
A pond of water is $5\;{\text{m}}$deep. The flame is held $2\;{\text{m}}$ above the surface of water. A fish is at depth $4\;{\text{m}}$ from water surface. The refractive index of water is $\dfrac{4}{3}$. The apparent height of flame from the eyes of fish is-
$a)\dfrac{8}{3}\;{\text{m}}$
$b)6\;{\text{m}}$
$c)5.5\;{\text{m}}$
$d)\dfrac{{20}}{3}\;{\text{m}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, the concept of the apparent height will be used and first draw the ray diagram and then calculate the apparent height of the flame. And then show at which point the fish see the flame.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will draw the following diagram as per the given situation,
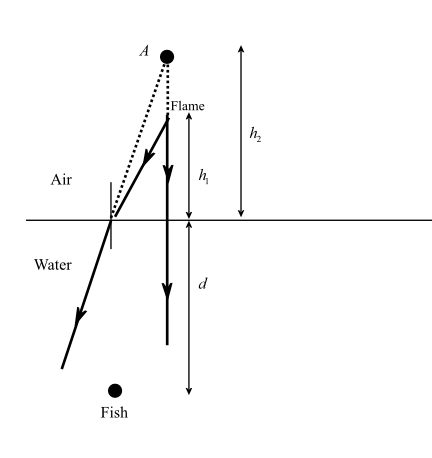
As per the given data in the question we have the height of the flame above the water surface is $2\;{\text{m}}$ and the fish is $4\;{\text{m}}$under the water. The total depth of the pond is $5\;{\text{m}}$.
If we discuss the ray diagram we can see a ray will come from the flame and fall straight into the water surface. In this case for this ray the angle of incident will be zero. Thus, the angle of reflection will also be zero. So the ray will directly go to the fish's eyes.
Now another ray supposes at an incident angle $i$ fall in the water medium. Since water is denser medium as compared to air, so the ray will bend towards the normal and if we extend these two rays in backward direction they will meet at point $A$. So, the fish actually see the flame at point $A$ as shown in the figure.
Thus, the height of point$A$ from the fisheye will be ${h_2} + d$
Now, we will calculate the apparent height of the flame from the water surface that is ${h_2}$ by using the formula,
$\dfrac{{{h_2}}}{{{h_1}}} = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}$
Where ${h_2}$ is apparent height from the water surface, ${h_1}$ is real height from the water surface, ${n_2}$ is refraction index of water, and ${n_1}$ is refraction index of air.
By substituting the values, we get,
$\implies {h_2} = {h_1} \times \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}$
$\implies {h_2} = 2 \times \dfrac{{\dfrac{4}{3}}}{1}$
By simplification we obtain,
${h_2} = \dfrac{8}{3}\;{\text{m}}$
Now, we calculate the distance of point $A$ from the fisheye as
${h_2} + d = \dfrac{8}{3} + 4$
By simplification we obtain the apparent height as,
${h_2} + d = \dfrac{{20}}{3}\;{\text{m}}$
Hence, the apparent height of flame from fisheyes is $\dfrac{{20}}{3}\;{\text{m}}$.
$\therefore $Option $\left( d \right)$ is the correct.
Note: In geometrical optics, to find their position of the image of a point source, it is necessary only to consider the paths of two light rays emanating from the source in different directions that reach the observer eyes and to find their point of intersection.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will draw the following diagram as per the given situation,

As per the given data in the question we have the height of the flame above the water surface is $2\;{\text{m}}$ and the fish is $4\;{\text{m}}$under the water. The total depth of the pond is $5\;{\text{m}}$.
If we discuss the ray diagram we can see a ray will come from the flame and fall straight into the water surface. In this case for this ray the angle of incident will be zero. Thus, the angle of reflection will also be zero. So the ray will directly go to the fish's eyes.
Now another ray supposes at an incident angle $i$ fall in the water medium. Since water is denser medium as compared to air, so the ray will bend towards the normal and if we extend these two rays in backward direction they will meet at point $A$. So, the fish actually see the flame at point $A$ as shown in the figure.
Thus, the height of point$A$ from the fisheye will be ${h_2} + d$
Now, we will calculate the apparent height of the flame from the water surface that is ${h_2}$ by using the formula,
$\dfrac{{{h_2}}}{{{h_1}}} = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}$
Where ${h_2}$ is apparent height from the water surface, ${h_1}$ is real height from the water surface, ${n_2}$ is refraction index of water, and ${n_1}$ is refraction index of air.
By substituting the values, we get,
$\implies {h_2} = {h_1} \times \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}$
$\implies {h_2} = 2 \times \dfrac{{\dfrac{4}{3}}}{1}$
By simplification we obtain,
${h_2} = \dfrac{8}{3}\;{\text{m}}$
Now, we calculate the distance of point $A$ from the fisheye as
${h_2} + d = \dfrac{8}{3} + 4$
By simplification we obtain the apparent height as,
${h_2} + d = \dfrac{{20}}{3}\;{\text{m}}$
Hence, the apparent height of flame from fisheyes is $\dfrac{{20}}{3}\;{\text{m}}$.
$\therefore $Option $\left( d \right)$ is the correct.
Note: In geometrical optics, to find their position of the image of a point source, it is necessary only to consider the paths of two light rays emanating from the source in different directions that reach the observer eyes and to find their point of intersection.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Define thermal expansion for alpha beta and gamma A class 11 physics JEE_Main

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning




