
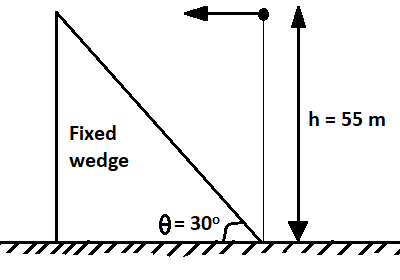
A particle is projected with a velocity $u$ in horizontal direction as shown in the figure. find $u$(approx.) so that the particle collides orthogonally with the inclined plane of the fixed wedge.
A) $10m/s$
B) $20m/s$
C) $10\sqrt 2 m/s$
D) None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question you have to break the velocity components of the moving particle and write the force equation and then apply the equilibrium condition. You should remember all the concepts related to wedges. Also, keep in mind that in this question the particle’s velocity component parallel to the inclined plane should be zero.
Complete step by step solution:
Considering plane along the wedge axis,
As we know that when a particle collides with the plane, its velocity component which is parallel to the inclined plane should be zero.
$ \Rightarrow u\cos \theta - g\sin \theta \times t = 0$
On further solving, we have
$ \Rightarrow t = \dfrac{u}{{g\tan \theta }}$
And also from the same equation, we get the value of u as
$ \Rightarrow u = gt \times \tan \theta $
On putting $\theta = 30^\circ $ in the above equation, we have
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{gt}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ …….(1)
Now, consider the plane along with the x-y axis, we have
Horizontal displacement before the particle hits the plane $ = ut$
And, the vertical displacement during the t time $ = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
Now, $\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{h - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}}}{{ut}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{h - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}}}{{ut}}$
On solving the above equation for t, we have
$ \Rightarrow t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{6h}}{{5g}}} $
On putting the given values $h = 55m$ and $g = 9.8m/{s^2}$ we get
$ \Rightarrow t = 2.5938\sec $
Now, putting that above value of time in the equation (1), we have
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{9.8 \times 2.5938}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On further solving this, we get the value of the initial velocity $u$ ,
$ \Rightarrow u = 14.69 \simeq 10\sqrt 2 m/s$
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note: Always keep in mind that if the wedge is at rest then the problem should be solved by the normal way in which we write the force equations and applying the equilibrium conditions and if the wedge is in accelerating motion then everything will be converted into a wedge frame of reference and then solve the question by applying pseudo force.
Complete step by step solution:
Considering plane along the wedge axis,
As we know that when a particle collides with the plane, its velocity component which is parallel to the inclined plane should be zero.
$ \Rightarrow u\cos \theta - g\sin \theta \times t = 0$
On further solving, we have
$ \Rightarrow t = \dfrac{u}{{g\tan \theta }}$
And also from the same equation, we get the value of u as
$ \Rightarrow u = gt \times \tan \theta $
On putting $\theta = 30^\circ $ in the above equation, we have
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{gt}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ …….(1)
Now, consider the plane along with the x-y axis, we have
Horizontal displacement before the particle hits the plane $ = ut$
And, the vertical displacement during the t time $ = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
Now, $\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{h - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}}}{{ut}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{h - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}}}{{ut}}$
On solving the above equation for t, we have
$ \Rightarrow t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{6h}}{{5g}}} $
On putting the given values $h = 55m$ and $g = 9.8m/{s^2}$ we get
$ \Rightarrow t = 2.5938\sec $
Now, putting that above value of time in the equation (1), we have
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{9.8 \times 2.5938}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On further solving this, we get the value of the initial velocity $u$ ,
$ \Rightarrow u = 14.69 \simeq 10\sqrt 2 m/s$
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note: Always keep in mind that if the wedge is at rest then the problem should be solved by the normal way in which we write the force equations and applying the equilibrium conditions and if the wedge is in accelerating motion then everything will be converted into a wedge frame of reference and then solve the question by applying pseudo force.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




