times 6000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}}{{0.1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
From equation 1
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{D} = \dfrac{{3 \times 6000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}}{{0.1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{{0.5}} = \dfrac{{3 \times 6000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}}{{0.1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{3 \times 6000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}} \times 0.5}}{{0.1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow x = 9mm$
Note: Students might find it difficult to understand this problem. To solve this problem with a better idea one should thoroughly learn about the mechanism of a single slit experiment.
Complete step by step answer
Single slit diffraction: Single slit diffraction occurs in a single slit experiment where light waves from a source passes through a single slit of width ‘w’ which is in the order of the wavelength of the light wave passing through it to get a distinctive pattern called diffraction pattern.

In the diagram
a is the width of the slit
D is the distance of the screen from the slit.
Y is the central minima
Given,
The single slit of width $0.1mm$ is illuminated by a parallel beam of light of wavelength and diffraction bands are observed on a screen $0.5m$ from the slit we have to find the The distance of the third dark band from the central bright band.
The condition for the nth minima is given by
${\text{a sin}}\theta {\text{ = n}}\lambda $
Minima for the single slit is given by the formula,
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{n\lambda }}{a}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{n\lambda }}{a} = \dfrac{x}{D}{\text{ }} \to {\text{1}}$
Where,
n is the number of fringe
a is the width of the slit
$\lambda $ is the wavelength
$\theta $ is the angle of deviation
D id the distance of the screen from the slit
X is the distance of the nth dark band from the central bright band
Given,
The number of dark fringe n is $3$
The wavelength of light $\lambda $ is
The width of the screen a is $0.1mm = 0.1 \times {10^{ - 3}}m$
Substitute these values in the formula
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{3 \times 6000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}}{{0.1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
One angstrom is equal to ${10^{ - 10}}m$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{3 \times 6000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}}{{0.1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
From equation 1
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{D} = \dfrac{{3 \times 6000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}}{{0.1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{{0.5}} = \dfrac{{3 \times 6000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}}{{0.1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{3 \times 6000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}} \times 0.5}}{{0.1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow x = 9mm$
Note: Students might find it difficult to understand this problem. To solve this problem with a better idea one should thoroughly learn about the mechanism of a single slit experiment.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

CBSE Class 10 Sanskrit Set 4 52 Question Paper 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




