
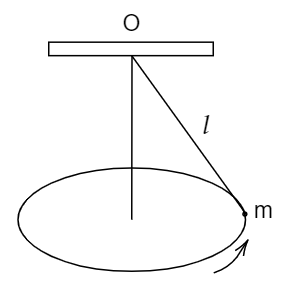
A point mass m is suspended from the light thread of length l, fixed at O, and is whirled in a horizontal circle at a constant speed as shown. From your point of view, stationary with respect to the mass, then find the force on the mass.
A. 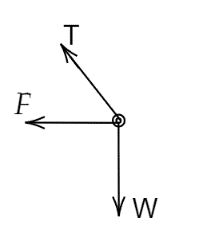
B. 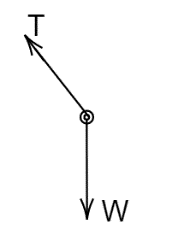
C. 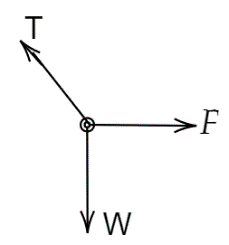
D. 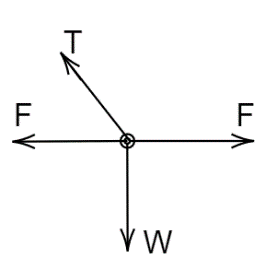
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: Whenever an object is moving in a circular path, a force that acts towards the center is known as the centripetal force. The centrifugal force is a pseudo force that acts on a particle that is moving in a circular motion, then the direction of this force away from the center is known as centrifugal force.
Complete step by step solution:
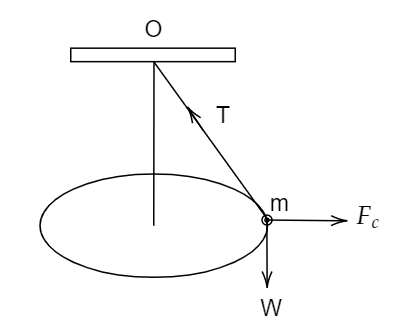
Image: A point mass m is suspended from the light thread of length fixed at O and is whirled in a horizontal circle at a constant speed.
Consider a point mass m that is suspended from the light thread of length l, fixed at O, and is whirled in a horizontal circle at a constant speed as shown in the figure. From your point of view, stationary with respect to the mass, we need to find the force on the mass. We know that the mass is m and if I am standing and watching on the ground, a force is acting on the mass i.e., tension. And also, mg towards the earth. If it is a circular motion, the necessary force for the circular motion is centripetal force.
Now, if our point of view with respect to mass is stationary, then, we are in the accelerated frame because the velocity is changing at every point, which means the acceleration is also changing. It is moving at a constant speed but the velocity is changing (direction changes at every point). If the frame is accelerated, we call it a non-inertial frame and, in this frame, we feel a force acting on it known as centripetal force. That is, the centripetal force is acting towards the center and the pseudo force is acting away from the center (outside). This pseudo force is nothing but centrifugal force.
Suppose if we are standing on the ground or earth as we said that we can only see two forces, that is tension and another is mg. Assuming that our point of view is on the mass then we are in a non-inertial frame and experience a pseudo force and are always outside from the center. So, we see three forces acting on the mass, one is tension, mg, and a pseudo force (centrifugal force) due to the non-inertial frame. Therefore, the force acting on the mass is tension, mg and centrifugal force.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note: Don’t get confused between the centripetal and centrifugal force since it always exists when a particle is moving in a circular motion. The centripetal force acts towards the center and the centrifugal acts away from the center.
Complete step by step solution:

Image: A point mass m is suspended from the light thread of length fixed at O and is whirled in a horizontal circle at a constant speed.
Consider a point mass m that is suspended from the light thread of length l, fixed at O, and is whirled in a horizontal circle at a constant speed as shown in the figure. From your point of view, stationary with respect to the mass, we need to find the force on the mass. We know that the mass is m and if I am standing and watching on the ground, a force is acting on the mass i.e., tension. And also, mg towards the earth. If it is a circular motion, the necessary force for the circular motion is centripetal force.
Now, if our point of view with respect to mass is stationary, then, we are in the accelerated frame because the velocity is changing at every point, which means the acceleration is also changing. It is moving at a constant speed but the velocity is changing (direction changes at every point). If the frame is accelerated, we call it a non-inertial frame and, in this frame, we feel a force acting on it known as centripetal force. That is, the centripetal force is acting towards the center and the pseudo force is acting away from the center (outside). This pseudo force is nothing but centrifugal force.
Suppose if we are standing on the ground or earth as we said that we can only see two forces, that is tension and another is mg. Assuming that our point of view is on the mass then we are in a non-inertial frame and experience a pseudo force and are always outside from the center. So, we see three forces acting on the mass, one is tension, mg, and a pseudo force (centrifugal force) due to the non-inertial frame. Therefore, the force acting on the mass is tension, mg and centrifugal force.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note: Don’t get confused between the centripetal and centrifugal force since it always exists when a particle is moving in a circular motion. The centripetal force acts towards the center and the centrifugal acts away from the center.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions




