
A plano-convex lens of refractive index 1.5 and radius of curvature 30cm is silvered at the curved surface. Now this lens has been used to form the image of an object. At what distance from this lens, an object has to be placed in order to have a real image of the size of the object?
A) 20cm
B) 30cm
C) 60cm
D) 80cm
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: When the curved side of the plano-convex lens is silvered, when it is viewed from the other end, it behaves like a concave mirror. Hence, we have to apply the rules of reflection on a concave mirror.
Complete step by step answer:
A plano-convex lens consists of two faces joined together, with one face straight and the other face bulged outward as shown:
If the bulged part of the lens is coated with silver, the plano-convex lens behaves as a concave mirror with the inner surface acting as the reflecting surface.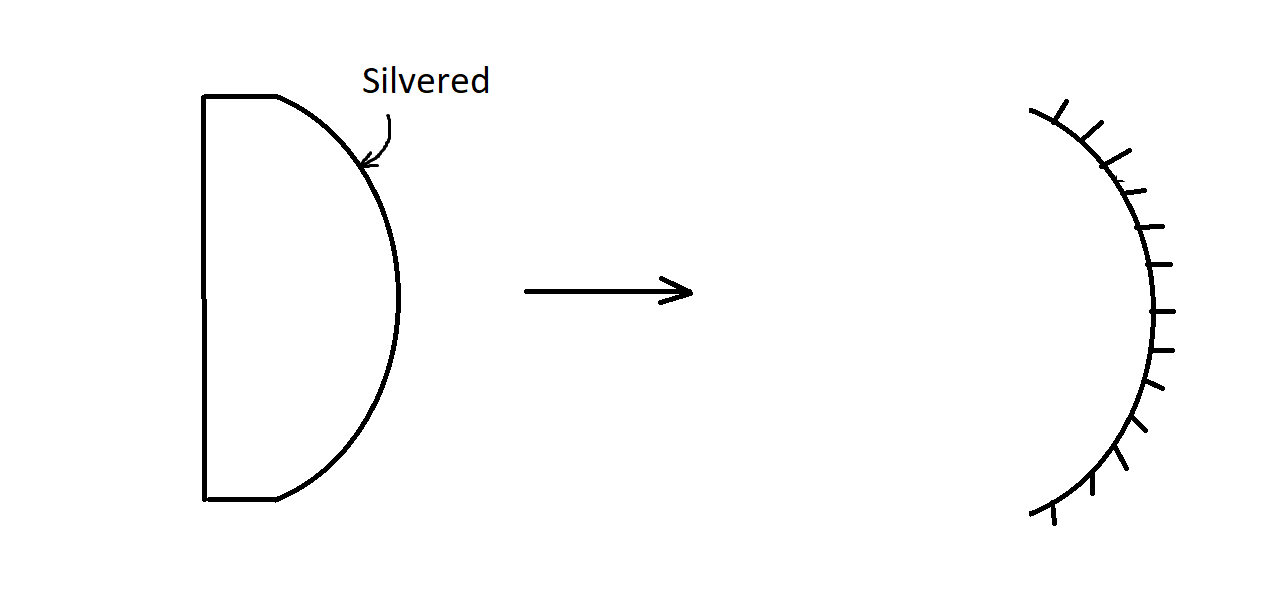
The radius of curvature of the curved surface, $R = 30cm$
Let us consider an object placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror as shown:
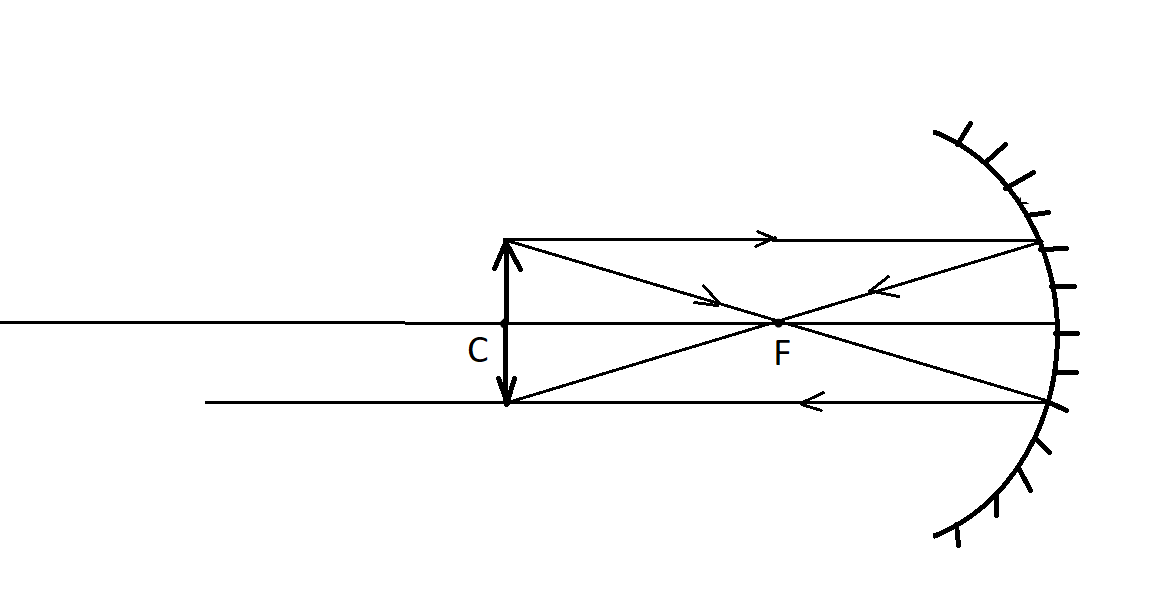
There are two rays emerging out of the object.
i) The first ray passes through the principal focus F and after reflection, passes parallel to the principal axis.
ii) The second ray passes parallel to the principal axis and after reflection, passes through the principal focus F.
The two rays meet and form an image at the centre of curvature, C.
The image formed is of the same size as that of the object and hence, the magnification is unity as there is no increase or decrease in the size of the object.
Hence, to produce a real image of the size of the object after reflection, the object must be placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
Here, the radius of curvature of the mirror is equal to $R = 30cm$.
Hence, the correct option is Option B.
Note: The radius of curvature of the mirror has the negative sign since the radius of curvature of a concave mirror and lens is always negative. Here, we have considered the magnitude of the radius of curvature. The actual designation of the radius of curvature, $R = - 30cm$.
Complete step by step answer:
A plano-convex lens consists of two faces joined together, with one face straight and the other face bulged outward as shown:
If the bulged part of the lens is coated with silver, the plano-convex lens behaves as a concave mirror with the inner surface acting as the reflecting surface.

The radius of curvature of the curved surface, $R = 30cm$
Let us consider an object placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror as shown:

There are two rays emerging out of the object.
i) The first ray passes through the principal focus F and after reflection, passes parallel to the principal axis.
ii) The second ray passes parallel to the principal axis and after reflection, passes through the principal focus F.
The two rays meet and form an image at the centre of curvature, C.
The image formed is of the same size as that of the object and hence, the magnification is unity as there is no increase or decrease in the size of the object.
Hence, to produce a real image of the size of the object after reflection, the object must be placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
Here, the radius of curvature of the mirror is equal to $R = 30cm$.
Hence, the correct option is Option B.
Note: The radius of curvature of the mirror has the negative sign since the radius of curvature of a concave mirror and lens is always negative. Here, we have considered the magnitude of the radius of curvature. The actual designation of the radius of curvature, $R = - 30cm$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 1 (55/1/1) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Marking Scheme




