
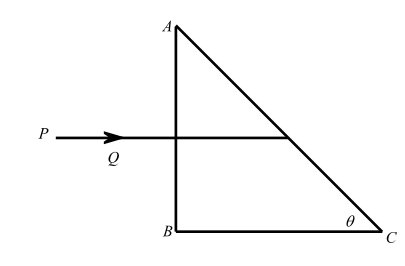
A right-angled prism made from a material of refractive index $\mu $ is kept in air. A ray PQ is incident normally on the side AB of the prism. Find (in terms of $\mu $ ) the maximum value of $\theta $ up to which this incident ray necessarily undergoes total internal reflection at the face AC of the prism.
Answer
239.4k+ views
Hint:In this question, we know that if the angle between two lines is the same as the angle between their perpendiculars and one angle of right angles prism is always $90^\circ $. The angle of incidence should be minimum for total internal reflection.
Complete step by step solution:
In this question we have given that a right-angled prism has the refractive index $\mu $. We need to calculate the maximum value of $\theta $ up to which this incident ray necessarily undergoes total internal reflection at the face AC of the prism.
In this question let us assume that the angle of incidence is $i$ and the angle of incidence is incident on $AC$.
The angle between two lines is same as the angle between their perpendiculars so we can write,
$i = A$
Since the prism is right angled, we can write,
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - A\]
Since $i = A$ we can write,
$ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - i......\left( 1 \right)$
We know that refractive index is expressed as,
$\mu = \dfrac{1}{{\sin i}}$
As we know that the angle of incidence should be minimum for the total internal reflection,
${i_c} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{\mu }......\left( 2 \right)$
Here, ${i_c}$ is a critical angle.
Now the maximum value of $\theta $ for total internal expression can be calculated by substituting the expression of ${i_c}$ to the equation (1) as,
$ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - {i_C}$
Now we substitute the value of critical angle as expressed in equation (2) in above equation to get the maximum value of $\theta $.
$\therefore {\theta _{\max }} = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{\mu }$
Therefore, the maximum value will be ${\theta _{\max }} = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{\mu }$.
Note:As we know that the minimum angle for total internal reflection is the critical angle. The angle of the right-angled prism is $90^\circ $. The maximum value of $\theta $ is calculated corresponding to the minimum value of $i$.
Complete step by step solution:
In this question we have given that a right-angled prism has the refractive index $\mu $. We need to calculate the maximum value of $\theta $ up to which this incident ray necessarily undergoes total internal reflection at the face AC of the prism.
In this question let us assume that the angle of incidence is $i$ and the angle of incidence is incident on $AC$.
The angle between two lines is same as the angle between their perpendiculars so we can write,
$i = A$
Since the prism is right angled, we can write,
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - A\]
Since $i = A$ we can write,
$ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - i......\left( 1 \right)$
We know that refractive index is expressed as,
$\mu = \dfrac{1}{{\sin i}}$
As we know that the angle of incidence should be minimum for the total internal reflection,
${i_c} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{\mu }......\left( 2 \right)$
Here, ${i_c}$ is a critical angle.
Now the maximum value of $\theta $ for total internal expression can be calculated by substituting the expression of ${i_c}$ to the equation (1) as,
$ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - {i_C}$
Now we substitute the value of critical angle as expressed in equation (2) in above equation to get the maximum value of $\theta $.
$\therefore {\theta _{\max }} = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{\mu }$
Therefore, the maximum value will be ${\theta _{\max }} = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{\mu }$.
Note:As we know that the minimum angle for total internal reflection is the critical angle. The angle of the right-angled prism is $90^\circ $. The maximum value of $\theta $ is calculated corresponding to the minimum value of $i$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Step-by-Step Guide to Young’s Double Slit Experiment Derivation

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Essential Derivations for CBSE Class 12 Physics: Stepwise & PDF Solutions

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis




