
A particle revolves in clockwise direction (as seen from point A) in a circle C of radius 1 cm and completes one revolution in 2 sec. The axis of the circle and the principal axis of the mirror M coincide, call it AB. The radius of curvature of the mirror is 20 cm. Then, the direction of revolution (as seen from A) of the image of the particle and its speed is
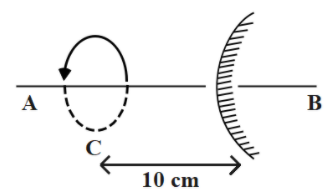
A. Clockwise, $1.57c{m^{ - 1}}$
B. Clockwise, $3.14c{m^{ - 1}}$
C. Anticlockwise, $1.57c{m^{ - 1}}$
D. Anticlockwise, $3.14c{m^{ - 1}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Given are the object distance and focal length of the convex mirror, using mirror formula to find the image distance. Then substitute its value to the mathematical expression for magnification of the image produced. Later use the relation of the time period and angular velocity to find the required speed.
Formula Used:
Mirror Formula:
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} \cr
& {\text{where }}v{\text{ is the distance of image from optical center,}} \cr
& u{\text{ is the distance of object from optical center,}} \cr
& f{\text{ is the focal length of the mirror used}}{\text{.}} \cr} $
Magnification produced by mirror is, $m = \dfrac{{ - v}}{u}$
Time Period, $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
Relation between linear velocity and angular velocity: $v = r \times \omega $
Complete step by step answer:
The rotating particle will result in a virtual image being formed by the convex mirror.
Given:
The distance of object from optical center, $u = - 10cm$
The radius of curvature of the convex mirror, $C = 20cm$
The focal length of the convex mirror, $f = \dfrac{C}{2} = \dfrac{{20}}{2} = 10cm$
Time Period of one revolution, $T = 2\sec $
Applying mirror formula to the given values we get:
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{10}} = \dfrac{1}{{10}} \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{10}} + \dfrac{1}{{10}} = \dfrac{2}{{10}} \cr
& \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{10}}{2} \cr
& \therefore v = + 5cm \cr} $
So, the magnification of the image produced by the mirror is:
$\eqalign{
& m = \dfrac{{ - v}}{u} \cr
& \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{{ - 10}} \cr
& \therefore m = 0.5cm \cr} $
We known that time period of one revolution is mathematically equal to the ratio of twice pi upon the angular velocity, so we have:
$\eqalign{
& T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega } \cr
& \Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }{\text{ }}\left[ {\because T = 2\left( {{\text{given}}} \right)} \right] \cr
& \therefore \omega = \pi \cr} $
Now, the linear velocity is related to the angular velocity by the following relation:
$\eqalign{
& v = r \times \omega \cr
& {\text{where }}r{\text{ is the magnification in this case}} \cr} $
Substituting values in the above equation we get:
$\eqalign{
& v = r \times \omega \cr
& \Rightarrow v = 0.5 \times \pi \cr
& \Rightarrow v = 0.5 \times 3.14 \cr
& \therefore v = 1.57c{m^{ - 1}} \cr} $
And the direction of revolution will be the same as the object that is in clockwise direction.
Therefore, the correct option is A i.e., Clockwise, $1.57c{m^{ - 1}}$
Note: Similar to plane mirrors, convex mirrors also produce virtual images. Additionally, the image formed is upright and reduced in size than the original object. It is located behind the mirror. Whereas in the concave mirror the characteristics of the formed image gets altered based on the location of the object on the optical axis.
Formula Used:
Mirror Formula:
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} \cr
& {\text{where }}v{\text{ is the distance of image from optical center,}} \cr
& u{\text{ is the distance of object from optical center,}} \cr
& f{\text{ is the focal length of the mirror used}}{\text{.}} \cr} $
Magnification produced by mirror is, $m = \dfrac{{ - v}}{u}$
Time Period, $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
Relation between linear velocity and angular velocity: $v = r \times \omega $
Complete step by step answer:
The rotating particle will result in a virtual image being formed by the convex mirror.
Given:
The distance of object from optical center, $u = - 10cm$
The radius of curvature of the convex mirror, $C = 20cm$
The focal length of the convex mirror, $f = \dfrac{C}{2} = \dfrac{{20}}{2} = 10cm$
Time Period of one revolution, $T = 2\sec $
Applying mirror formula to the given values we get:
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{10}} = \dfrac{1}{{10}} \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{10}} + \dfrac{1}{{10}} = \dfrac{2}{{10}} \cr
& \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{10}}{2} \cr
& \therefore v = + 5cm \cr} $
So, the magnification of the image produced by the mirror is:
$\eqalign{
& m = \dfrac{{ - v}}{u} \cr
& \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{{ - 10}} \cr
& \therefore m = 0.5cm \cr} $
We known that time period of one revolution is mathematically equal to the ratio of twice pi upon the angular velocity, so we have:
$\eqalign{
& T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega } \cr
& \Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }{\text{ }}\left[ {\because T = 2\left( {{\text{given}}} \right)} \right] \cr
& \therefore \omega = \pi \cr} $
Now, the linear velocity is related to the angular velocity by the following relation:
$\eqalign{
& v = r \times \omega \cr
& {\text{where }}r{\text{ is the magnification in this case}} \cr} $
Substituting values in the above equation we get:
$\eqalign{
& v = r \times \omega \cr
& \Rightarrow v = 0.5 \times \pi \cr
& \Rightarrow v = 0.5 \times 3.14 \cr
& \therefore v = 1.57c{m^{ - 1}} \cr} $
And the direction of revolution will be the same as the object that is in clockwise direction.
Therefore, the correct option is A i.e., Clockwise, $1.57c{m^{ - 1}}$
Note: Similar to plane mirrors, convex mirrors also produce virtual images. Additionally, the image formed is upright and reduced in size than the original object. It is located behind the mirror. Whereas in the concave mirror the characteristics of the formed image gets altered based on the location of the object on the optical axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Mass vs Weight: Key Differences Explained for Students

Area of an Octagon Formula Explained Simply

Absolute Pressure Formula Explained: Key Equation & Examples

Central Angle of a Circle Formula Explained Quickly

Difference Between Vapor and Gas: JEE Main 2026

Difference Between Atom and Molecule: JEE Main 2026

Trending doubts
Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Main Response Sheet 2026 Released – Key Dates and Official Updates by NTA

JEE Main 2026 Answer Key OUT – Download Session 1 PDF, Response Sheet & Challenge Link

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

Other Pages
Essential Physics Formulas for Class 9: Complete Chapterwise List

Class 11 Physics MCQs: Chapterwise Practice with Answers

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

One Day International Cricket

Valentine Week 2026: Complete List of Valentine Week Days & Meaning of Each Day

List of Highest T20 Scores in International Cricket




