
A plane mirror is placed on level ground at a distance $60m$ from the foot of a tower, the ray coming from the top of the tower and its reflected ray from the mirror subtends an angle $90^\circ $. What is the height of the tower?
A) $30m$
B) $60m$
C) $90m$
D) $120m$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:When a plane mirror reflects a ray of light, the angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence. The ray of incidence, reflection and the normal all lie on the same plane. This principle will help us solve the problem in hand. If an incident ray subtends a certain angle then this means that that angle represents the sum of both reflected angle and incident angle.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s first analyse the scenario. The mirror is at a distance of $60m$ from the foot of the tower.
The incident ray from the top of the tower will hit the mirror to subtend an angle of $90^\circ $. This means that when the incident ray, coming from the tip of the tower hits the mirror it creates a $45^\circ $ angle with the normal and the angle of reflection is $45^\circ $. This is because reflection is based on the principle that angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence.
Let’s look at the following figure for better understanding.
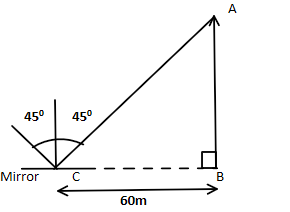
From the figure we can see that in the right angled triangle $\vartriangle ABC$ the value of angle $\angle C$ is $45^\circ $.
This implies that the right-angled triangle is an isosceles triangle too. So the lengths of arms $\overline {AB} $ and $\overline {BC} $ are equal.
So the height of the tower will be $\left| {\overline {AB} } \right| = \left| {\overline {BC} } \right| = 60m$
Thus our correct answer is option (B).
Note:Any kind of reflecting surface works on the principle that angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. In some cases we might need to use trigonometric calculations in order to find an angle or length of an arm.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s first analyse the scenario. The mirror is at a distance of $60m$ from the foot of the tower.
The incident ray from the top of the tower will hit the mirror to subtend an angle of $90^\circ $. This means that when the incident ray, coming from the tip of the tower hits the mirror it creates a $45^\circ $ angle with the normal and the angle of reflection is $45^\circ $. This is because reflection is based on the principle that angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence.
Let’s look at the following figure for better understanding.

From the figure we can see that in the right angled triangle $\vartriangle ABC$ the value of angle $\angle C$ is $45^\circ $.
This implies that the right-angled triangle is an isosceles triangle too. So the lengths of arms $\overline {AB} $ and $\overline {BC} $ are equal.
So the height of the tower will be $\left| {\overline {AB} } \right| = \left| {\overline {BC} } \right| = 60m$
Thus our correct answer is option (B).
Note:Any kind of reflecting surface works on the principle that angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. In some cases we might need to use trigonometric calculations in order to find an angle or length of an arm.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




